Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : Platforms and Sensors
Pay Load Description Of Important Earth Resources And Meterological Satellites
PAY LOAD DESCRIPTION OF IMPORTANT
EARTH RESOURCES AND METEROLOGICAL SATELLITES
1 EARTH
RESOURCES SATELLITES
There are three distinct groups
of earth resources satellites. The first group of satellites record visible and
near visible wavelengths. The five satellites of Landsat series which are the
first generation earth resources satellites are a classic example of this
group. The four IRS satellites and the more improved SPOT series of these
satellites may be considered the second generation earth resources satellites
of the same group. Group two satellites carry sensors that record thermal
infrared wavelengths and include the Heat Capacity Mapping Mission sate·llites,
namely, Explorer series. Group three satellites are deployed with sensors that
record micro wavelengths. The seasat series and the ERS are examples of this
group.
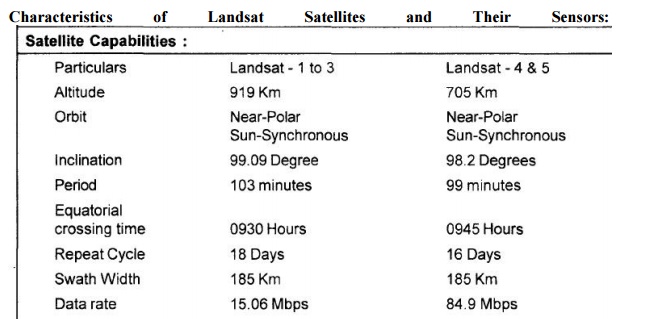
2 LANDSAT
SATELLITE PROGRAMME
National Aeronautics and Space
Administration (NASA) of USA with the cooperation of the U.S. Department of
Interior planned the launching of a series of Earth Resources Technology
Satellites (ERTS). ERTS-1 was launched by a ThorDelta rocket on July 23, 1972
and it operated until January 6,1978. It represented the first unmanned
satellite designed to acquire data about the earth resources on a systematic,
repetitive, medium resolution, multispectral basis. Subsequently, NASA renamed
the ERTS programme as "Landsat" programme to distinguish it from the
series of meteorological and oceanographic satellites that the USA launched
later. ERTS-1 was retrospectively named Landsat-1. Five Landsat satellites have
been launched so far and this
experimental programme has evolved into an operational global resource
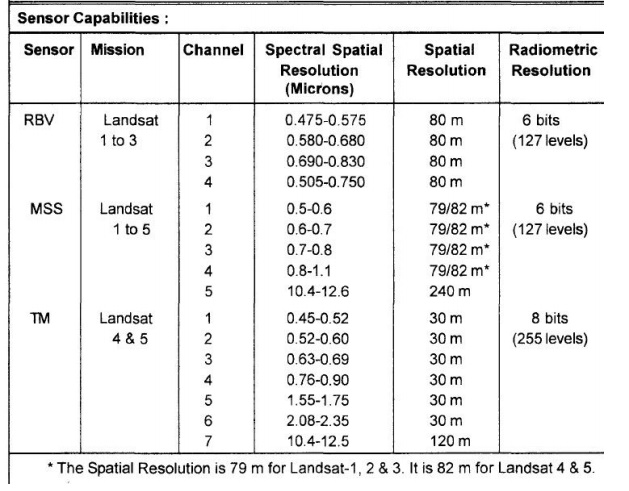
monitoring programme. Three different types of sensors have been flown in
various combinations on the five missions. These are Return Beam Vidicon (RBV)
camera system, the Multispectral Scanner (MSS) system and the Thematic Mapper
(TM).
Characteristics
of
Landsat
Satellites
and
Their Sensors:
3 SPOT
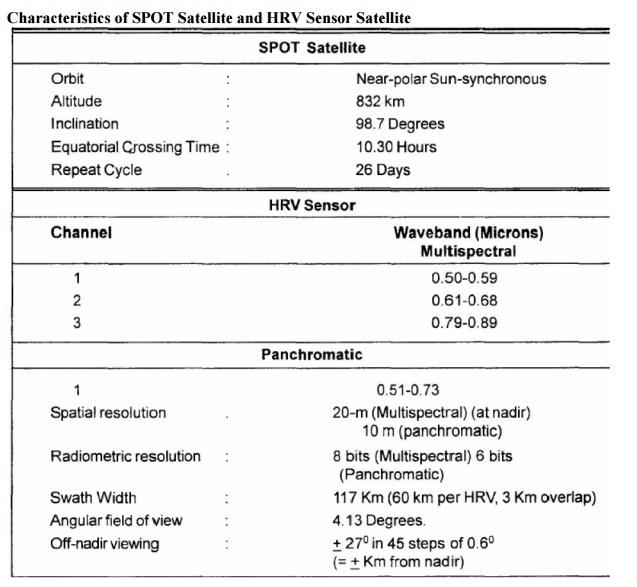
SATELLITE PROGRAMME
France, Sweden and Belgium joined
together and pooled up their resources to develop the System Pourl' Observation
dela Terre (SPOT), an earth observation satellite programme. The first
satellite of the series, SPOT-1 was launched from Kourou LaunchRange in French
Guiana on February 21,1986 aboard an Ariance Launch vehicle (AIV).This is the
first earth resource satellite system to include a linear array sensor
employing the push broom scanning technique. This enables side-to-side
oft-nadir viewing capabilities and affords a full scene stereoscopic imaging
from two different viewing points of the same area. The high resolution data
obtained from SPOT sensors, namely, Thematic Mapper (TM) and High Resolution
Visible (HRV), have been extensively usedfor urban planning, urban growth
assessment, transportation planning, besides the conventional applications related
to natural resources.
