Computation of ratios | Accountancy - Liquidity ratios | 12th Accountancy : Chapter 9 : Ratio Analysis
Chapter: 12th Accountancy : Chapter 9 : Ratio Analysis
Liquidity ratios
Liquidity ratios
Liquidity means
capability of being converted into cash with ease. Liquidity ratios help to
assess the ability of a business concern to meet its short term financial
obligations. Short term assets (current assets) are more liquid as compared to
long term assets (fixed assets). Liquidity ratios are also called as short term
solvency ratios.
Liquidity ratios
include: (i) Current ratio and (ii) Quick ratio.
(i) Current ratio
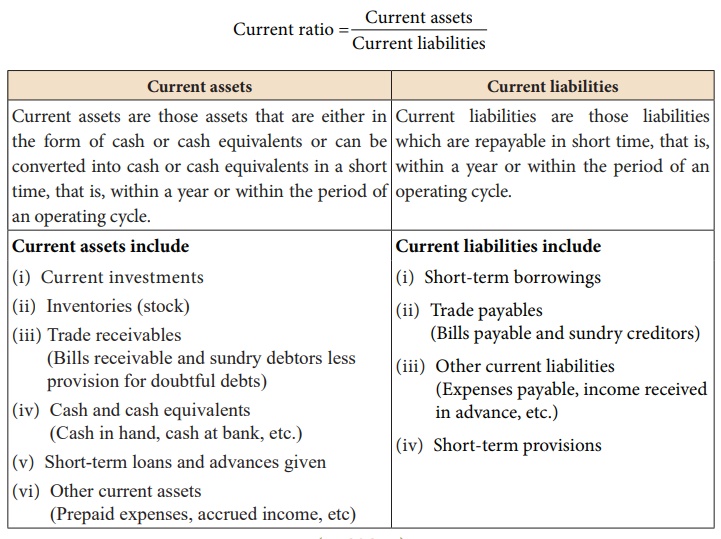
Current ratio gives the
proportion of current assets to current liabilities of a business concern. It
is computed by dividing current assets by current liabilities. Current ratio
indicates the ability of an entity to meet its current liabilities as and when
they are due for payment. It is calculated as follows:
Higher the current
ratio, the better is the liquidity position, as the firm will be in a better
position to pay its current liabilities. However, a much higher ratio may
indicate inefficient investment policies of the management.
Illustration 1
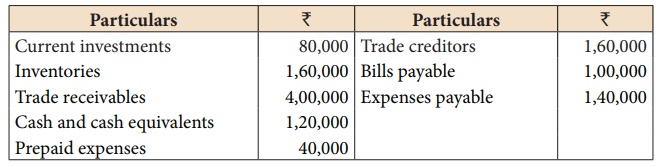
Calculate current ratio
from the following information:
Solution

Current assets = Current investments + Inventories + Trade receivables + Cash and cash equivalents + Prepaid expenses
= 80,000 + 1,60,000 + 4,00,000 + 1,20,000 + 40,000 = ₹ 8,00,000
Current liabilities = Trade creditors +Bills payable + Expenses payable
= 1,60,000 + 1,00,000 + 1,40,000 = ₹ 4,00,000
(ii) Quick ratio
Quick ratio gives the
proportion of quick assets to current liabilities. It indicates whether the
business concern is in a position to pay its current liabilities as and when
they become due, out of its quick assets. Quick assets are current assets
excluding inventories and prepaid expenses. It is otherwise called liquid ratio
or acid test ratio. It is calculated as follows:
Quick ratio = Quick
assets / Current liabilities
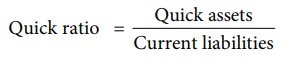
Quick assets = Current
assets – Inventories – Prepaid expenses
Higher the quick ratio, better is the short-term financial position of an enterprise.
Illustration 2
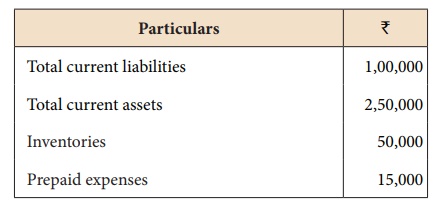
Calculate quick ratio of
Ananth Constructions Ltd from the information given below.
Solution

Quick assets = Current assets – Inventories – Prepaid expenses
= 2,50,000 – 50,000 – 15,000
= ₹ 1,85,000
Illustration 3
Following is the balance
sheet of Magesh Ltd. as on 31st March, 2019:
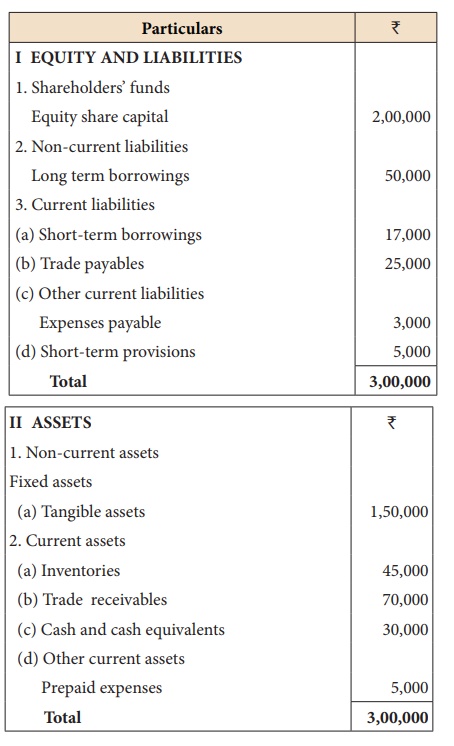
Calculate: (i) Current ratio (ii) Quick ratio
Solution
(i) Current ratio = Current assets/Current liabilities = 1,50,000/50,000 = 3:1
Current assets = Inventories + Trade receivables + Cash and cash equivalents + Prepaid expenses
= 45,000 + 70,000 + 30,000 + 5,000 = ₹ 1,50,000
Current liabilities = Short term borrowings + Trade payables + Expenses payable + Short term provisions
= 17,000 + 25,000 + 3,000 + 5,000 = ₹ 50,000
(ii) Quick ratio = Quick assets / Current liabilities
= 1,00,000/50,000 = 2:1
Quick assets = Total current assets – Inventories – Prepaid expenses
= 1,50,000 – 45,000 – 5,000 = ₹ 1,00,000
Related Topics