Integers | Term 3 Chapter 2 | 6th Maths - Ordering of Integers | 6th Maths : Term 3 Unit 2 : Integers
Chapter: 6th Maths : Term 3 Unit 2 : Integers
Ordering of Integers
Ordering
of Integers
We have already seen the ordering of numbers in
the set of natural and whole numbers.
The ordering is possible for integers also.
1.
Predecessor and Successor of an Integer
Recall that for a given number its predecessor is
one less than it and its successor is one more than it. This applies for integers
also.
Example 5
Find the predecessor and successor of i) 0 and ii)
−8 on a number line.
Solution
Place the given numbers on the number line then
move one unit to their right and left to get the successor and the predecessor respectively.

We can see that the successor of 0 is +1 and the
predecessor of 0 is −1 and the successor of −8 is −7 and the predecessor of −8 is
−9.
Note
● Every positive integer is greater
than each of the negative integers. Example: 3 > −5
● 0 is less than every positive integer
but greater than every negative integer. Example: 0<2 but 0> −2
2.
Comparing Integers
Ordering of integers is to compare them. It is very
easy to compare and order integers by using a number line.
When we move towards the right of a number on the
number line, the numbers become larger. On the other hand, when we move towards
the left of a number on the number line, the numbers become smaller.
We know that 4 < 6, 8 > 5 and so on. Now let
us consider two integers say −4 and 2.
Mark them on the number line as shown below.
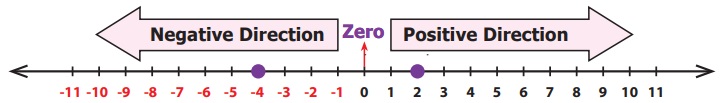
Fix −4 now. See whether 2 is to the right or the
left of −4. In this case, 2 is to the right of−4 and in the positive direction.
So, 2 > −4 or otherwise −4 < 2.
Example 6
Compare −14 and −11
Solution
Draw number line and plot the numbers −14 and −11
as follows.
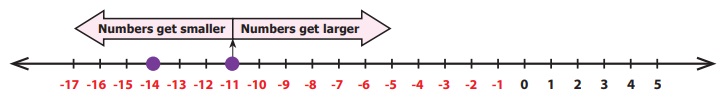
Fixing −11, we find −14 is to the left of −11. So,
−14 is smaller than −11. That is, −14 < −11.
Think
For two numbers, say 3 and 5, we know
that 5 > 3. Will there be a change in the inequality if both the numbers have
negative sign before them?
Activity
Take two cards from a deck of playing
cards and identify, which is greater between them, assuming that the Joker card
represents zero, black cards represent positive integers, red cards represent negative
integers and the cards A, J, Q and K represent 1,11,12 and 13 respectively.
Example 7
Arrange the following integers in ascending order:
−15, 0, −7, 12, 3, −5, 1, −20, 25, 18
Solution
Step 1: First, separate the positive integers
as 12, 3, 1, 25, 18 and
the negative integers as −15, −7, −5,
−20
Step 2: We can easily arrange positive integers
in ascending order as 1, 3, 12, 18, 25 and negative
integers in ascending order as −20, −15, −7, −5.
Step 3: As 0 is neither positive nor negative,
it stays at the middle and now the arrangement
−20, −15, −7, −5, 0, 1, 3, 12, 18 and 25 is in ascending order.
Try these
i) Is −15 < −26? Why?
−15 < −26 is false. When we move towards The right of a
number on the number line, the numbers become larger. On the other hand, when
we move towards the left of a number on the number line, the numbers become
smaller.
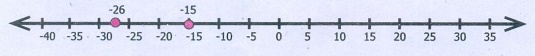
−26 is left of −15. So − 26 is less than −15
−26 < −15
ii) Which is smaller −3 or −5? Why?
−5 < −3
In the number line −5 is left of −3. So −5 is less than −3.
iii) Which is greater 7 or −4? Why?
7 > −4.
In the number line 7 is right of −4
So 7 is greater than −4.
iv) Which is the greatest negative integer?
The greatest negative
integer −1
v) Which is the smallest positive integer?
The smallest positive
integer +1
ICT CORNER
Integers
Expected Outcome
Step 1
Open the Browser by typing the URL Link
given below (or) Scan the QR Code. GeoGebra work sheet named “Integers” will open.
There is a worksheet under the title Number Line basics.
Step 2
Click on the “New Number” to get new
question and type your answer in the respective check boxes, next to Predecessor
and Successor and press enter..
Browse
in the link:
Integers: https://ggbm.at/mt7qxxn7 or
Scan the QR Code.
Related Topics