Economic Activities - Primary activities | 12th Geography : Chapter 4 : Economic Activities
Chapter: 12th Geography : Chapter 4 : Economic Activities
Primary activities
Primary activities
Primary activities help man to fulfill
his needs and desires, by using resources which are gifted to man by nature. These
activities are directly connected with nature. Hunting, Gathering, Pastoralism,
Fishing, Forestry, Mining and Agriculture are the primary activities.
Hunting and Gathering
Until 12,000 years ago, all humans lived
as hunters and gatherers. At present only 0.0001% human live as hunters and gatherers.
Gathering and hunting are the oldest known economic activity in the world. It often
involves primitive societies which collect both plants and animals to satisfy their
needs for food, shelter and clothing. These primitive activities are being carried
out still in a very few parts of the world. Gathering is practiced in the areas
of High altitude zones of Northern Canada, Northern Eurasia and Southern Chile and
in the low altitude zones of the Amazon Basin, Tropical Africa, Northern fringe
of Australia and interior parts of South East Asia. Present day gatherers and hunters
are confined to a few pockets. Inuit in the Arctic region, Pygmies of Kalahari,
Pintupi, Aborgines of Australians, and Paliyan of South India are the examples of
foragers.
Pastoralism
Pastoralism is the process of grazing
and rearing of different types of animals like cattle, sheep, goats, etc in an organised
manner to get animals products. The animals rearing can be primitive which is carried
on by nomads or highly scientific means on a commercial scale. So, animal grazing
and rearing can be divided into two broad categories as Nomadic Herding and Commercial
Livestock Rearing.
Nomadic Herding (or) Pastoral Nomadism
It is a primitive subsistence activity
in which the herders rely on animals for food, clothing, shelter, tools and transport.
They move from place to place along with their livestock, depending on the availability
of pastures and water. These people do not lead a settled life but keep on moving
from place to place. Pastoral nomadism is commonly practiced in regions with little
arable land, typically in the developing world. They are mostly found in central
and western Asia, Northern and Western regions of Africa and some parts of southern
Africa and Tundra regions.
Transhumance
Transhumance is the seasonal movement
of people with their livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In mountain
region it implies movement between higher altitude pastures during summer and valleys
in winter.

Gujiars, Bakarwals, Gaddis and Bhotiyas
in the Himalayan region migrate from plains to the mountain in summer and to the
plains from the high altitude pastures in winter. In the tundra regions, herders
move from south to north in summer and from north to south in winter. The number
of pastoral nomads has been decreasing and the areas operated by them shrinks due
to developments and spreading of other economic activities.

Agriculture
Agriculture
is the most fundamental form of human activity and includes not only cultivation
of crops but also the domestication of animals. The following are the major agricultural
types and their characteristic features.
Employees of the economic
activity called as
Economic Activity Name
Primary - Red collar
Secondary - Blue
collar
Tertiary - Pink collar
Quaternary - White collar
Quinary - Gold collar
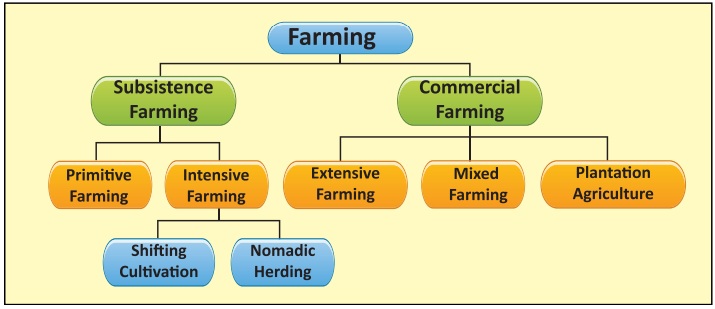
Subsistence Agriculture is a type of farming in which output
is consumed almost entirely by the farmers and their families leaving only a small
proportion for sale. Farmers follow traditional method of cultivation in this kind
of farming.

