Chapter: Civil : Remote Sensing Techniques and GIS : Platforms and Sensors
Meterological Satellites
METEROLOGICAL SATELLITES:
Meteorological satellites
designed specifically to assist. in weather predictionand monitoring, generally
incorporate sensors that have very coarse spatial resolution compared to
land-oriented systems. These satellites, however, afford a high frequency global
coverage. USA has launched a multiple series of meteorological satellites with
a wide range of orbit and sensing system designs. The first of these series is
called the NOAA, an acronym for National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Administration. These satetlites are in near-polar, sunsynchronous orbits
similar to those of 'Landsat and IRS'. In contrast, another series of
satellites which are of essentially meteorological type, called Geostationary
Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) series and Meteosat operated by
European Space Agency, are geostationary, remaining in a constant relative
position over the equator.
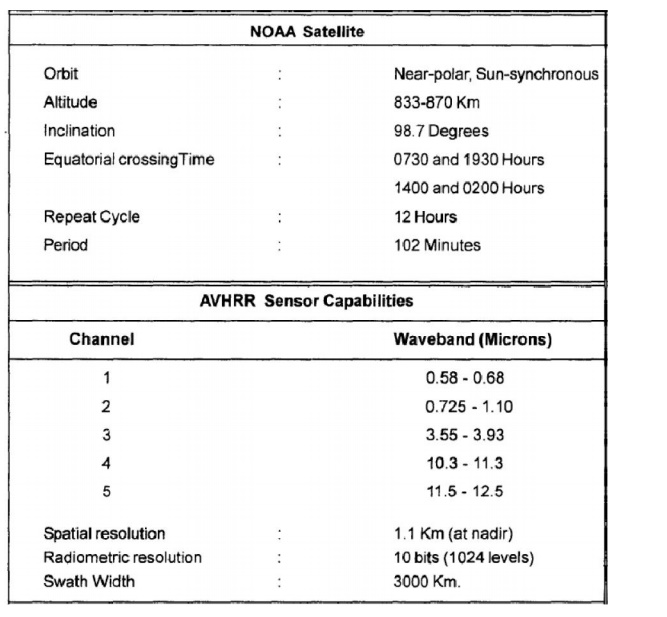
1 NOAA SATELLITES
Several generations of satellites
in the NOAA series have been placed in orbit.The satellites NOAA-6 through
NOAA-10 contained Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR). The
even-numbered missions have daylight (7.30 A.M.) north-to-south equatorial
crossing and the odd-numbered missions have night time (2.30 A.M.)
north-to-south equatorial crossing. The basic characteristics of these missions
and the AVHRR instrument are listed in Table 4.8. Apart from routine
climatological analyses, the AVHRR data have been used extensively in studies
of vegetation dynamics, flood monitoring, regional soil moisture analysis, dust
and sandstorm monitoring, forest wild fire mapping, sea surface temperature
mapping, and various geological applications, including observation of volcanic
eruptions, and mapping of regional drainage and physiographic features.
Details of NOAA Satellite and AVHRR Sensor
Characteristics
of Satellite
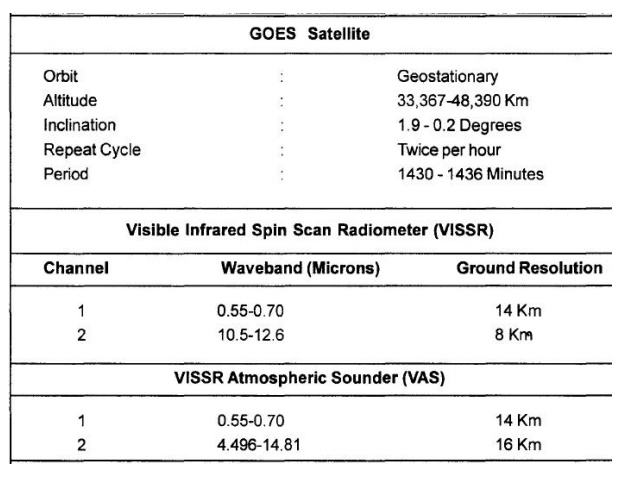
2 GOES SATELLITES
The GOES
programme is a cooperative venture between NOM and NASA. The Geo-stationary
Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) are part of a global network of
meteorological satellites spaced about 70 o longitude apart around the world.
The GOES images are distributed in near real-time for use in local
weatherforecasting. They have also been used in certain large area analyses
such as regional snow cover mapping.
3 NIMBUS SATELLITES
This is
one of the ocean monitoring satellites launched in October 1978. This satellite
carries the Coastal Zone Colour Scanner (CZCS) designed specifically to measure
ocean parameters. The details of the six bands in which the CZCS operates and
the characteristics of NIMBUS-7 satellite are presented in Table 4.10 The CZCS
has been used to measure sea surface temperatures, detection of chlorophyll and
suspended solids of near-shore and coastal waters.
Related Topics