Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : Platforms and Sensors
Air Borne and Space borne TIR and Microwave Sensors
AIR BORNE AND SPACEBORNE TIR AND MICROWAVE SENSORS
Components of sensor systems operating in the visible, infrared,
thermaland microwave regions of the electromagnetic spectrum are described in
this section.Although analogue
photographic imagery has many advantages, this book is mainly concerned with
image data collected by scanning systems that ultimately generate digital image
products. It is apparent that the useful wavebands are mostly in the visible
and the infrared for passive remote sensing detectors and in the radar and
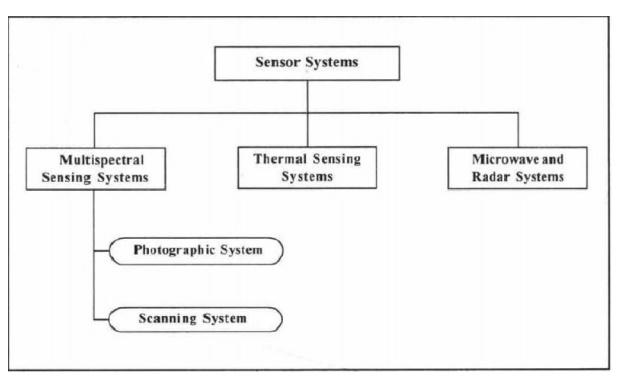
microwave region for active type of sensors. Accordingly the imaging sensor
systemsin remote sensing are classified as shown in Fig.2.4
In the
case of multiband photographic system, different parts of the spectrumare
sensed with different film-filter combinations. Multiband digital camera images
and video images are also typically exposed on to the camera's CCD or CMOS
sensor (s) through different filters. Electro-optical sensors, such as, the
thematic mapper of Landsat, typically sense in atleast several bands of
electromagnetic spectrum.
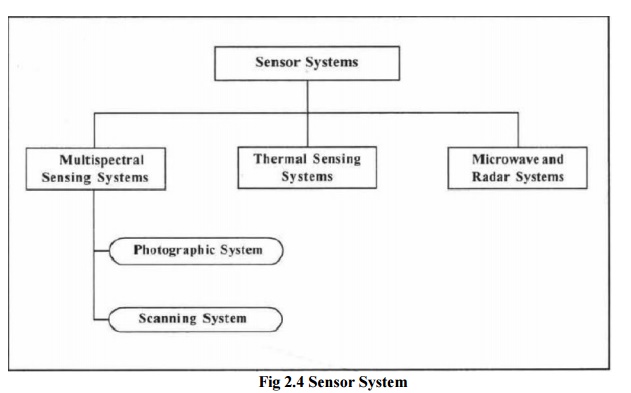
Fig 2.4
Sensor System
The photographic system suffers
from one major defect of considerable distortion at the edges. This is due to a
large lens opening. From lens theory, we know that distortions can be minimised
and resolution considerably improved by using a narrow beam of light. This can
be achieved by a system called scanning system. A multispectral scanner (MSS)
operates on the same principle of selective sensing in multiple spectral bands,
but such instruments can sense in many more bands and over a great range of the
electromagnetic spectrum. Because of the advancement in utilising electronic
detectors, MSS can extend the range of sensing
from 0.3 flm to 14 flm. Further
MSS can sense in very narrow bands. Multispectral scanner images are acquired
by means of two basic process: across-track and along-track scanning.
Multispectral scanner systems build up two-dimensional images of the terrain
for a swath beneath the platform. Across-track systems are also called whisk
broom scanner systems. This type of scanning system scans the terrain along
scanlines that are right angles to the direction of the spaceborne/airborne
platform. Fig. 4.8 illustrates the operation across-track system.
In this type of scanning system,
scanner repeatedly measures the energy from one side of the aircraft to the
other. Data are collected within an arc below the aircraft typically of 900 to
1200. Successive scan lines are covered as the aircraft moves forward, yielding
a series of contiguous or narrow strips of observation comprising a two-dimensional
image of rows (scan lines) and columns. At any instant, the scanner'sees' the
energy within the systems IFOV. This explains the spatial resolution of the sensing.
The second type of multispectral
scanning system is along-track scanning systemor push broom systems. This type
of scanners record multiband image data along a swath beneath an aircraft. As
the aircraft/spacecraft advances in the forward direction, the scanner scans
the earth with respect to the designed swath to build a twodimensional image by
recording successive scanlines that are oriented at right angles to the
direction of the aircraft/spacecraft.
1THERMAL SENSING SYSTEMS
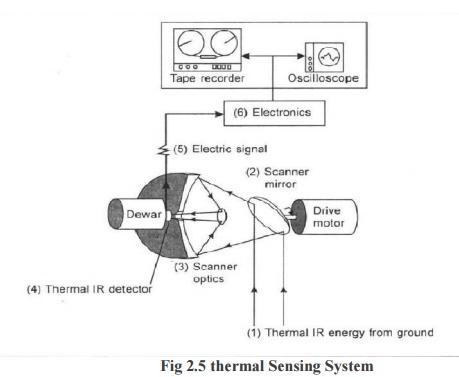
Thermal scanner is one of the most important thermal sensing
systems, particular kind of across track multispectral scanner which senses in the thermal portion of the electromagnetic spectrum by means of inbuilt
detectors. These systems are
restricted to operating in either 3 to
5 I-lm or 8 to 14 I-lm range of wavelengths. The operation and the efficiency of this type
of scanning systems are based on thecharacteristics of the detectors. Quantum or photon detectors are
typically used to detect the
thermal radiation. These detectors operate on the principle of direct
interaction between photons of radiation incident on them and the energy levels of electrical charge
carriers within the detector material.
2 MICROWAVE IMAGING SYSTEMS
The
fundamental principle of microwave sensing and the conceptual design of radar
have been discussed in chapter 3, where it is stated that the microwave region
of the electromagnetic spectrum includes radiation with wavelengths longer than
1 mmImaging. Microwave instruments do not, however, rely on the detection of
solar or terrestrial emissions. In the following sections of this chapter, the
properties of the operational synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems and
Radarsat systems are presented along with other sensing systems.
Related Topics