Chapter: Design of Electrical Machines : Induction Motors
Output equation of Induction motor
Output equation of Induction motor
output equation is the mathematical
expression which gives the relation between the various physical and electrical
parameters of the electrical machine.
In an induction motor the output
equation can be obtained as follows
Consider an ‘m’ phase machine, with
usual notations
Out put Q in kW = Input x efficiency
Input to motor = mVph Iph
cos Φ x 10-3 kW For a 3 Φ machine m = 3
Input to motor = 3Vph Iph
cos Φ x 10-3 kW Assuming
Vph = Eph, Vph
= Eph = 4.44 f Φ TphKw
= 2.22 f ΦZphKw
f = PNS/120 = Pns/2,
Output = 3 x 2.22 x Pns/2
x ΦZphKw Iph η cos Φ x 10-3 kW
Output = 1.11 x PΦ x 3Iph
Zph x ns Kw η cos Φ x 10-3kW
PΦ = BavπDL, and 3Iph Zph/ πD = q
Output to motor = 1.11 x BavπDL
x πDq x ns Kw η cos Φ x 10-3 kW
Q = (1.11 π2 Bav
q Kw η cos Φ x 10-3) D2L ns kW
Q = (11 Bav q Kw η cos Φ
x 10-3) D2L ns kW
Therefore Output Q = Co D2L
ns kW
where
Co = (11 Bav q Kw η cos Φ
x 10-3)
Vph = phase voltage ;
Iph = phase current
Zph = no of
conductors/phase
Tph = no of turns/phase
Ns = Synchronous speed in rpm
ns = synchronous speed in rps
p = no of poles,
q = Specific electric loading
Φ = air gap flux/pole;
Bav = Average flux
density
kw = winding factor
η = efficiency cosΦ= power factor
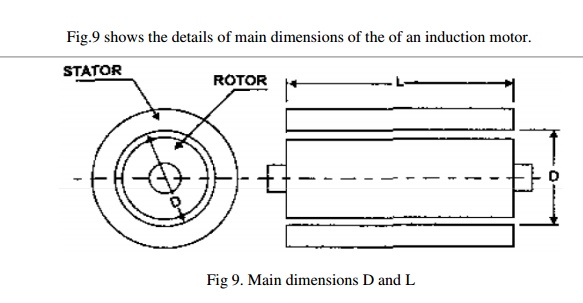
D = Diameter of the stator,
L = Gross core length
Co = Output coefficient
Related Topics