Recent Developments in Physics - Physics in medical diagnosis and therapy | 12th Physics : UNIT 11 : Recent Developments in Physics
Chapter: 12th Physics : UNIT 11 : Recent Developments in Physics
Physics in medical diagnosis and therapy
Physics in medical diagnosis and therapy
Medical science very much revolves around physics principles. Medical instrumentation has widened the life span due to the technology integrated diagnosis and treatment of most of the diseases. This modernisation in all fields is possible due to efficient application of fundamental physics.
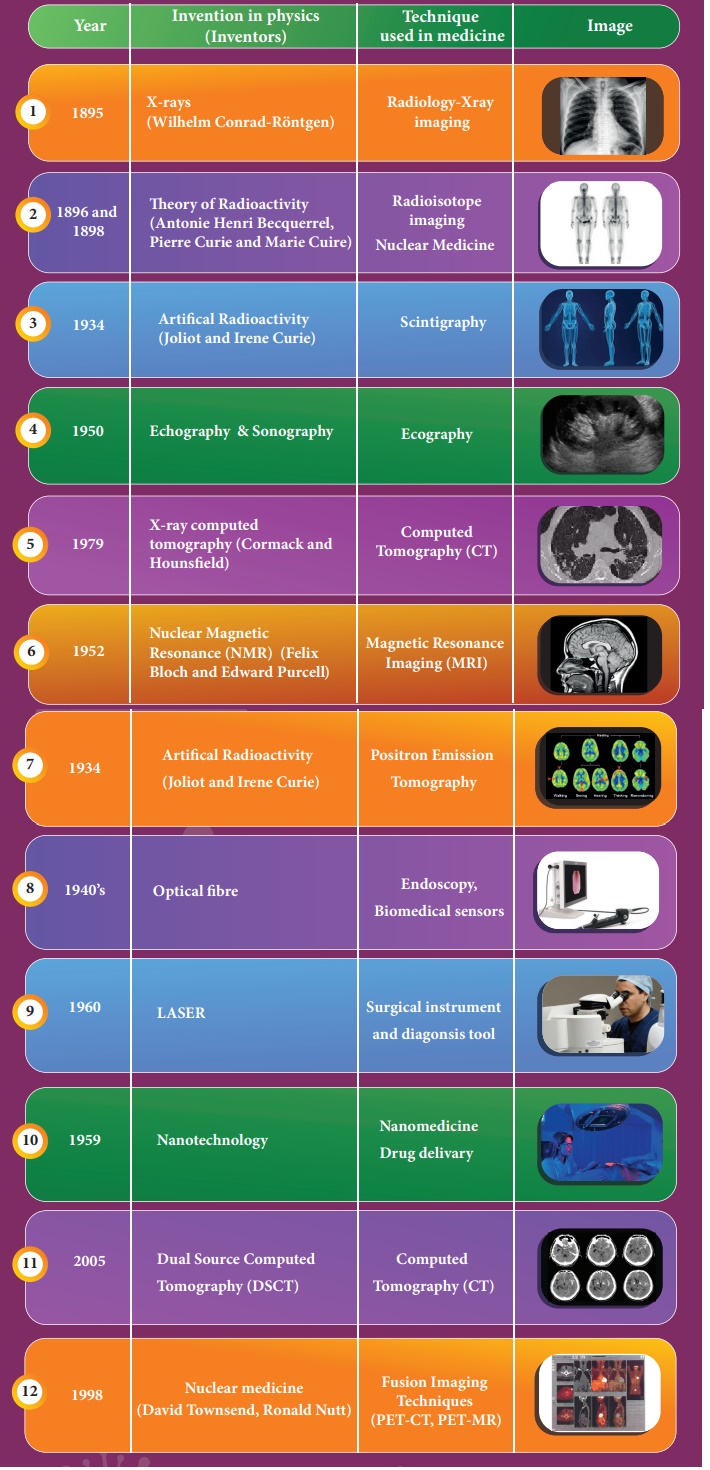
The development in medical field has been proportional to the evolution of physics as indicated below (Not for examination)
1. 1895 :
X-rays (Wilhelm Conrad-Röntgen) - Radiology-Xray imaging
2. 1896 and 1898 : Theory of Radioactivity (Antonie Henri Becquerrel, Pierre Curie and
Marie Cuire) - Radioisotope imaging Nuclear Medicine
3. 1934: Artifical
Radioactivity (Joliot and Irene Curie) - Scintigraphy
4. 1950: Echography
& Sonography - Ecography
5. 1979: X-
ray computed tomography (Cormack and Hounsfield) - Computed Tomography (CT)
6. 1952: Nuclear
Magnetic Resonance (NMR) (Felix Bloch and Edward Purcell) - Magnetic
Resonance Imaging (MRI)
7. 1934: Artifical
Radioactivity (Joliot and Irene Curie) - Positron Emission Tomography
8. 1940’s: Optical
fibre - Endoscopy, Biomedical sensors
9. 1960: LASER
- Surgical instrument and diagonsis tool
10. 1959: Nanotechnology
