Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 4 : Enzymes
Nomenclature and Classification of Enzymes
Nomenclature and Classification of Enzymes:
In early days the suffix – ase was added to the substrate for naming the enzymes.
Example : Lipase acts on lipids.
These names are known as trivial names. They do not convey complete information about the enzymatic reaction.
The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB) have assigned a systematic nomenclature for enzymes. The systematic name has two parts.
· The first part represents the substrate. In enzyme catalyzed reactions the reactants are known as substrates.
· The second part, ending in –ase, indicates the type of reaction catalysed.
Each enzyme is assigned a four-digit code number called Enzyme Commission (EC) number.
· The first digit represents the major class to which the enzyme belongs.
· The second digit denotes the subclass.
· The third digit denotes the sub-sub class of the enzyme within the major class.
· The fourth digit represents the serial number of the enzyme within the sub-sub class.
Example: Hexokinase (EC 2.7.1.1) and Glutamine synthetase (EC 6.3.1.2)
According to International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, the enzymes are classified into six major classes on the basis of the reaction they catalyse. The six major classes of enzymes are,
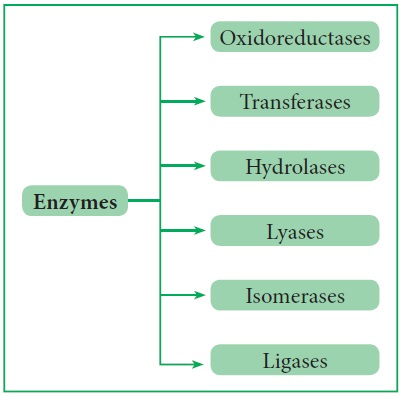
1) Oxidoreductases:
These are enzymes which catalyze the oxidation – reduction reactions between two substrates.
Examples:
a) Dehydrogenase (Alcohol Dehydrogenase)
b) Oxidase (Cytochrome Oxidase)
c) Peroxidase (Glutathione Peroxidase)
Alcohol dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.1) :
This enzyme oxidizes ethanol into acetaldehyde. It requires the coenzyme NAD+ (Niacinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) which gets reduced to NADH.
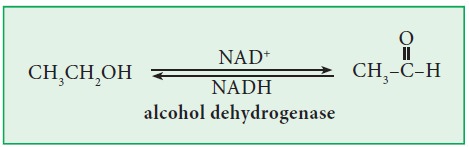
2) Transferases:
These are enzymes which catalyze the transfer of certain groups such as phosphate, amino or acetyl groups from one substrate to another.
Examples:
· Transaminase (Transfers an amino group Example Aspartate amino transferase)
· Transacylase (Transfers an acyle group Example Malonyl transacylase)
· Phosphorylase (Transfers a phosphate group Example Glycogen phosphorylase)
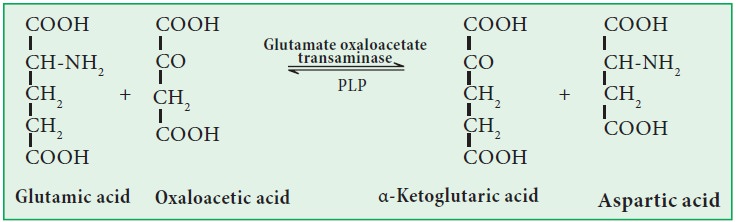
Transaminase:
They catalyse the transfer of amino group from amino acid to keto acid. Example: Glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT) or Aspartate transaminase (AST; EC 2.6.1.1). This enzyme catalyses the transfer of amino group from glutamic acid to oxaloacetic acid. It requires pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) as coenzyme for its activity.
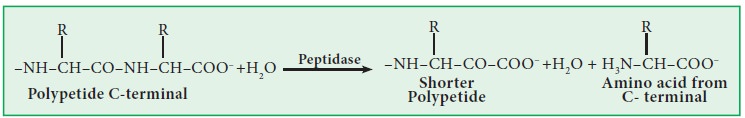
3) Hydrolase:
These are enzymes which catalyze the hydrolysis of substrates. They bring about the hydrolysis by adding water.
