Chapter: Physics : Photonics and fibre Optics
Principle of Laser action and Methods of pumping action
Principle of Laser action
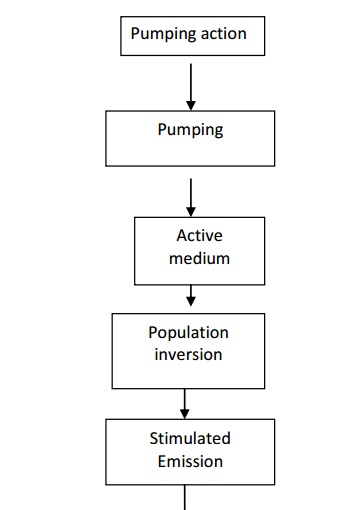
Principle: Due to stimulated emission the photons multiply in each step-giving rise to an intense beam of photons that are coherent and moving in the same direction. Hence the light is amplified by Stimulated Emission of the Radiation. Termed LASER.
ACTIVE MEDIUM:
A medium in which population inversion can be achieved is known as active medium.
Active Center: The material in which the atoms are raised to the excited state to achieve Population Inversion is called Active Center.
PUMPING ACTION:
The process to achieve the population inversion in the medium is called
Pumping action.
It is essential requirement for producing a laser beam.
Methods of pumping action:
The methods commonly used for pumping action are:
1. Optical pumping (Excitation by Photons)
2. Electrical discharge method(Excitation by electrons)
3. Direct conversion
4. In elastic atom – atom collision between atoms
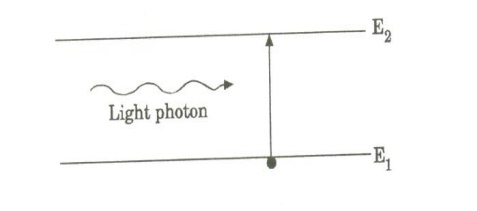
a. Optical pumping:
When the atoms are exposed to light radiations energy hv , atoms in the lower energy state absorb these radiations and they go to the excited state. This method is called Optical pumping. It is used in solid state lasers like ruby laser and Nd-YAG laser. In ruby laser, xenon flash lamp is used as pumping source.
b. Electrical discharge method (Excitation by electrons)
In this method, the electrons are produced in an electrical discharge tube. These electrons are accelerated to high velocities by a strong electrical field. These accelerated electrons collide with the gas atoms.
By the process, energy from the electrons is transferred to gas atoms. Some atoms gain energy and they go to the excited state. This results in population inversion. This method is called Electrical discharge method.
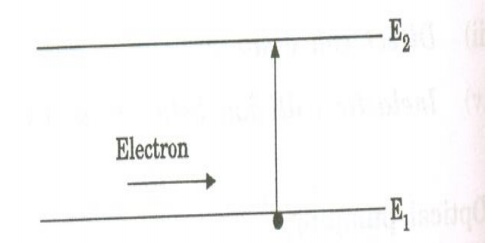
It is represented by the equation
A + e* = A* + e
Where A – gas atom in the ground state
A* = same gas atom in the excited state e* = Electrons with higher Kinetic energy e – Same electron with lesser energy.
This method of pumping is used in gas lasers like argon and CO2 Laser.
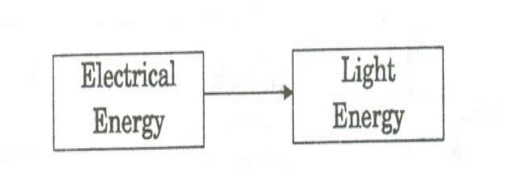
C. Direct Conversion
In this method, due to electrical energy applied in direct band gap semiconductor like Ga As, recombination of electrons and holes takes place. During the recombination process, the electrical energy is directly is converted into light energy.
d. In elastic atom – atom collision
In this method, a combination of two gases (Say A and B are used). The excited states of A and B nearly coincides in energy.
In the first step during the electrical discharge atoms of gas A are excited to their higher energy state A* (metastable state) due to collision with the electrons .
A + e* = A* + e
Now A* atoms at higher energy state collide with b atoms in the lower state. Due to inelastic atom - atom collision B atoms gain energy and they are excited to a higher state B* . Hence, A atoms lose energy and return to lower state.
A* + B = A + B*
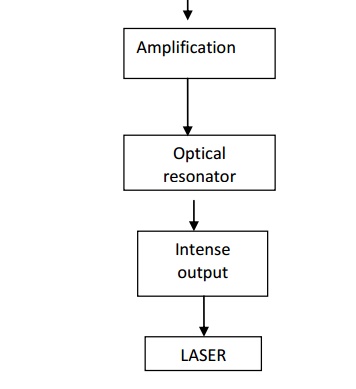
Optical resonator
An optical resonator consists of a pair of reflecting surfaces in which one is fully reflecting (R1) and the other is partially reflecting (R2). The active material is placed in between these two reflecting surfaces.
The photons generated due to transitions between the energy states of active material are bounced back and forth between two reflecting surfaces.
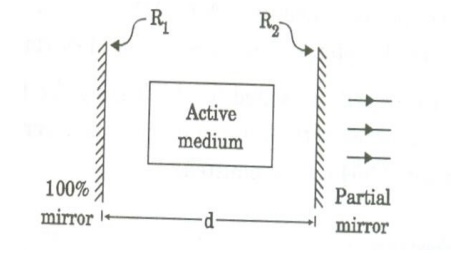
This will induce more and more stimulated transition leading to laser action.
Flow Chart of Laser action
Types of Laser
Based on the type of active medium, Laser systems are broadly classified into the following categories.
S.NO TYPE OF LASER EXAMPLES
1. Solid State laser : Ruby Laser Nd:YAG laser
2. Gas laser : He-Ne Laser, CO2 Laser, Argon – ion laser
3. Liquid Laser : SeOCL2 Laser, Europium Chelate Laser
4. Dye laser : Rhodamine 6G laser, Coumarin dye laser
5. Semiconductor Laser : GaAs laser, GaAsP laser
Related Topics