- Nanomedicine Drug delivary
11. 2005: Dual Source Computed Tomography (DSCT) -
Computed Tomography (CT)
12. 1998: Nuclear medicine (David Townsend, Ronald
Nutt) - Fusion Imaging Techniques
(PET-CT, PET-MR)
The recent advancement in medical technology includes
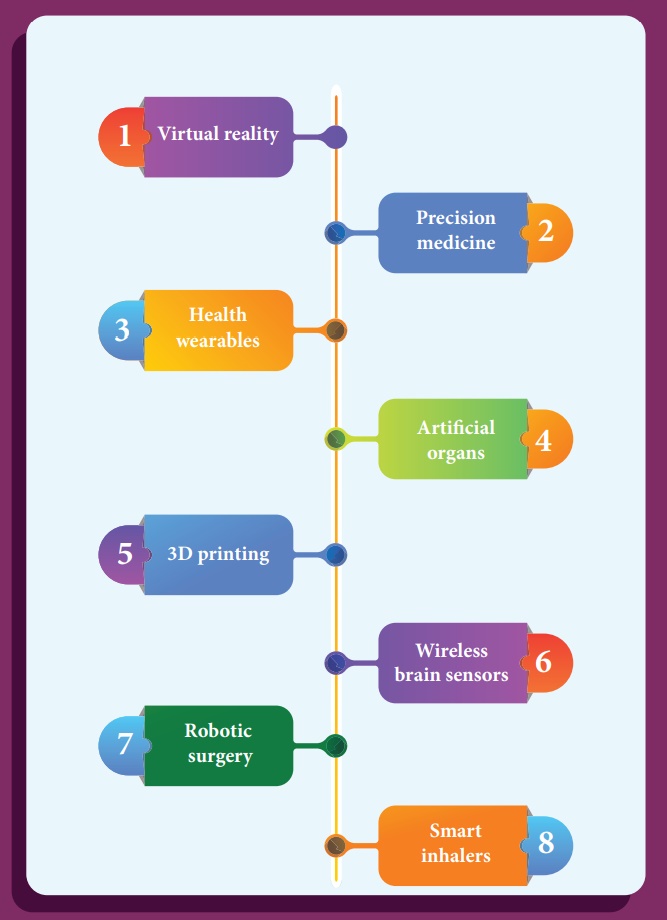
The innovation in medical diagnosis has taken
leaps and bounds due to the integration of technology and basic physics. A few
of such advancements are discussed.
1. Virtual reality
Medical virtual reality is effectively used to
stop the brain from processing pain and cure soreness in the hospitalized
patients. Virtual reality has enhanced surgeries by the use of 3D models by
surgeons to plan operations. It helps in the treatment of Autism, Memory loss,
and Mental illness.
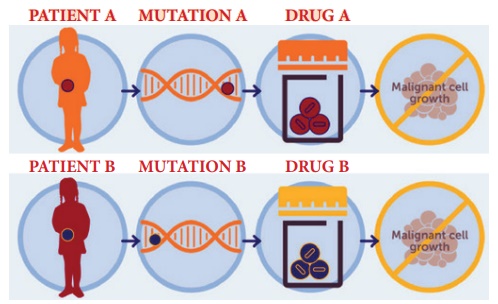
2. Precision medicine
Precision medicine is an emerging approach for
disease treatment and prevention that takes into account individual variability
in genes, environment, and lifestyle for each person. In this medical model it
is possible to customise healthcare, with medical decisions, treatments,
practices, or products which are tailored to the individual patient.
3. Health wearables
A health wearable is a device used for tracking a
wearer's vital signs or health and fitness related data, location, etc. Medical
wearables with artificial intelligence and big data provide an added value to
healthcare with a focus on diagnosis, treatment, patient monitoring and
prevention.

