Geography | Social Science - Population in India | 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 6 : India - Population, Transport, Communication & Trade
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Geography : Chapter 6 : India - Population, Transport, Communication & Trade
Population in India
Population
The total number of people residing in a country at
a specified period of time is called the 'Population'
of that country. India is the second most populous country in the world next
only to china. India covers only 2.4 percent of the land area of the world, but
is the home of about 17.5 percent of the world’s population. It shows that the
proportion of population of India is far higher than the proportion of its
area. Thus, a little more than one out of every six persons in the world is
from India.
Census
Population census is the total process of
collecting, compiling, analysing or otherwise disseminating demographic,
economic and social data pertaining, at a specific time, of all persons in a
country or a well-defined part of a country. It happens in an interval of ten
years. The data collected through the census are used for administration,
planning, policy making as well as management and evaluation of various
programmes by the government.
In India the first census was carried
out in the year 1872. But the first complete and synchronous census was
conducted in 1881. And the 2011 census represents the fifteenth census of
India.
Distribution and Density of Population
The term 'Population Distribution' refers to the
way the people are spaced over the earth’s surface. The distribution of population
in India is quite uneven because of the vast variation in the availability of
resources. Population is mostly concentrated in the regions of industrial
centres and the good agricultural lands. On the other hand, the areas such as
high mountains, arid lands, thickly forested areas and some remote corners are
very thinly populated and some areas are even uninhabited. Terrain, climate,
soil, water bodies, mineral resources, industries, transport and urbanization
are the major factors which affect the distribution of population in our
country.
Uttar Pradesh is the most populous state in the
country with a population of 199.5 million followed by Maharashtra (112.3
million), Bihar (103.8 million) West Bengal (91.3 million) and the combined
Andhra Pradesh and Telangana (84.6 million). These five states account for
about half of the country’s population. Sikkim is the least populous state of
India(0.61 million). Delhi with 16.75 million population tops among the Union
territories.
The uneven distribution of population in the
country is the result of several factors such as physical, socio-economic and
historical ones. The physical factors include relief, climate, water, natural
vegetation, minerals and energy resources. Socio-economic factors consists of the
religion, culture, political issues, economy, human settlements, transport
network, industrialization, urbanization, employment opportunity etc.
Density of population
It is
expressed as number of persons per sq km. According to 2011, the average
density of population of India is 382 persons per sq.km. India is one of the
most thickly populated ten countries of the world. The most densely populated
state of India is Bihar and the state with least population density is
Arunachal Pradesh. Among the union territories, Delhi is the densely populated
one with 11,297 per sq.km, while Andaman and Nicobar Islands have the lowest
density of population.
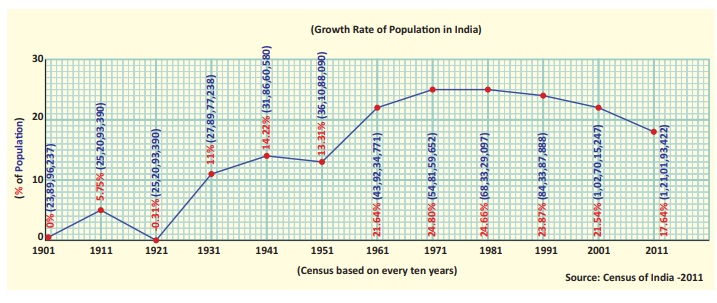
Population Growth and Change
Population change refers to
an increase or decrease of
population of an area from one period to another period. Population growth is
influenced by the birth rate, death rate and migration. These three make the
changes in population.
Birth rate refers to the number of live births per
thousand people in a year and the Death rate refers to the number of deaths per
thousand people in a year. The rapid decline in death rate is the major cause
of the rapid growth of population in India.
The following table shows the decadal growth rate
of population from 1901 to 2011.
Related Topics