Chapter: Satellite Communication : Satellite Access
Multiple Access Techniques
Multiple Access
Techniques:
The transmission from the BS in the downlink can be heard by each and every
mobile user in the cell, and is referred as broadcasting. Transmission from the
mobile users in the uplink to the BS is many-to- one, and is referred to as
multiple access.
Multiple access schemes to allow many users to share simultaneously a finite
amount of radio spectrum resources.
·
Should not result in severe degradation
in the performance of the system as compared to a single user scenario.
·
Approaches can be broadly grouped into
two categories: narrowband and wideband.
Multiple Accessing Techniques : with possible conflict and conflict- free
·
Random access
·
Frequency division multiple access
(FDMA)
·
Time division multiple access (TDMA)
·
Spread spectrum multiple access (SSMA) :
an example is Code division multiple access (CDMA)
·
Space division multiple access (SDMA)
Duplexing:
For voice or data communications, must assure two way communication (duplexing,
it is possible to talk and listen simultaneously). Duplexing may be done using
frequency or time domain techniques.
·
Forward (downlink) band provides traffic
from the BS to the mobile
·
Reverse (uplink) band provides traffic
from the mobile to the BS.
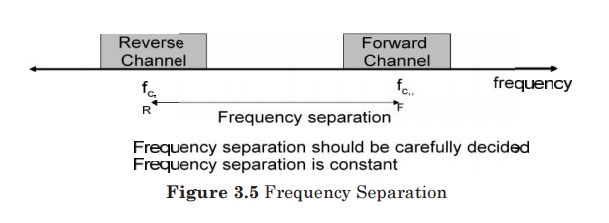
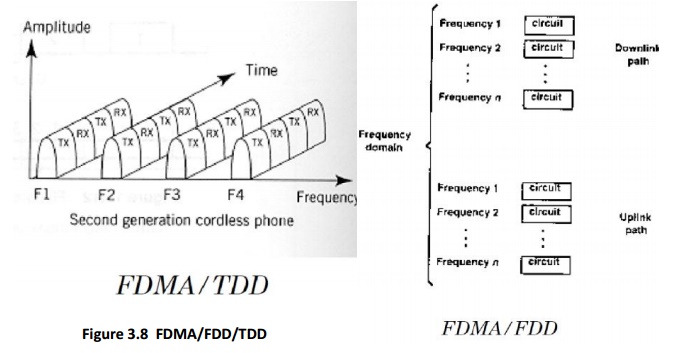
1. Frequency
division duplexing (FDD):
Provides two distinct bands of frequencies for every user, one for downlink and
one for uplink.
A large interval between these frequency bands must be allowed so that
interference is minimized.
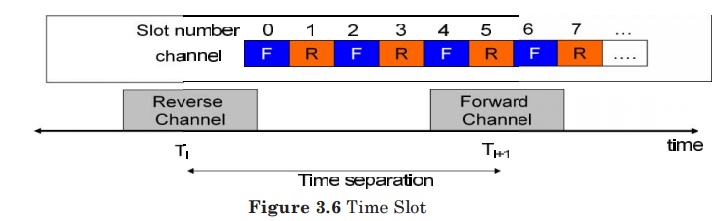
2. Time division
duplexing (TDD):
In TDD communications, both directions of transmission use one contiguous
frequency allocation, but two separate time slots to provide both a forward and
reverse link.
Because transmission from mobile to BS and from BS to mobile alternates in time,
this scheme is also known as “ping pong”.
As a consequence of the use of the same frequency band, the communication
quality in both directions is the same. This is different from FDD.
3. FDMA:
In FDMA, each user is allocated a unique frequency band or channel.
During
the period of the call, no other user can share the same frequency band.
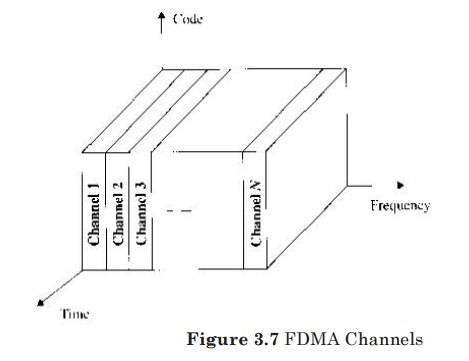
All channels in a cell are available to all the mobiles. Channel assignment is
carried out on a first-come first- served basis.