NOTE
Big Data: Extremely large data sets that may be
analysed computationally to reveal patterns, trends, and associations,
especially relating to human behaviour and interactions.
4. Artificial organs
An artificial organ is an engineered device or
tissue that is implanted or integrated into a human. It is possible to
interface it with living tissue or to replace a natural organ. It duplicates or
augments a specific function or functions of human organs so that the patient
may return to a normal life as soon as possible.
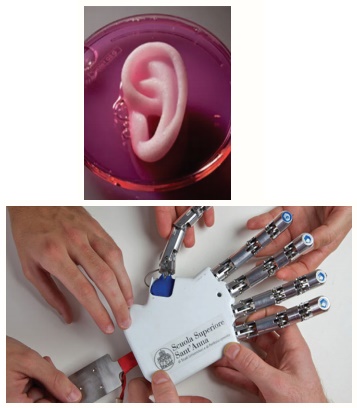
5. 3D printing
Advanced 3D printer systems and materials assist
physicians in a range of operations in the medical field from audiology,
dentistry, orthopedics and other applications.
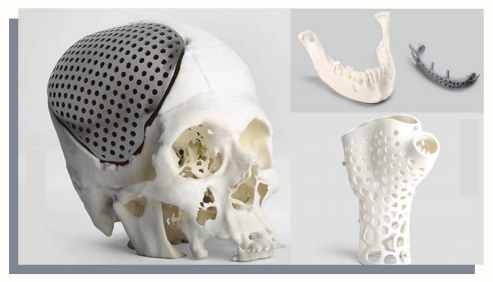
6. Wireless brain sensors
Wireless brain sensors monitor intracranial
pressure and tempera- ture and then are absorbed by the body. Hence there is no
need for surgery to remove these devices.
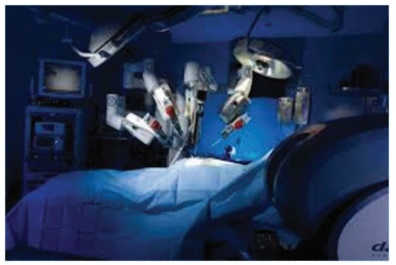
7. Robotic surgery
Robotic surgery is a type of surgical procedure
that is done using robotic systems. Robotically-assisted surgery helps to
overcome the limitations of pre-existing minimally-invasive surgical procedures
and to enhance the capabilities of surgeons performing open surgery.
8. Smart inhalers
Inhalers are the main treatment option for asthma.
Smart inhal- ers are designed with health systems and patients in mind so that
they can offer maximum benefit. Smart inhalers use bluetooth technology to
detect inhaler use, remind patients when to take their medication and gather
data to help guide care.

Other recent developments in physics
Particle Physics
Particle physics deals with the theory of
fundamental particles of nature and it is one of the active research areas in
physics. Initially it was thought that atom is the fundamental entity of
matter. In 1930s, it was established that atoms are made up of electrons,
protons and neutrons.
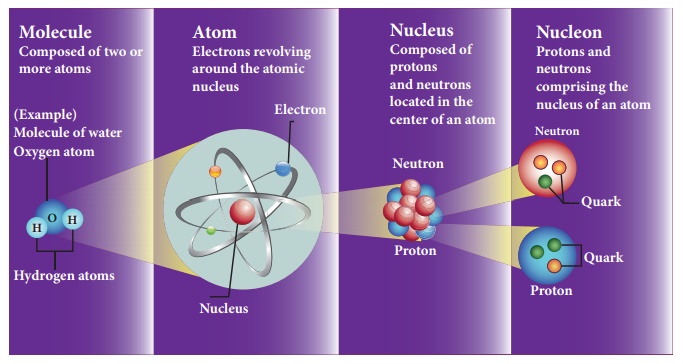
In the 1960s, quarks were discovered and it was understood that proton and neutron are made up of quarks. In the meantime, the particle physics research gained momentum and has grown exponentially both in theoretical and experimental perspective. Later it was found that the quarks interact through gluons. It is the field which received more number of noble prizes. Recently in the year 2013, famous ‘Higgs particles’ also known as “God” particles were discovered and for this, Peter Higgs and Englert received noble prize in physics. It is the ‘Higgs particle’ which gives mass to many particles like protons, neutrons etc.
