Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
Predisposing Factors And Symptoms
PREDISPOSING FACTORS
AND SYMPTOMS
1.
Heredity - The strongest predisposing factor is
family history. Offspring of diabetics have insulin resistance and decreased
insulin sensitivity.
a.
List : Familial Risk of Developing Diabetes
b.
Your risk chance
c.
If both parents are diabetics 99%
d.
If one parent is a diabetic and the other
e.
from a family with a history of diabetes 70%
f.
If only one parent is a diabetic 40%
g.
If there is no history of diabetes in family 20%
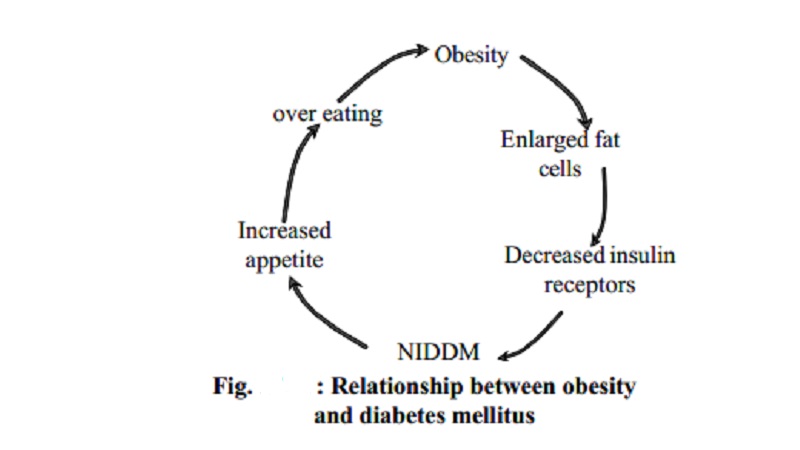
2.
Obesity - The chances of developing diabetes in
obese individuals is 3 times higher than in non obese individuals.
3.
Waist circumference is a reliable method of
identifying people with a higher risk of developing diabetes. Waist
circumference expands with increasing body waist. If waist circumference is
greater than 94 cm in women and 80 cm in men, the person is twice as likely to
have more than 2 risk factors. Diabetics have a higher waist to hip ratio
(WHR). If the WHR is greater than 1.0 in men and greater than 0.8 in women,
there is a greater risk to develop diabetes mellitus.
4. Age and sex - Individuals over 35 years of age have a 2 - 3 fold
increase in developing diabetes especially if they are 50%
5.
above desirable weight. The prevalence of
diabetes is more in men in India and more in females in western countries.
6.
Physical Activity - Lack of physical activity
increases the chance to develop obesity which increases the risk for developing
diabetes. Physically inactive individuals have a 40% chance of developing
diabetes mellitus.
7.
Under nutrition - Under nutrition impairs b cell function by increasing the susceptibility
of individuals to genetic and environmental influences.
8.
Stress - Stress precipitates diabetes in
susceptible individuals. In stress the body releases adrenaline, noradrenaline,
cortisone that raise blood glucose levels and counteract available insulin.
9.
Intake of simple sugars - A high intake of sugar
is associated with a prevalence of obesity and hence diabetes mellitus. Sugar
also depletes chromium which is essential for regulating blood sugar levels.
10.
Alcohol - Short term risk of heavy or continuous
alcohol intake include hypoglycaemia, glucose intolerance and ketone
accumulation.
Symptoms :
Many diabetics are not aware that they have the disease. Following are the
symptoms:
1.
Polydipsia (Excessive thirst)
2.
Polyphagia (Increased appetite especially for
sweets)
3.
Polyuria (frequent urination) and nocturia
4.
Itching
5.
Easy tiring, weakness or irritability
6.
Drowsiness
7.
Slow healing of cuts and wounds
8.
Frequent infections of the skin, gums and vagina
and pain in the legs, feet, urinary tract or fingers
9.
Blurred vision
10. Hyperglycaemia (elevated blood sugar level) above 140 mg / 100 ml, the normal level being 80-100 mg/100 ml - A deficient supply of functioning insulin affects the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and Proteins. As a consequence glucose enters the circulation and hyperglycaemia follows.
11. Glycosuria (sugar in the urine)
Related Topics