Occurrence, Physical and Chemical properties, Uses - Carbon dioxide | 8th Science : Chapter 11 : Air
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 11 : Air
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical
compound in which one carbon and two oxygen atoms are bonded together. It is a
gas at room temperature. It is represented by the formula CO2. It is
found in the earth’s atmosphere and it sends back the solar energy which is
reflected by the surface of the earth, to make it possible for living organisms
to survive. When carbon dioxide accumulates more in the atmosphere it produces
harmful effects.
Occurrence of Carbon
dioxide
Carbon dioxide is present in air to
the extent of about 0.03% by volume. It is evolved by the plants and animals
during respiration and is produced during fermentation reactions. Much of the
naturally occurring CO2 is emitted from the magma through volcanoes.
CO2 may also originate from the bio degradation of oil and gases.
Carbon dioxide emitted by human upset the natural balance of the carbon cycle.
Man-made CO2 in the atmosphere has increased global temperatures
which is warming the planet. While CO2 derived from fossil-fuel is a
very small component of the global carbon cycle, the extra CO2 is
cumulative because the natural carbon exchange cannot absorb all the additional
CO2.
Physical properties of
Carbon dioxide
* Carbon dioxide is a colourless and
odourless gas.
* It is heavier than air.
* It does not support combustion.
* It is fairly soluble in water and
turns blue litmus slightly red. So it is acidic in nature.
* It can easily be liquified under
high pressure and can be solidified. This solid form of CO2 is
called dry ice which undergoes sublimation.
The process of
conversion of solid into vapour without reaching liquid state is called
sublimation.
Chemical properties of
Carbon dioxide
1.
Combustibility
It is non-combustible gas and not a
supporter of combustion.
2.
Reaction with metals
Lighter metals like sodium,
potassium and calcium, combine with CO2 to form corresponding
carbonates whereas magnesium gives its oxide and carbon.
Example
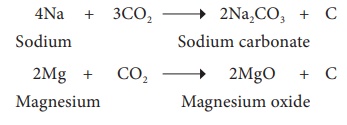
4Na(Sodium) + 3CO2(Sodium
carbonate) → 2Na2CO3+C
2Mg(Magnesium) + CO2 → 2MgO(Magnesium
oxide) + C
3. Reaction
with sodium hydroxide (Alkali)
Sodium hydroxide (base) is
neutralized by carbon dioxide (acidic) to form sodium bicarbonate (salt) and
water.
NaOH +
CO2 → NaHCO3(Sodium bicarbonate) + H2O
4. Reaction with Lime water (Calcium
hydroxide)
When a limited amount of CO2
is passed through lime water, it turns milky due to the formation of insoluble
calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2
+ CO2 → CaCO3(Calcium carbonate) + H2O
When an excess amount of CO2
is passed through lime water, it first turns milky and the milkyness disappears
due to the formation of soluble calcium hydrogen carbonate, Ca(HCO3) 2.
Venus’ atmosphere consists
of roughly 96 -97% carbon dioxide. Because of theamount of carbon dioxide
present, the surface of Venus continually retains heat and as such, the surface
temperature of Venus is roughly 462°C, making it the hottest planet in our
solar system.
Uses of Carbon dioxide
* CO2 is used to prepare
soft drinks or aerated drinks
* It is used in fire extinguishers
* It is used in the manufacturing of
sodium carbonate by Solvay process.
* Solid carbon dioxide, called as
dry ice is used as a refrigerant. The gas is so cold that moisture in the air
condenses on it, creating a dense fog which is used in stage shows and movie
effects.
* It is used along with ammonia in
the manufacture of fertilizers like urea.
* CO2 can be used in the
preservation of food grains, fruits etc.

Aerated water is
nothing but carbon dioxide dissolved in water under pressure. This is also
called ‘soda water’.
Related Topics