Cosmology
Cosmology is the branch that involves the origin
and evolution of the universe.
It deals with formation of stars, galaxy etc. In
the year 2015, the existence of “gravitational waves” was discovered and noble
prize was awarded for this discovery in the year 2017.
Gravitational waves are the disturbances in the curvature of space-time and it travels with speed of light. Any accelerated charge emits electromagnetic wave. Similarly any accelerated mass emits gravitational waves but these waves are very weak even for masses like earth. The strongest source of gravitational waves are black holes. The discovery of gravitational waves made it possible to study the structure of black holes since it is the strongest source of gravitational waves. In fact, the recent discoveries of gravitational waves are emitted by two black holes when they merge to a single black hole. In fact, Albert Einstein theoretically proposed the existence of ‘gravitational waves’ in the year 1915. After 100 years, it is experimentally proved that his predictions are correct.
Gravitational wave

Black holes are end stage of stars which are highly dense massive object. Its mass ranges from 20 times mass of the sun to 1 million times mass of the sun. It has very strong gravitational force such that no particle or even light can escape from it. The existence of black holes is studied when the stars orbiting the black hole behave differently from the other stars. Every galaxy has black hole at its center. Sagittarius A* is the black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy.
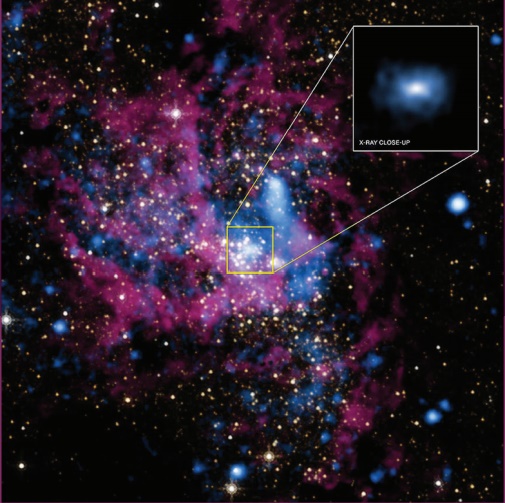

Black hole sagittarus A*
The famous physicist Stephen Hawking worked in the
field of black holes.

Actual photograph of a super massive black hole M87*
Super computers and eight telescopes stationed on
five continents (EVENT HORIZON TELESCOPE) were used to develope a huge data to
accomplish this. It has once again confirmed the Einstein’s theory of general
relativity.
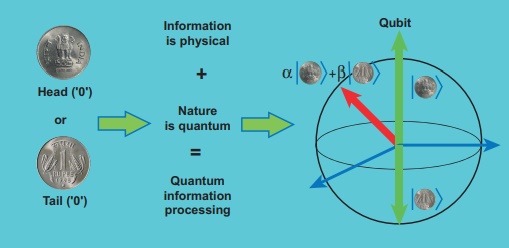
Quantum information theory (Not for examination)
It is another fast developing research area which
deals with improving the information storage using quantum computers. The
present computers store information in the form of ‘bits’ but quantum computers
store information in the form of ‘qubits’. ‘qubit’ refers to quantum bit and it
is the basic unit of quantum information. Classical bit implies either 0 or 1.
But qubit not only includes 0 or 1 and also linear superposition of 0 and 1.
This technology reduces the calculating time exponentially. This research field
has very promising application in future.
Many striking innovations and
discoveries originate from scientific fictions. Robots are also no exception to
this. The word robotics was derived from the word robot. It was introduced in
the play ‘Rossum Universal Robots’ by the Zech writer Karel Capek in 1920. The
word robot comes from the Slavic word rabota, which means labour or work. The
play begins in a factory that makes artificial people called robots. They
looked like creatures that can be mistaken for humans (picture shown). These
characters were very similar to the modern ideas of androids.
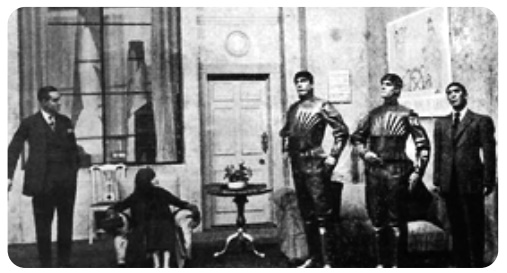
(A scene from the play Rossum Universal Robots,
showing three robots)
Related Topics