Management By Objectives (MBO) - Process of MBO | 12th Commerce : Chapter 3 : Management Process : Management By Objectives (MBO) Management By Exception (MBE)
Chapter: 12th Commerce : Chapter 3 : Management Process : Management By Objectives (MBO) Management By Exception (MBE)
Process of MBO
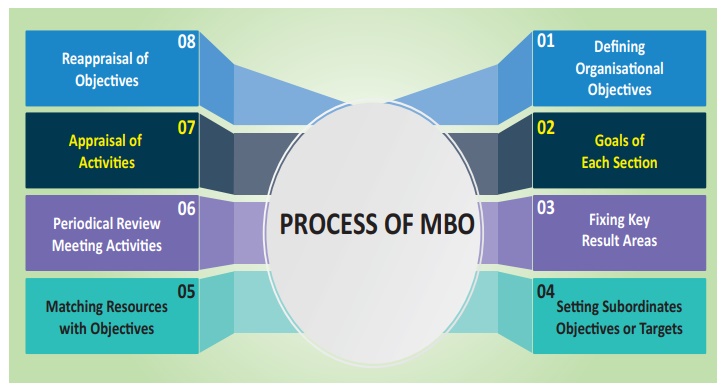
Process of MBO
The MBO process is characterised by the balance of
objectives of the organisation and individual. The process of MBO is explained
below:
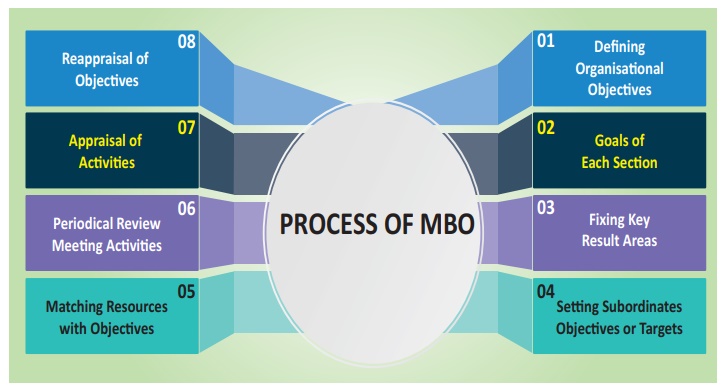
1. Defining Organisational Objectives
Initially, organisational objectives are framed by
the top level employees of an organisation. Then, it moves downwards. The
definition of organisational objectives states why the business is started and
exists. First, long-term objectives are frames. Then, Short-term objectives are
framed taking into account the feasibility of achieving the long-term
objectives.
2. Goals of Each Section
Objectives for each section, department or division
are framed on the basis of overall objectives of the organisation. Period
within which these objectives should be achieved is also fixed. Goals or
objectives are expressed in a meaningful manner.
3. Fixing Key Result Areas
Key result areas are fixed on the basis of organisational objectives premises. Key Result Areas (KRA) are arranged on a priority basis. KRA indicates the strength of an organisation. The examples of KRA are profitability, market standing, innovation etc.
4. Setting Subordinate Objectives or Targets
The objectives of each subordinate or individual
are fixed. It is preferable to fix the objectives at lower level in
quantitative units. There should be a free and frank discussion between the
superior and his subordinates. Subordinates are induced to set standards
themselves by giving an opportunity. If subordinates are allowed to do so, they
may set high standards and the chances of their accomplishment are higher. In
this way, the objectives or targets of the subordinates are fixed.
5. Matching Resources with Objective
The objectives are framed on the basis of
availability of resources. If certain resources (technical personnel or scarce
raw material) are not adequately available, the objectives of an organisation
are changes accordingly. So, there is a need for matching resources with
objectives. Next, the available resources should be properly allocated and
utilized.
6. Periodical Review Meetings
The superior and subordinates should hold meetings
periodically in which they discuss the progress in the accomplishment of
objectives. The fixed standards may be changed in the light of progress. But
the basic conditions do not change. The periodical review meeting is held
during the period set for achieving the objectives.
7. Appraisal of Activities
At the end of the fixed period for achieving the
objectives, there should be a discussion between the superior and subordinates.
The discussion is related with subordinates’ performance against the specified
standards. The superior should take corrective action.
The superior should identify the reasons for
failure of achieving objectives. The problems faced by the subordinates should
be identified and steps should be taken to tackle such problems.
8. Reappraisal of Objectives
An organisation is a part of the dynamic world.
There are a lot of changes within short period. The survival and growth of a
modern business organisation largely depends upon putting up with the changing
conditions. So, the top management executive should review the organisation’s
objectives to frame the objectives according to the changing situation.
Related Topics