Rajya Sabha, Lok Sabha | Qualification, terms, Election, Functions, The Speaker, Powers and Functions - Parliament of India | 10th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 2 : Central Government of India
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 2 : Central Government of India
Parliament of India
Parliament of India
The
parliament is the legislative organ of the Union government. The Parliament of
India consists of three parts they are the 1) President, 2) Rajya Sabha (the
council of States) 3) Lok Sabha (the House of the People). The Rajya Sabha is
the Upper House and the Lok Sabha is the Lower House it is termed as bicameral
legislature.

Rajya Sabha
The
council of State or Rajya Sabha consists of 250 members out of whom 238
represent the states and the Union Territories, elected by the method of
indirect election.
The
12nominated members shall be chosen by the President from amongst persons
having ‘special knowledge or practical experience in the field of literature,
science, sports, art and social service.
Qualification of the Members
• He
should be a citizen of India.
• He
should not be less than 30 years of age.
• He
should not hold any office of profit under any Government.
• He
should be a person with sound mind and monetarily solvent.
• He
should not be the member of Lok Sabha or any other legislature.
Term of House
The Rajya
Sabha is a permanent house and it cannot be dissolved. The members of the Rajya
Sabha are elected for a term of six years. One third of the members of Rajya
Sabha retire every two years, and new members are elected to fill the seats
thus vacated. The Vice President of India is the Ex-officio Chairperson of the
Rajya Sabha. The Deputy Chairperson of the Rajya Sabha is elected by the
members of the Rajya Sabha.
Money Bill: Rajya
Sabha does not have any power to amend or reject the Money bill. Lok Sabha can
only introduce Money bill and once it is approved by the Lok Sabha, it is
passed to Rajya Sabha for its approval. If Rajya Sabha fails to pass it within
14 days then the bill gets passed without the approval of Rajya Sabha. Also,
Lok Sabha does not need to consider the amendments proposed by the Rajya Sabha.
Lok Sabha can reject all the proposals and pass it.
Election
Members
of Rajya Sabha are elected by the elected members of the ‘State Legislative
Assemblies’ in accordance with the system of proportional representation by
means of the single transferable vote. This process of election is called
“indirect election” as they are not elected by the people directly.
Lok Sabha
The Lok
Sabha is the popular house of the Indian Parliament and contains elected
representatives of the people. Maximum number of members can be elected for Lok
Sabha is 552. The Lok Sabha as of today has 543 elected members. Out of these,
530 members are elected from different states and 13 members from the Union
Territories. The President generally nominates two members belonging to the
Anglo-Indian community. At present, the Lok Sabha consists of 545 members.
Qualification of the Members
• He
should be a citizen of India.
• He
should not be less than 25 years of age.
• He
should have his name in electoral rolls in some part of the country.
• He
should not hold any office of profit under the Union or State Government.
• He
should be mentally sound and economically solvent.
The term of the House
Generally
the Lok Sabha enjoys a term of five years from the date of its first session.
It can be dissolved by the President before the expiry of its term on the
advice of the Prime Minister. The emergency provisions of the Constitution
enable the President to prorogue or dissolve the Lok Sabha either on the advice
of the Prime Minister or on being convinced that no party or no alliance of
parties enjoys necessary majority support in the House.
Election
The
members of the Lok Sabha are directly elected by the people of the
constituencies created on the basis of population. The Election Commission of
India arranges, supervises and conducts elections to the Lok Sabha.
“Universal
Adult Franchise” is followed while electing the members of the Lok Sabha. All
Indian Citizens above 18 years of age who are registered as voters will vote
for their representatives.

Functions of the Lok Sabha
• Any
bill can be introduced and passed in the Lok sabha (Including Money Bill).
• It has
the same power as Rajya Sabha to participate in case of impeachment of
president and the judges of Supreme Court.
• It has
equal power as Rajya Sabha in passing any bill for constitutional amendment.
Elected members of
the Parliament from Tamil Nadu.
• Rajya Sabha – 18 members
• Lok Sabha – 39 members
The Speaker
The Lok
Sabha is presided over by the ‘speaker’ who is elected by its members. The
office of the Speaker occupies an essential position in our Parliamentary
democracy. The Speaker continues to be in the office even in the houses
dissolved, till a new Speaker is elected by the new Lok Sabha. The Speaker
presides over a joint sitting of the two Houses of Parliament. He has the power
to decide whether a Bill is Money Bill or an ordinary one. While the office of speaker
is vacant or the speaker is absent from the sitting of the house, the deputy
speaker presides, except when a resolution for his own removal is under
consideration.
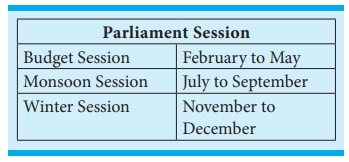
Powers and Functions of the Parliament
• The
Parliament of India has the functions of Legislation, overseeing of
administration, passing of Budget, ventilation of public grievances, discussion
of various subjects like development plans, international relations and
internal policies.
• Parliament
is also vested with powers to impeach the President and to remove Judges of the
Supreme Court and High Courts, Chief Election Commissioner and Comptroller and
Auditor-General of India in accordance with the procedure laid down in the
Constitution.
• The
Parliament has the power to change the boundaries of the States.
Related Topics