Computation of ratios | Accountancy - Long term solvency ratios | 12th Accountancy : Chapter 9 : Ratio Analysis
Chapter: 12th Accountancy : Chapter 9 : Ratio Analysis
Long term solvency ratios
Long term solvency ratios
Long term solvency means
the firm’s ability to meet its liabilities in the long run. Long term solvency
ratios help to determine the ability of the business to repay its debts in the long
run. The following ratios are normally computed for evaluating long term
solvency of the business:
i.
Debt equity ratio
ii.
Proprietary ratio
iii.
Capital gearing ratio
(i) Debt equity ratio
Debt equity ratio is
calculated to assess the long term solvency position of a business concern.
Debt equity ratio
expresses the relationship between long term debt and shareholders’ funds.
It is computed as
follows:
Debt equity ratio = Long term debt / Shareholders'funds
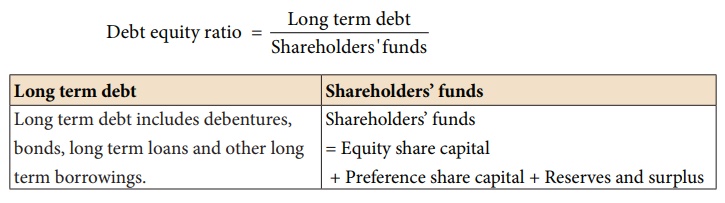
In general, lower the debt equity ratio, lower is the risk to the long-term lenders. A high ratio indicates high risk as it may be difficult for the business concern to meet the obligation to outsiders.
Illustration 4
From the following
information, calculate debt equity ratio:
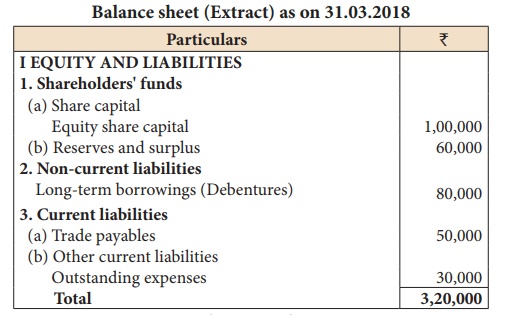
Solution
Debt equity ratio = Long term debt/Shareholders'funds = 80,000/1,60,000 = 0.5:1
Long term debt = Debentures = ₹ 80,000
Shareholders’ funds = Equity share capital + Reserves and surplus
= 1,00,000 + 60,000 = ₹ 1,60,000
(ii) Proprietary ratio
Proprietary ratio gives
the proportion of shareholders’ funds to total assets. Proprietary ratio shows
the extent to which the total assets have been financed by the shareholders’
funds. It is calculated as follows:
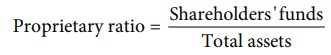
Higher the proprietary
ratio, greater is the satisfaction for lenders and creditors, as the firm is
less dependent on external sources of finance.
Illustration 5
From the following
Balance Sheet of Pioneer Ltd. calculate proprietary ratio:
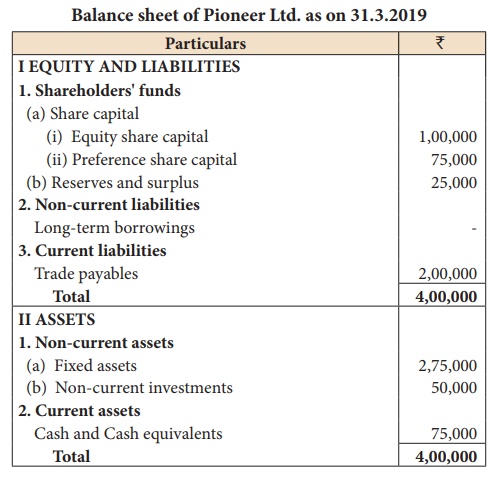
Solution
Proprietary ratio =
Shareholders'funds / Total assets = 2,00,000 / 4,00,000 = 0.5:1
Shareholders’ funds =
Equity share capital + Preference share capital + Reserves and surplus
= 1,00,000 + 75,000 +
25,000
= ₹ 2,00,000
(iii) Capital gearing ratio
Capital gearing ratio is
the proportion of fixed income bearing funds to equity shareholders’ funds.
