Chapter: Design of Electrical Machines : Induction Motors
Important Short Questions and Answers: Design of Electrical Machines - Induction Motors
INDUCTION MOTORS
1.
Define slot space factor.
The
slot space factor is the ratio of conductor area per slot and slot area. It
gives an indication of the space occupied by the conductors and the space
available for insulation. The slot space factor for induction motor varies from
0.25 to
0.4.
2.
Define distribution factor or breadth factor.
It
is defined as the ratio of resultant emf when the winding is uniformly
distributed to the resultant emf when the winding is bunched in the slot.
3.
Define winding factor.
It
is defined as the product of the pitch factor and the distribution factor.
Kw
= Kp * Kd
4.
Why the low voltage winding is
placed nearer to the core and the high voltage winding in case of a core type
transformer.
Ø
Insulation
required will be less
Ø
Less
possibility for fault occurrence
Ø
Easy
to provide tapings
5.
Why is it possible to design
alternators to generate much higher voltage than dc generator?
In alternator the winding is
provided in stator and hence maximum voltage can be
provided.
In dc generator the winding is
provided in rotor and hence it is not possible to generate maximum voltage
6. Why rotating machines with aluminum
armature coils have increased leakage reactance?
Aluminum coils in armature require
more space for accommodation of conductors. Large size slots are designed.
Hence with large size slots the value of leakage reactance increases.
7. Why the harmonic leakage flux in squirrel
cage induction is motor is zero?
Since the rotor current balances the
stator current at every point there is no harmonic leakage flux.
8. Stepped core section is preferred to a
square section for transformer, give reason?
Diameter of circumscribing circle
can be reduced giving use of less copper
Due to increase in core area flux
density can be reduced which results less iron loss.
9.
Why choice of high specific loading
in the design of synchronous generators loads to poor voltage regulation?
High value of specific electric
loading will mean more number of turns per phase. This will cause high value of
leakage reactance and poor voltage regulation.
10.
Define real flux density.
It is defined as the ratio of actual
flux through the tooth to the tooth area.
11.
List the advantages and
disadvantages of using closed type of rotor slot in squirrel cage induction
motor.
Advantages:
Ø
Low
reluctances
Ø
Less
magnetizing current
Ø
Quitter
operation
Ø
Large
leakage reactance and so starting current is limited
Disadvantages:
Ø
Reduced
over load capacity
12.
Write the expression for rotor current.
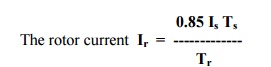
Where Ts = number of
turns per phase for stator
Tr = number of turns per
phase for rotor
Is = Stator current
13.
What are the ranges of efficiency and power factor in induction motor?

14.
The approximate efficiency of a
three phase, 50 Hz, 4 pole induction motor running at 1350 rpm is
----------------------------------------
i)
90%
ii) 40% iii) 65% iv) None of the above.
Ans
: i) 90%
15.
What is the approximate efficiency of a 60 Hz, 6 pole, 3 phase induction motor
running at 1050 rpm?
i)
72%
ii) 81.2% iii) 76.8% iv) 87.5%.
Ans
: iv) 87.5%
16.
What is integral slot winding and
fractional slot winding?
In integral slot winding, the total
number of slots is chosen such that the slots per pole are an integer, which
should be a multiple of number of phases. In fractional slot winding, the total
number of slots is chosen such that the slots per pole are not an integer.
17.
Why fractional slot winding is not
used for induction motor?
Windings with fractional number of
slots per pole per phase create asymmetrical mmf distribution around the air
gap and favour the creation of noise in the motor. Therefore, fractional
windings are not used in induction motor starter.
18.
Write the expression for length of
mean turn of stator winding?
Length of mean turn of stator, Lmts = 2L + 2.3 τ + 0.24
Where L = Stator core length
τ= pole pitch = П D / p
19.
Name the methods used for reducing harmonic torques.
Ø
Chording
Ø
Integral
slot winding
Ø
Skewing
and
Ø
Increasing
the length of air gap
20.
What is Skewing?
Skewing is twisting either the
stator or rotor core. The motor noise, vibrations, cogging and synchronous
cusps can be reduced or even entirely eliminated by skewing either the stator
or the rotor.
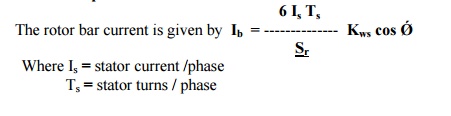
Sr = Number of rotor
slots
22.
What is full pitch and short pitch
or chording?
When the coil span is equal to pole
pitch (180 deg electrical), the winding is called full pitched winding. When
the coil span is less than pole pitch (180 deg electrical), the winding is
called short pitched or chorded.
23.
What are the different types of
stator windings in induction motor?
Ø
Mush
winding
Ø
Lap
winding and
Ø
Wave
winding
24.
How the induction motor can be
designed for best power factor?
For best power factor, the pole
pitch τ is chosen such that τ = SQRT [(0.18 L)].
25. What are the ranges of specific magnetic loading and specific electric loading in induction motor?
Specific magnetic loading = 0.3 to
0.6 Wb / m2
Specific electric loading = 5000 to 45000 amp.cond/m
26.
What are the materials used for slip
rings and brushes in induction motor?
The slip rings are made of brass or
phosphor bronze. The brushes are made of metal graphite, which is an alloy of
copper and carbon.
27.
Write the expression for output
equation and output co-efficient of induction motor.
The equation for input KVA is
considered as output equation in induction motor.