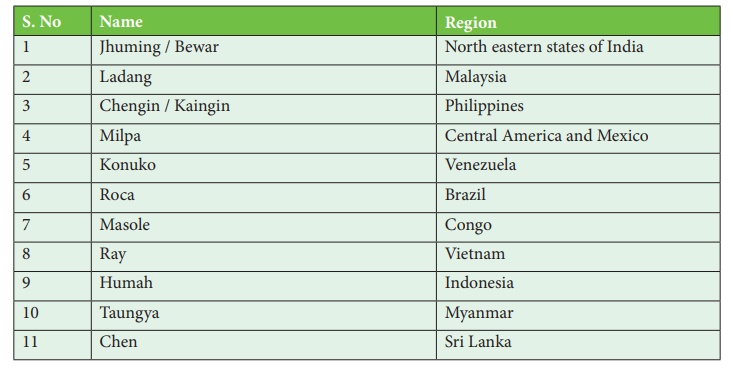
Shifting Cultivation
Shifting
Cultivation is a kind of traditional farming practiced by tribes in the hilly and
forest regions. It is practiced especially in tropical Africa. In this farming an
area of ground is cleared of vegetation and cultivated for a few years and then
abandoned for a new area until its fertility has been naturally restored. They are
called with different names in different regions.

Intensive Agriculture is the one in which the agricultural land is utilised intensively.
Farmers prefer the cultivation of short duration crops which enables the cultivation
of two or three crops in the same piece of land in a year. Generally it is practiced
wherein the size of the agricultural land holding is small.

Extensive Farming
It is a kind
of farming practiced in the regions where the size of the land holding is very large.
It is practiced in the Interior parts of semi-arid lands of the mid-latitudes. Wheat
is the major crop of this region and the farming is highly mechanized.

Mixed Farming
It is an
agricultural system in which a farmer conducts different agricultural practice together,
such as crops, fishing and livestock. The aim is to increase income through different
sources and to complement land and labour demands across the year.
Pomology – The study of growing
fruits.
Olericulture – science of vegetable growing.
Floriculture – refers to cultivation
of flowers.
Sericulture – refers to Rearing of
Silkworms
Viticulture – The study of grape cultivation`


Plantation
Agriculture
Plantation
agriculture is a form of commercial farming where crops are grown for profit. Large
land areas are needed for this type of agriculture. Countries that have plantation
Agriculture usually experience high annual temperatures and receive high annual
rainfall. Plantation is mainly found in countries that have a tropical climate.
The important plantation crops are tea, coffee, cocoa, rubber, oil palm, sugarcane,
bananas and pineapples.

Mediterranean Agriculture
Mediterranean
agriculture is highly specialised commercial agriculture. It is practised in the
countries on either side of the Mediterranean Sea, Europe and in North Africa from
Tunisia to Atlantic coast, southern California, central Chile, south western parts
of South Africa and south and south western parts of Australia. This region is an
important supplier of citrus fruits. Viticulture or grape cultivation is a speciality
of the Mediterranean region. Best quality wines in the world with distinctive flavours
are produced from high quality grapes in various countries of this region. The inferior
grapes are dried into raisins and currants. This region also produces olives and
figs. The advantage of Mediterranean agriculture is that more valuable crops such
as fruits and vegetables are grown in winters when there is great demand in European
and North American markets.
Horticulture
Specialised
cultivation of flowers, vegetables and fruits is called horticulture. It is also
termed as “truck farming”. These crops are grown on small farms which are well connected
to the markets by cheap and efficient means of transportation. It is labour and
capital intensive crops. The main areas are northwest Europe, northern eastern USA
and Mediterranean region.