Example : a) Lipase b) Urease c) Glycosidase.
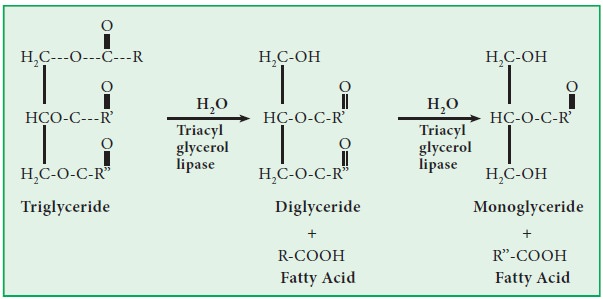
Lipase (EC 3.1.1.3):
These are enzymes which hydrolyze the ester linkage. For example triacyl glycerol lipase (EC 3.1.1.3) splits the ester linkage between glycerol and fatty acid.
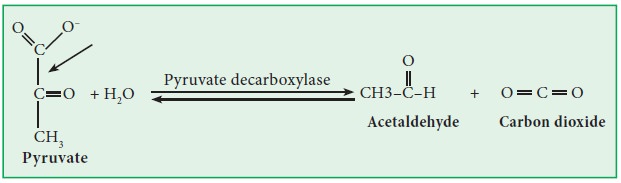
4) Lyases:
These enzymes catalyze the addition or elimination of groups like H2O, CO2, and NH3 etc. Example: Aldolase, decarboxylase
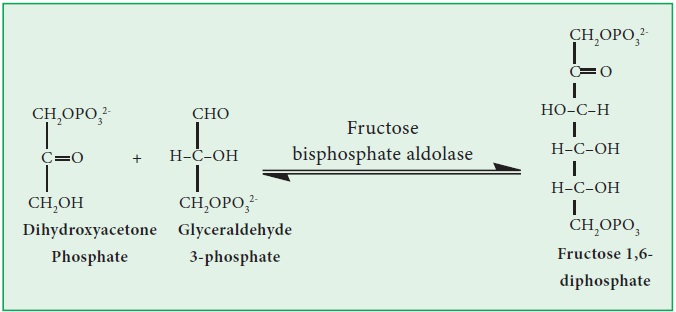
a. Fructose bisphosphate aldolase (EC 4.1.2.13):
It catalyzes the reversible conversion of fructose-1,6-bisphosphate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate by aldol cleavage of the C3–C4 bond.
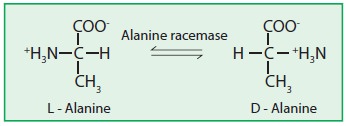
5) Isomerases:
These enzymes catalyze the inter-conversion of isomers such as optical, geometrical or positional isomers.
Example :
a)Alanine racemase (EC 5.1.1.1)
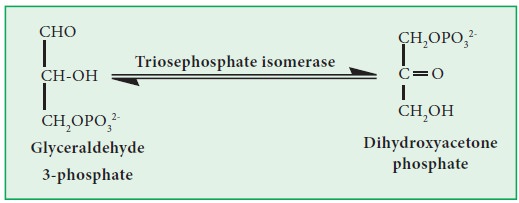
b) Triosephosphate isomerase (EC 5.3.1.1):
This enzyme catalyzes the isomerization of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate into dihydroxy acetone phosphate.
6) Ligases:
These enzymes catalyze the synthetic reactions. They link two substrates together with the utilization of ATP or GTP.
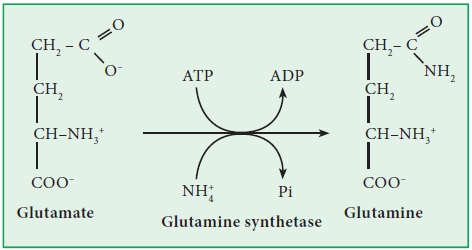
Example : Glutamine synthetase.
Glutamine synthetase (EC 6.3.1.2):
This is a ligase which catalyzes the synthesis of glutamine from glutamate and NH3.
Related Topics