The input KVA, Q = C0 D2
L ns in KVA
Output co-efficient C0 = 11 Bav ac Kws
*10-3 in KVA/ m3 – rps.
28.
List the advantages of using open
slots.
The advantages are:
Ø
The
winding coils can be formed and fully insulated before installing and also it
is easier to replace the individual coils.
Ø
It
avoids excessive slot leakage thereby reducing the leakage reactance.
29.
Give the advantages of using
semi-enclosed stator slots.
The advantages are less air gap
contraction factor giving a small value of magnetizing current, low tooth
pulsation loss and mush quiter operation(less noise). Semi enclosed slots are
mostly preferred for induction motor.
30.
What is the maximum value of flux
density in stator teeth?
The maximum value of flux density in
stator tooth should not exceed 1.7 Wb/m2.
A high value of flux density leads
to a higher iron loss and a greater magnetizing mmf.
28.
What are the problems that occur in
induction motor due to certain combinations of stator and rotor slots?
The problems in induction motor due
to certain combinations of stator and rotor slots are
Ø
The
motor may refuse to start
Ø
The
motor may crawl at some sub-synchronous speed
Ø
Severe
vibrations are developed and so the noise will be excessive
32.
. List the rules for selecting rotor slots.
Number
of stator slots should not be equal to rotor slots satisfactory results are
obtained when Sr is 15 to 30% larger or smaller than Ss.
The
difference (Ss - Sr) should not be equal to + or - p, + or – 2p or + or – 5 p
to avoid synchronous cusps.
The
difference (Ss - Sr) should not be equal to + or - 1, + or – 2 , + or – (p+1)
or + or – (p+2) to avoid noise and vibrations.
32.
What are the main dimensions of
induction motor?
Ø
Stator
core internal diameter
Ø
Stator
core length
33.
Why induction motor is called as
rotating transformer?
The principle of operation of
induction motor is similar to that of a transformer. The stator winding is
equivalent to primary of a transformer. The rotor winding is equivalent to
short circuited secondary of a transformer. In transformer, the secondary is
fixed but in induction motor it is allowed to rotate.
35.
How slip ring motor is started?
The slip ring motor is started by
using rotor resistance starter. The starter consists of star connected variable
resistances and protection circuits. The resistances are connected to slip
rings. While starting, full resistance is included in the rotor circuit to get
high starting torque. Once the rotor starts rotating, the resistances are
gradually reduced in steps. At running condition, the slip rings are shorted
and so it is equivalent to squirrel cage rotor.
36.
What are the special features of the
cage rotor of induction machine?
Ø
The
cage rotor can adopt itself for any number of phases and poles
Ø
It
is suitable for any type of starting method except using rotor resistance
starter
Ø
It
is cheaper and rugged
Ø
Rotor
over hang leakage reactance is lesser which results in better power factor,
greater pull out torque and over load capacity.
37.
Name the materials used to insulate
the laminations of the core of induction motor.
The materials used to insulate the
laminations of the core of induction motor are kaolin and varnish.
38.
Where mush winding is used?
The mush winding is used in small
induction motors of ratings less than 5HP.
39.
What is the minimum value of slot pitch of a 3 phase induction motor?
The minimum value of slot pitch of a
3 phase induction motor is 15 mm.
40.
Write the formula for air-gap in
case of three phase induction motor in terms of length and diameter.
The length of air-gap, lg = 0.2 + 2 SQRT[(D L)] in mm
Where D and L are expressed in
meters.
40.
What is crawling and cogging?
Crawling is a phenomenon in which
the induction motor runs at a speed lesser than sub synchronous speed.
Cogging is a phenomenon in which the
induction motor refuses to start.
42.
What is harmonic induction torque and harmonic synchronous torque?
Harmonic induction torques are
torques produced by harmonic fields due to stator winding and slots.
Harmonic synchronous torques are
torques produced by the combined effect of same order of stator and rotor
harmonic fields.
43.
What is the condition for obtaining
the maximum torque in case of 3-phase induction motor?
The maximum torque occurs in
induction motor when rotor reactance is equal to rotor resistance.
44.
What is runaway speed?
The runaway speed is defined as the
speed which the prime mover would have, if it is suddenly unloaded, when
working at its rated speed.
45.
State three important features of
turbo-alternator rotors.
Ø
The
rotors of turbo-alternators have large axial length and small diameters
Ø
Damping
torque is provided by the rotor itself and so there is no necessity for
additional damper winding
Ø
They
are suitable for high speed operations and so number of poles is usually 2 or
4.
46.
Distinguish between cylindrical pole
and salient pole construction.
In cylindrical pole construction the
rotor is made of solid cylinder and slots are cut on the outer periphery of the
cylinder to accommodate field conductors.
In salient pole construction, the
circular or rectangular poles are mounted on the outer surface of a cylinder.
The field coils are fixed on the pole.
The cylindrical pole construction is
suitable for high speed operations, whereas the salient pole construction is
suitable for slow speed operations.
47.
Mention the factors that govern the design of field system of alternator.
Number of poles and voltage across each field coil
Amp-turn per pole
Copper
loss in field coil
Dissipating
surface of field coil
Specific loss dissipation and allowable temperature rise
48.
Mention the different tests that conducted in an induction motor.
No load test or open circuit test
Short circuit test or load test
49.
Give the different runaway speeds for various turbines.

50. What are the factors that are affected due
to SCR.
Voltage regulation
Stability
Short circuit current
Parallel operation
Related Topics