Chapter: Civil : Prefabricated Structures : Introduction
Prefabricated Structures: Modular Coordination
Modular Coordination
Modular coordination means the
interdependent arrangement of a dimension based on a primary value accepted as
a module. The strict observance of rules of modular coordination facilitated,
1. Assembly
of single components into large components.
2. Fewest
possible different types of component.
3. Minimum
wastage of cutting needed.
Modular coordination is the basis for a standardization of a
mass production of component. A
set of rules would be adequate
for meeting the requirements of conventional and prefabricated construction.
These rules are adaptable for,
a. The
planning grid in both directions of the horizontal plan shall be
1. 3M for
residential and institutional buildings,
2. For
industrial buildings,
15M for
spans up to 12m
30M for
spans between 12m and 18m
60M for
spans over 18m
The
centre lines of load bearing walls shall coincide with the grid lines
b. In case
of external walls the grid lines shall coincide with the centre line of the
wall or a line on the wall 5 cm from the internal face of the wall
C. The planning module in the
vertical direction shall be 1M up to and including a ht of2.8M.
d.
Preferred increments foa the still
heights,doors,windows and other fenestration shall be1M.
e. In case
of internal coluums the grid lines shall coincide with the centre lines of
columns.In case of external columns,the grid lines shall coincide with the centre
lines of the columns in the storey or a line in the column from the internal
face of the column in the topmost storey.
A basic module can be represented
as module andfor larger project modules are represented aMp.
For eg: For a project module in
horizontal coordination,the component can be of 30cm and for vertical component
size be of 10cm.
The storey height is fixed
between finished floor levels as 2.8m and if the thickness of slab is<15cm
storey height is fixed as 2.7m. The centre distance between the load bearing
walls can be chose from a set of modules. The use of other dimensions is not
allowed.
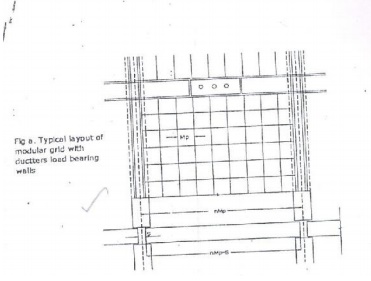
In the design of a
building,modular grid can be used consisting of parallel line spaced at a value
of module M or Mp and a grid line chosen as a base for setting out a part of a
building becomes a modular axis. In the fig (a),, a typical grid is chosen for
load bearing walls without duct. The interior walls are placed so that their
centerlines coincide with the modular axis. In the fig (b), a grid is shown for
load bearing walls with hollw ducts in between. The centre line of the grid is
found by deducting the size of duct.
Related Topics