Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Class Nursing Health Care Hospital Hygiene Higher secondary school College Notes
Parboiling and Milling - Effect on nutrient content
PARBOILING AND MILLING - EFFECT ON NUTRIENT CONTENT
Parboiling is a process of soaking paddy in water at 65 o - 70 o C for 3 - 4 hours. The water is drained and the soaked
paddy is steamed in the same vessel for 5 to 10 minutes. The paddy is dried in
the sun or mechanically dried.
Advantages of Parboiling:
1.
Dehusking of parboiled rice is easy.
2.
Grains become tougher resulting in
reduced losses during milling.
3.
Part of the scutellum and germ which
are rich in B - Vitamins get fixed to the grain and hence loss of B - Vitamins
are less. The retention of thiamine, riboflavin, niacin and folic acid in
parboiled rice is greater than that of polished or hand pounded rice.
4.
It improves digestibility.
5.
It swells more when cooked to
desired softness.
Milling:
Milling is the process, which removes the coarse outer layer
of bran and germ. Paddy is milled by hand pounding or mechanical rice millers.
The process of milling involves the
following steps.
Rice is passed through two stone or
rubber discs rotating at different speeds and by shearing action on the grain,
the hull is pulled away. The whole kernel from which the hulls have been
removed is known as brown rice.
This is then milled in a machine called pearler to remove
coarse outer layers of bran and germ by a process of rubbing, resulting in
unpolished milled rice. Some amount of breakage of rice occurs in this milling.
Unpolished rice is liable to develop rancidity and so it is
polished in a brush machine which removes the aleurone layer and yields
'polished rice'.
Sometimes the polished rice is
further treated in a device known as trumbol to give a coating of sugar and
talc to produce a brighter shine on the grains.
Rice is separated from the broken
kernels. Large kernels are called second heads, medium ones are called
screenings, smallest ones are called the brewers rice.
The percentage loss of different
nutrients during milling are
protein 15%
fat 82%
thiamine 85%
riboflavin 70%
pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) 50%.
The
degree of milling determines the amount of nutrients removed.
Losses
during milling can be compensated by the following processes.
By under-milling or unpolishing rice
the loss of nutrients can be reduced.
A second method is that of
increasing vitamin retention by processing the rough rice prior to milling.
This is done by parboiling which is commercially known as converted rice.
Another means of remedying the
losses occurring in the milling of rice is the artificial enrichment of the
grain.
A premix has been developed in which the rice is wetted with
a solution of thiamin and niacin, then dried. A second coating of iron pyro
phosphate is distributed on the rice.
The
rice premix is highly resistant to washing, cooking and storage losses.
1.
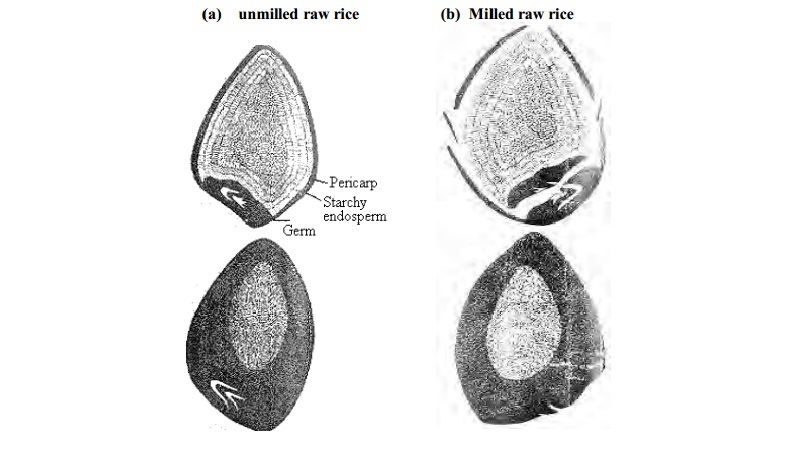
Unmilled
raw rice - Germ and pericarp are intact in raw rice, Vitamin B1 and other
vitamins are concentrated mainly in the germ and pericarp. When these are
removed by milling, the grain has lost most of its vitamins.
2.
Milled
raw rice - Germ and pericarp are removed
3.
Unmilled
parboiled rice- The vitamin has diffused through the endosperm
4.
Milled parboiled rice : Although
germ and pericarp have been removed, the grains still contains most of the
vitamins
Related Topics