Von Thunen model of agriculture
The Von Thunen
model of agricultural land use was created by the farmer, landowner, and economist
Von Thunen in 1826 in a book called The Isolated State. Von Thunen model was created
before industrialization and is based on the following limiting assumptions:
The city is located centrally within
an "Isolated State" that is self-sufficient and has no external influences.
* The Isolated
State is surrounded by an unoccupied wilderness.
* The land
of the State is completely flat and has no rivers or mountains to interrupt the
terrain.
* The soil
quality and climate are consistent throughout the State.
* Farmers
in the Isolated State transport their own goods to market via ox cart, across the
land, directly to the central city. Therefore, there are no roads.
* Farmers act to maximise profits.
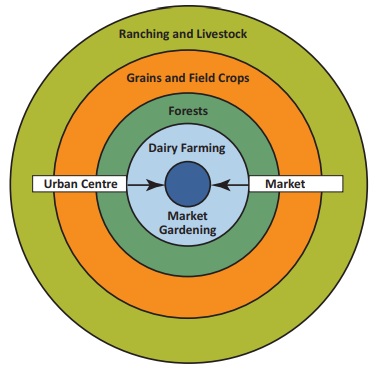
In an Isolated
State with the foregoing statements being true, Von Thunen hypothesized that a pattern
of rings around the city would develop based on land cost and transportation cost.
The Four Rings
Ring
1: Dairying and intensive farming occur in the ring closest to the city.
Because vegetables, fruit, milk, and other dairy products must get to market quickly,
they would be produced close to the city. The first ring of land is also more expensive,
so the agricultural products would have to be highly valuable ones and the rate
of return is maximized.
Ring
2: Timber and firewood would be produced for fuel and building materials
in the second zone. Before industrialization and coal power, wood was a very important
fuel for heating and cooking. Wood is very heavy and difficult to transport, so
it is located as close to the city as possible.
Ring 3: The third zone consists of extensive field crops such as grains for bread. As grains last longer than dairy products and they are much lighter than fuel, to reduce transport costs, they can be located farther from the city.
Ring 4: Ranching is located in the final ring surrounding the central city. Animals can
be raised far from the city because they are self-transporting.
What the Model Tells Us?
Even though
the Von Thunen model was created in a time before factories, highways, and even
railroads, it is still an important model in geography. The Von Thunen model is
an excellent illustration of the balance between land cost and transportation costs.
When one gets closer to a city, the price of land increases. The farmers of the
Isolated State balance the cost of transportation, land, and profit and produce
the most cost-effective product for market. Of course, in the real world, things
do not happen as they would in a model.
Mining
The process
of extracting minerals from the earth crust is known as mining. The discovery of
minerals in the history of human development is reflected in many stages in terms
of copper, Bronze and Iron age. The use of minerals in ancient times was largely
confined to making of tools, utensils and weapons. The actual development of mining
began with the industrial revolution and its importance is continuously increasing.
Types of Mining
Open-pit or opencast mining
Open pit mining involves mining minerals
ore that can be found near the surface layer of the site. Some quarries can be over
1000 meters deep. This form of mining doesn’t require tunneling into the earth and
is a simple method of mining that yields high production.
Surface Mining
Surface mining is the process of mining
the ores found on the surface of the earth. In this process, any unwanted soil is
stripped off from the land and the ore beneath is extracted. Surface mining often
leaves behind large areas of infertile land and waste rock as 70% of the mined earth
is waste materials.
Underground or sub surface mining/Shaft mining
Sub-surface mining involves the digging
of a network of shafts and tunnels into the earth to reach and extract the deposit
of mineral ore beneath the earth. In comparison to other methods, underground mines
impacts are less on the environment and are more harmful to those working within
them. In modern practice, underground mines are pre-assessed for oxygen toxicity
levels and a system of ventilation machines and protocols are in place to ensure
workplace safety.
In-Situ Mining
It is a rarely
used method of mining material. It is also called as solution mining. It is the
process of pumping a solution into the ore body, which dissolves the ore and is
then extracted by a second pump. This method is used most in mining uranium deposits.

Related Topics