Chapter: Physics : Photonics and fibre Optics
Characteristics of Laser
Introduction.
LASER stands for Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation.
Laser is a device which emits a powerful, monochromatic collimated beam of light. The emitted light waves are coherent in nature.
Characteristics of Laser:
1. Directionality
Ordinary light spreads in all directions and its angular spread is 1m/m. But it is found that laser is highly directional and is angular spread is 1mm/m. For example, the laser beam can be focused to very long distance with a few divergence or angular spread.
Divergence or angular spread is given by
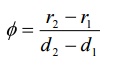
Where d1 , d2 are any two distances for the laser source emitted and r1, r2 are the radii of the beam spots at a distance d1, and d2respectively as shown
2. Intensity:
Since an ordinary light spreads in all directions, the intensity reaching the target is very less. But in the case of laser, due to high directionality, the intensity of laser beam reaching the target is of high intense beam. For example, 1 mill watt power of He-Ne laser appears to be brighter than the sunlight.
3. Monochromatic:
Laser beam is highly monochromatic; the wavelength is single, whereas in ordinary light like mercury vapour lamp, many wavelengths of light are emitted.
4 Coherence:
It is an important characteristic of laser beam. In lasers the wave trains of same frequency are in phase, the radiation given out is in mutual agreement not only in phase but also in the direction of emission and polarization. Thus it is a coherent beam. Due to high coherence it results in an extremely high power.
Differences between ordinary light and Laser beam.
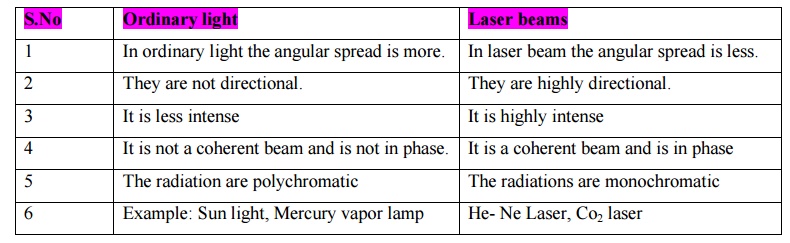
Ordinary light
1 In ordinary light the angular spread is more.
2 They are not directional.
3 It is less intense
4 It is not a coherent beam and is not in phase.
5 The radiation are polychromatic
6 Example: Sun light, Mercury vapor lamp
Laser beams
1 In laser beam the angular spread is less.
2 They are highly directional.
3 It is highly intense
4 It is a coherent beam and is in phase
5 The radiations are monochromatic
6 He- Ne Laser, Co2 laser
Related Topics