Fixed income bearing funds include fixed interest and fixed dividend bearing
funds. It is calculated as follows:
Capital gearing ratio =
Equity shareholders'funds / Funds bearing Fixed interest or Fixed dividend
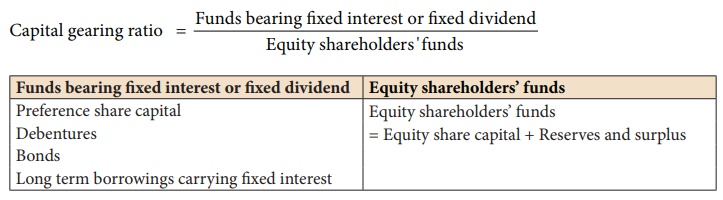
Capital gearing ratio is
a measure of long term solvency as well as capital structure. When the capital
gearing ratio is greater than one, the firm is said to be high geared.
Illustration 6
From the following
information calculate capital gearing ratio:
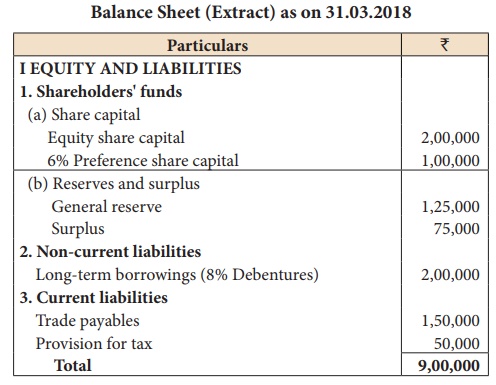
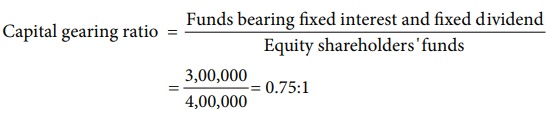
Funds bearing fixed interest and
dividend = 6% Preference share capital + 8% Debentures
= 1,00,000 + 2,00,000 = ₹ 3,00,000
Equity shareholder’s funds = Equity
share capital + General reserve + Surplus
= 2,00,000 + 1,25,000 + 75,000 = ₹
4,00,000
Illustration 7
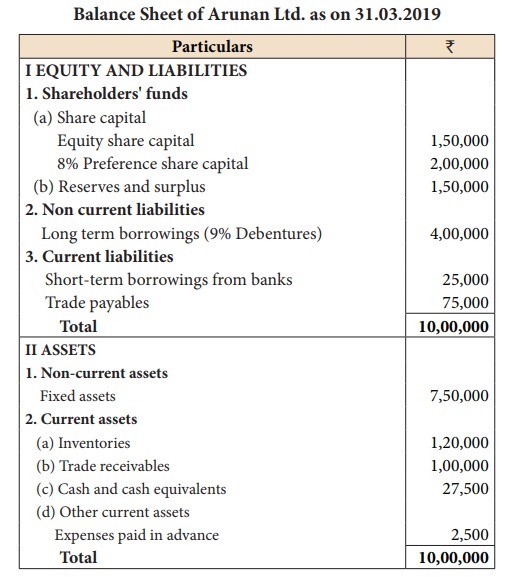
From the following
Balance Sheet of Arunan Ltd. as on 31.03.2019 calculate (i)
Debt-equity ratio (ii) Proprietary ratio and (iii) Capital gearing ratio.
Solution
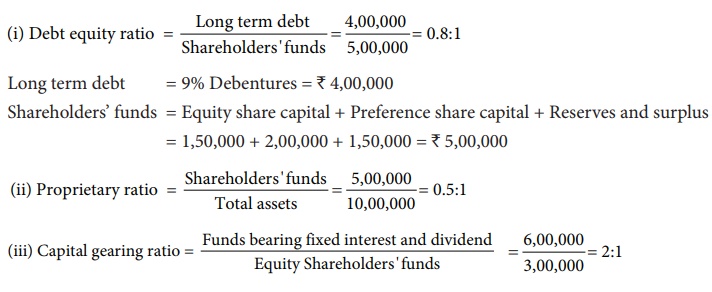
Funds bearing fixed
interest or dividend = 8% Preference
share capital + 9% Debentures
= 2,00,000 + 4,00,000 = ₹ 6,00,000
Equity shareholders’
funds = Equity share capital + Reserves and surplus
= 1,50,000 + 1,50,000 = ₹ 3,00,000
Related Topics