Characteristics
of SPOT Satellite and HRV Sensor Satellite
4 INDIAN
REMOTE SENSING SATELLITE (IRS)
The IRS mission envisages the
planning and implementation of a satellite based remote sensing system for
evaluating the natural resources. The principal components of the mission are: a three axis stabilised polar
sunsynchronous satellite withmultispectral sensors, a ground based data
reception, recording and processingsystems for the multispectral data, ground
systems for the in-orbit satellite controlincluding the tracking network with
the associated supporting systems, and
hardwareand software elements for the generation of user oriented data
products, data analysis and archival. The principal aim of the IRS mission is
to use the satellite data in conjunction with supplementary/complementary
information from other sources forsurvey and management of natural resources in
important areas, such as, agriculture, geology and hydrology in association
with the user agencies. IR$ series of satellites are IRS lA, IRS IB, IRS IC,
IRS ID and IRS P4 apart from other satellites which were launched by the
Government of India. The orbital and sensor characteristics of IRS IAand IB are
the same and IRS IC and IRS ID have almost similar characteristics. IRSP4is an
oceanographic satellite, and this will be discussed in the next section. IRS
has application potential in a wide range of disciplines such as management of
agricultural resources, inventory of forest resources, geological mapping,
estimation of water resources, study of coastal hydrodynamics, and water
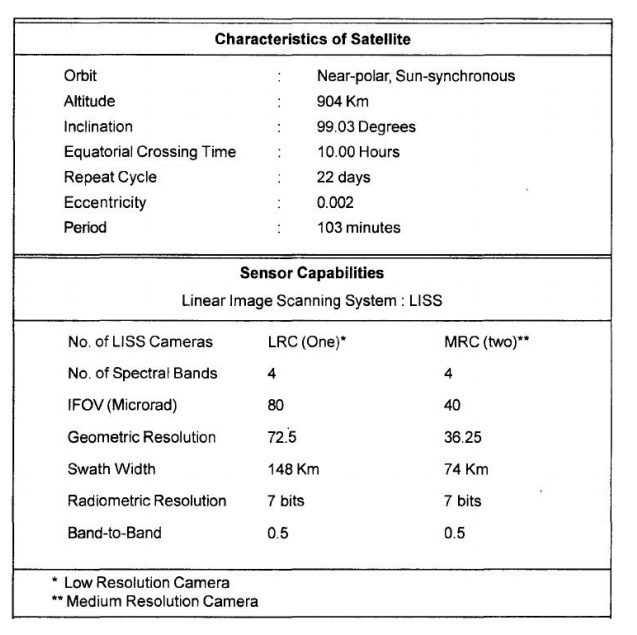
quality surveying. The sensor payload system consists of two push broom cameras
(LiSS-II) of36.25 m resolution and one camera .(LlSS-I) of 72.5 m resolution
employing linear Charge Coupled Device (CCD) arrays as detectors. Each camera
system images in four spectral bands in the visible and near IR region. The
camera system consists of collecting optics, imaging detectors, inflight
calibration equipment, and processing
devices. The orbital
characteristics of the IRS-1A, 1 B satellites and the sensorcapabilities are
given in Table 4.3. As IRS-1 D satellite is the latest satellite of theseries
and hence the system overview of IRS - 1 D is provided.
The IRS-1 D is a three-axes body
stabilized satellite, similar to IRS-1 C. SinceIRS-1 C and 1 D are similar in
orbital characteristics and sensor capabilities, the detailsof IRS-1 D are
discussed as it is a very recent satellite. It will have an operational lifeof
three years in a near polar sun synchronous orbit at a mean altitude of 780 Km.
The payload consists of three sensors, namely, Panchromatic camera (PAN),
linear imaging and self-scanning sensor (LiSS-III) and wide Field sensor
(WiFs). The satellite is equipped with an On-Board Tape Recorder (OBTR) capable
of recording limited amount of specified sensor data. Operation of each of the
sensors can be programmed.
The payload operation sequence
for the whole day can be loaded daily on to theon-board command memory when the
satellite is within the visibility range. The ground segment consists of a
Telemetry Tracking and Command (TTC) segment comprisinga TTC network, and an
Image segment comprising data acquisition, data processing and product
generation system along with data dissemination centre. The over view of IRS-1
D mission is to provide optimum satellite operation and a mission control centre
for mission management, spacecraft operations and scheduling. The three sensors
on board IRS-1 D and IRS-1 C are described in the following paragraph.
The
panchromatic camera provides data with a spatial resolution of 5.2-5.8 m(at
nadir) and a ground swath between 63 Km -70 Km (at nadir). It operates in
the0.50 - 0.75 microns spectral band. This camera can be steered upto ± 26 deg.
storable upto ±398 Km across the track from nadir, which in turn increases the
revisit capability to 3 days for most part of the cycle and 7 days in some
extreme cases.
Related Topics