Chapter: Modern Pharmacology with Clinical Applications: Calcium Channel Blockers
Pharmacological Effects on the Cardiovascular System
PHARMACOLOGICAL
EFFECTS ON THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
The effects of the
prototypical calcium channel blockers are seen most prominently in the
cardiovascular system (Table 19.1), although calcium channels are widely
dis-tributed among excitable cells. The following calcium channel–blocking
drugs are clinically the most widely used compounds in this very extensive
class of pharma-cological agents: amlodipine, diltiazem, isradipine,
nifedipine, nicardipine, nimodipine, and verapamil.
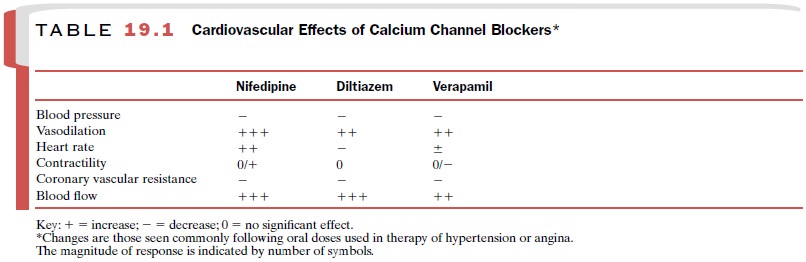
Vascular Effects
Vascular tone and contraction
are determined largely by the availability of calcium from extracellular
sources (influx via calcium channels) or intracellular stores. Drug-induced inhibition of calcium influx
via voltage-gated channels results in widespread dilation and a de-crease in
contractile responses to stimulatory agents. In general, arteries and arterioles are more sensitive to the
relaxant actions of these drugs than are the veins, and some arterial beds
(e.g., coronary and cerebral ves-sels) show greater sensitivity than others.
Peripheral vasodilation and the consequent fall in blood pressure are commonly
accompanied by reflex tachycardia when nifedipine and its analogues are used;
this is in contrast to verapamil and diltiazem, whose effects on peripheral
vessels are accompanied by cardiodepres-sant effects.
Cardiac Effects
Calcium currents in cardiac tissues serve the functions of inotropy, pacemaker activity (sinoatrial (SA) node), and conduction at the atrioventricular (A-V) node. In principle, the blockade of calcium currents should result in decreased function at these sites.
In clinical use, however, dose-dependent
depression is seen only with vera-pamil and diltiazem and not with nifedipine,
reflecting mainly differences in the kinetics of their interaction at calcium
channels (see section on calcium antagonism). Characteristic cardiac effects include a variable slowing of the heart
rate, strong depression of conduction at the A-V node, and inhibition of
contractility, especially in the presence of preexisting heart failure.
Related Topics