Chapter: Maternal and Child Health Nursing : Anatomy and physiology of female reproductive
Part of the fetal skull
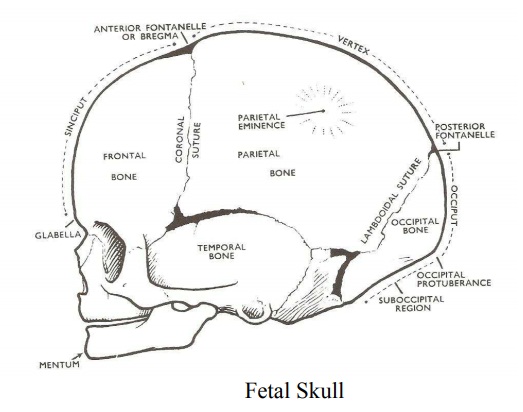
The fetal skull
The bones
of the skull develop from membranes, ossification starts as early as the 5th
week following conception. At term ossification is almost complete except for
the thin lines of membranes separating the bones from each other known as the
sutures. Ossification of the skull is not complete until early adulthood.
The part of the fetal skull
1. The vault: Is from the line from the nape of
the neckto the orbital ridge. The vault is made up of 5 bones and two enter
into the lateral wall. These are:
2 Frontal
bones
2
Parietal bones:
1
Occipital bone
2
Temporal bones and the wings of the sphenoid bones form the side wall of the
skull.
2. The face: This area extends from the
orbital ridge tothe junction of the neck with the chin. It is composed of 14
fused bones.
3. The base: These bones are also firmly
united and helpto protect the brain.
4. The Sutures
These are
membranous lines found at the junction between the bones of the vault. There
are four important sutures on the vault where ossification has not been
completed.
The Frontal Suture: Separates
the two frontal bones, itextends from the root of the nose to the bregma.
The Coronal Suture: Separates
the frontal and the parietalbones.
Sagittal Suture: Separates the two parietal bones. Lambdoidal suture: Separates the
occipital and the parietalbones.
Others
are the sutures that separate the parietal bones from the temporal bones.
5. The Fontanelles
Fontanelles
are formed where two or more sutures meet between the bones. There are 6
sutures on the vault but only two are of importance. These are:
Anterior Fontanelle (or bregma): Formed at
the junctionof the Sagittal, Fontal, and coronal sutures. It is a diamond
shaped membranous space. It has four angles which correspond with the entry of
each suture. It is about 3-4cm long and 1.5cm wide. It is a valuable aid in
vaginal examination to determining the position. Cerebral pulsation can be felt
through it and it is a guide to baby’s health – It bulges in brain infection or
increase p ressure and depressed in dehydration. Closes 18-24months after
birth.
The Posterior fontanell – (lambda): Formed at
thejunction of the sagittal and lambdoidal sutures. It is a small triangular
membranous space. It is felt on vaginal examination during labour in a well
flexed head. It closes at 6 weeks after birth.
6. The region of the fetal skull
1.
Vertex
2.
Face
3.
Brow (Sinciput)
4.
Occiput
Other
regions are:
Glabella
– is the bridge of the nose, between the e yebrows.
Bregma –
anterior fontanelle
Lambda –
Posterior fontanelle
Mentum –
Chin.
Related Topics