Occurrence, Physical and Chemical properties, Uses - Oxygen | 8th Science : Chapter 11 : Air
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 11 : Air
Oxygen
Oxygen
All living things in the world need
oxygen. We cannot imagine the world without oxygen. Swedish chemist C. W. Scheele
first discovered oxygen in 1772. He called the gas fire air or vital life
because it was found to support the process of burning. It was independently
discovered by the British scientist Joseph Priestley in 1774. Lavoisier named
oxygen. The name oxygen comes from the Greek word ‘oxygenes’ which means ‘acid
producer’. It is called so because early chemists thought that oxygen is
necessary for producing acids.
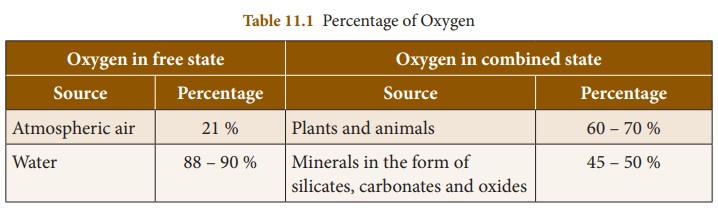
1. Occurrence of Oxygen
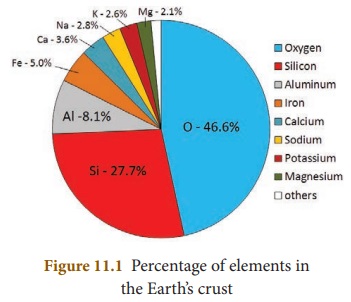
Oxygen is the most abundant element
on the earth by mass and the third most abundant element after Hydrogen and
Helium in the universe. It occurs both in free state and combined state. It is
present in free state as diatomic molecule (O2) in the atmosphere.
Most of this has been produced by photosynthesis in which the chlorophyll
present in the leaves of plants uses solar energy to produce glucose.
6CO2 + 6H2O Energy
from the Sun → C6H12O6 + 6O2
In combined state it is present in
the earth’s crust as silicates and metal oxides. It is also found in water on
the surface of the earth. Tri atomic molecule (O3) known as ozone is
present in the upper layers of the atmosphere.
2. Physical properties of
Oxygen
* Oxygen is a colourless, odourless
and tasteless gas.
* It is a poor conductor of heat and
electricity
* Oxygen dissolves readily in cold
water.
Oxygen is about two
times more soluble in water than nitrogen. If it had the same solubility as
nitrogen, then less oxygen would be present in seas, lakes and rivers that will
make life much more difficult for living organisms.
* It is denser than air.
* It can be made into liquid
(liquified) at high pressure and low temperature.
* It supports combustion.
3. Chemical properties of
Oxygen
1.
Combustibility
Oxygen is a non-combustible gas as
it does not burn on its own. But, it supports the combustion of other
substances.
If oxygen has the
capacity toburn itself, striking a match stick will be enough to burn allthe
oxygen in our planet’s atmosphere.
2.
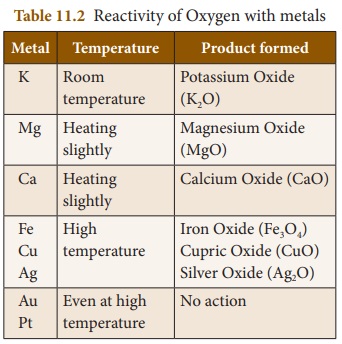
Reaction with metals
Oxygen reacts with metals like
sodium, potassium, magnesium, aluminium, iron etc. , to form their
corresponding metal oxides which are generally basic in nature. But the metals
differ in their reactivity towards oxygen.
Metal + Oxygen → Metal oxide
Example
4Na + O2
→ 2Na2O
Sodium +
Oxygen → Sodium oxide
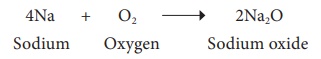
Activity 1
Heat a strip of
magnesium ribbon in the flame till it catches fire and introduce it into the
jar containing oxygen. It burns with a dazzling bright light and white ash of
magnesium oxide is formed.
3.
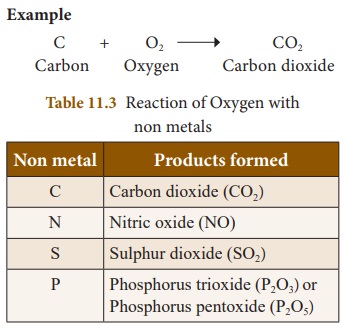
Reaction with non metals
Oxygen reacts with various
non-metals like hydrogen, nitrogen, carbon, sulphur, phosphorus etc. , to give
corresponding non metallic oxides, which are generally acidic in nature.
Non-metal + Oxygen → Non-metallic
oxide
Example
Activity 2
Heat a small piece of
phosphorous and introduce it into the oxygen jar. Phosphorous burns with
suffocating smell and gives phosphorous pentoxide (white fumes).

4.
Reaction with Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons (compounds containing C
and H) react with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water vapour. E.g. Wood,
Petrol, Diesel, LPG, etc. When they burn in oxygen, they produce heat and light
energy. Hence they serve as fuel.
Hydrocarbon + O2 → CO2
+ Water vapour + Heat energy + Light
5.
Rusting
The process of conversion of iron
into its hydrated form of oxide in the presence of air and moisture (humid
atmosphere) is calle d rusting. Rust is hydrated ferric oxide.
4Fe+3O2 → 2Fe2O3
Fe2O3+ x H2O
→ Fe2O3 • x H2O (rust)
(x is the number of water molecules
which is variable)
4. Uses of Oxygen
* It is used as oxy-acetylene
cylinder for cutting and welding metals.
* It is used to remove carbon
impurities from steel.
* Plants and animals use oxygen from
the air for respiration.
* It is used as rocket fuel.
* It is used for artificial
respiration by scuba divers, mountaineers, astronauts, patients etc.
* Mixed with powdered charcoal it is
used as explosives.
* It is used in the synthesis of
methanol and ammonia.

Related Topics