Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Genetic Engineering and Molecular Methods
Nucleic Acid Probes
Nucleic Acid Probes
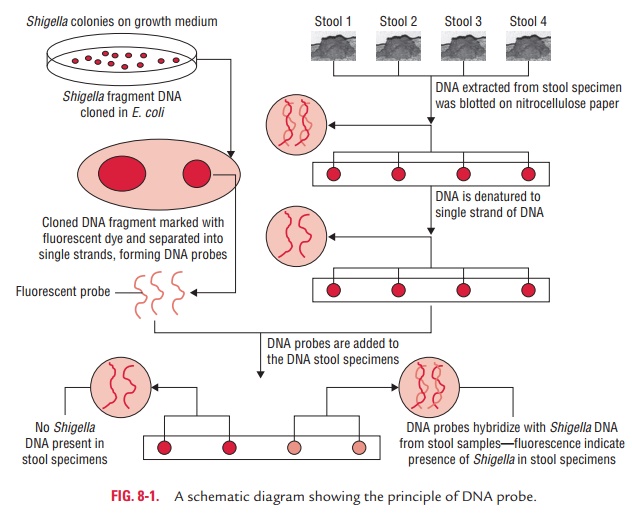
Nucleic acid probes are segments of DNA and RNA labeled with radioisotopes or enzymes that can hybridize to com-plementary nucleic acids with high degree of specificity. Hybridization probes have practical value, because they can detect specific nucleotide sequences in unknown samples. The probes carry reporter molecules, such as radioactive labels, which are isotopes that emit radiation, or luminescent labels, which give off visible light. Reactions can be revealed by placing photographic film in contact with the test reaction. Fluorescent probes contain dyes that can be visualized with ultraviolet light. Probes can be used in a broad range of ana-lytic procedures.
Two different nucleic acids can hybridize by uniting at their complementary sites. All different combinations are possible: single-stranded DNA can unite with other single-stranded DNA or RNA, and RNA can hybridize with other RNA. This property forms the basis of specially formulated oligonucle-otide tracers called gene probes.
Related Topics