Chapter: 11th Biochemistry : Chapter 4 : Enzymes
Factors influencing Enzyme activity
Factors influencing Enzyme activity
The
important factors that influence the enzyme catalyzed reaction are; pH,
Temperature, Substrate concentration, Enzyme concentration, Activators and
inhibitors.
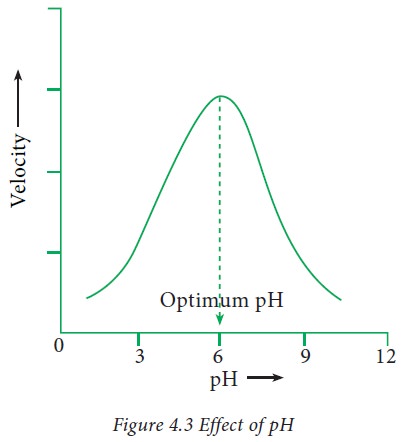
1. Effect of pH :
1. Change
in hydrogen ion concentration influences the enzyme activity. When the velocity
is plotted against pH, a bell shaped curve is obtained.
2. The
pH at which the enzymatic reaction has maximum velocity is known as optimum pH. Most of the enzymes possess optimum pH between 5 and 9. However
there are exceptions like pepsin,
alkaline phosphatase etc.
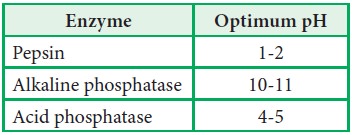
3. The
optimum pH of some of the common enzymes are as follows:
4. Enzymes
possess only low activity or even become inactive at extreme pH values.
This is
due to the following reasons;
· The hydrogen ion concentration affects the ionic
charges on the active site of the enzyme.
· Thus the extreme pH values lower the effective
concentration of active form of enzyme and substrate. Therefore, the reaction
velocity will be lowered.
· Denaturation of enzyme occurs at extreme pH values.
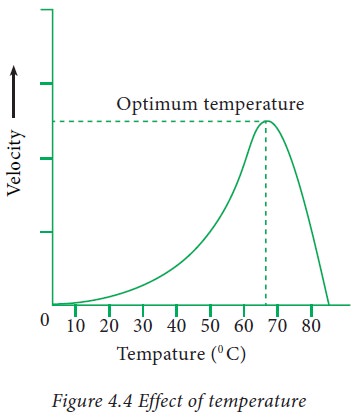
2. Effect of temperature on enzyme acitivity:
Velocity
of an enzyme reaction increases with increase in temperature upto a maximum and
then declines.
When the
velocity is plotted against temperature we obtain a plot as shown in the figure
3.4.
The
temperature at which the enzymatic reaction has maximum velocity is known as optimum temperature.
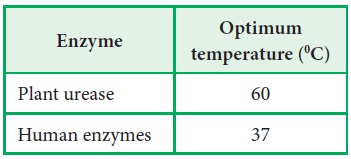
The
optimum temperature of some of the common enzymes are as follows:
But
enzymes like venom phosphokinase, muscle adenylate kinase are active even at
1000C.
In
general, at high temperatures the enzymes undergo denaturation and this leads
to the rapid loss of catalytic activity.
Temperature
co-efficient or Q10 is defined as increase in velocity of the
enzymatic reaction when the temperature is increased by 100 C. For
most of the enzymes the value of Q10 is “2” in the temperature range
00 C to 400 C.
3. Concentration of substrate:
Formation
of an enzyme-substrate complex (ES complex) is the first step in enzyme
catalysis. Increase in the substrate concentration gradually increases the
velocity of enzymatic reaction up to a particular value.
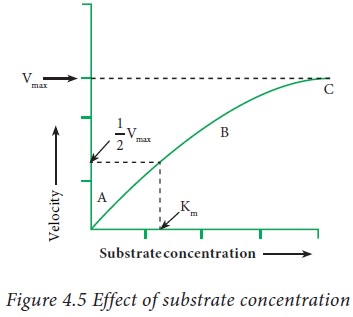
A
hyperbolic curve is obtained when velocity is plotted against the substrate
concentration. This graph shows three distinct phases.
· In the first phase (A), the velocity of the
reaction is directly proportional to the substrate concentration.
· In the second phase (B), the substrate
concentration is not directly proportional to the enzyme activity.
· In the third phase (C), the velocity remains
constant and does not change with increase in the substrate concentration.
(plateau)
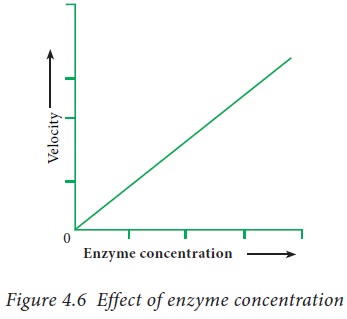
4. Concentration of enzyme
At a
constant substrate concentration, the velocity of enzyme catalyzed reaction
increases proportionately with the increase in the concentration of the enzyme.
This property is utilized in determining the level of serum enzymes for the
diagnosis of diseases. On plotting the velocity of the enzymatic reaction with
the enzyme concentration, a straight line is obtained.
5. Activators
Activators
are the inorganic ions (cations or anions) or compounds that enhances the
activity of the enzymes.
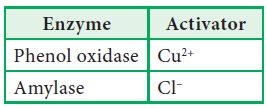
Metal
ions can be bound to the enzyme permanently or can be used just for activation.
When metal ions used only for the activation of enzyme, they are called metal
activated enzymes.
Examples: ATPase (Mg2+, Ca2+) and Enolase (Mg2+).
If metal
ions are bound with enzymes using chemical bond, they are called
metalloenzymes.
Examples: Alcohol dehydrogenase-Zn2+
and Carbonic anhydrase-Zn2+,
Time,
radiations and co-enzymes are also the other factors which affect the velocity
of an enzyme reaction.
Related Topics