The number of channels, given a frequency spectrum BT , depends on the
modulation technique (hence Bw or Bc ) and the guard bands between the channels
2Bguard .
These guard bands allow for imperfect filters and oscillators and can be used
to minimize adjacent channel interference.
FDMA is usually implemented in narrowband systems.
Nonlinear effects in FDMA:
In a FDMA system, many channels share the same antenna at the BS. The power
amplifiers or the power combiners, when operated at or near saturation are
nonlinear.
The nonlinear ties generate inter-modulation frequencies.
Undesirable harmonics generated outside the mobile radio band cause
interference to adjacent services.
Undesirable harmonics present inside the band cause interference to other users
in the mobile system.
4. TDMA:
TDMA systems divide the channel time into frames. Each frame is further
partitioned into time slots. In each slot only one user is allowed to either
transmit or receive.
Unlike FDMA, only digital data and digital modulation must be used.
Each user
occupies a cyclically repeating time slot, so a channel may be thought of as a
particular time slot of every frame, where N time slots comprise a frame.
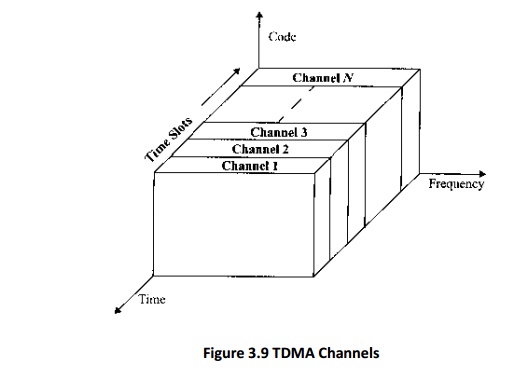
Features:
Multiple channels per carrier or RF channels.
Burst transmission since channels are used on a timesharing basis.
Transmitter
can be turned off during idle periods.
Narrow or wide bandwidth – depends on factors such as modulation scheme, number
of voice channels per carrier channel.
High ISI – Higher transmission symbol rate, hence resulting in high ISI.
Adaptive
equalizer required.
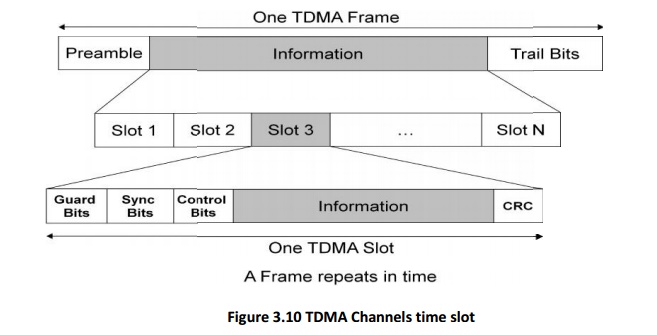
A guard time between the two time slots must be allowed in order to avoid
interference, especially in the uplink direction. All mobiles should
synchronize with BS to minimize interference.
Efficient power utilization : FDMA systems require a 3- to 6-dB power back off
in order to compensate for inter-modulation effects.
Efficient handoff : TDMA systems can take advantage of the fact that the
transmitter is switched off during idle time slots to improve the handoff
procedure. An enhanced link control, such as that provided by mobile assisted
handoff (MAHO) can be carried out by a subscriber by listening to neighboring
base station during the idle slot of the TDMA frame.
Efficiency of TDMA
Efficiency of TDMA is a measure of the percentage of bits per frame which
contain transmitted data. The transmitted data include source and channel
coding bits.
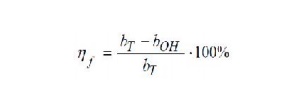
bOH includes all overhead bits such as preamble, guard bits, etc.
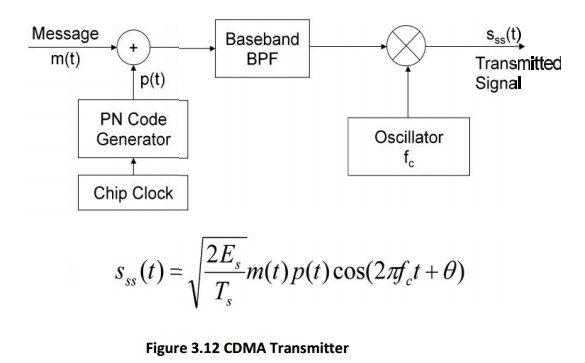
5. Code Division
Multiple Access (CDMA):
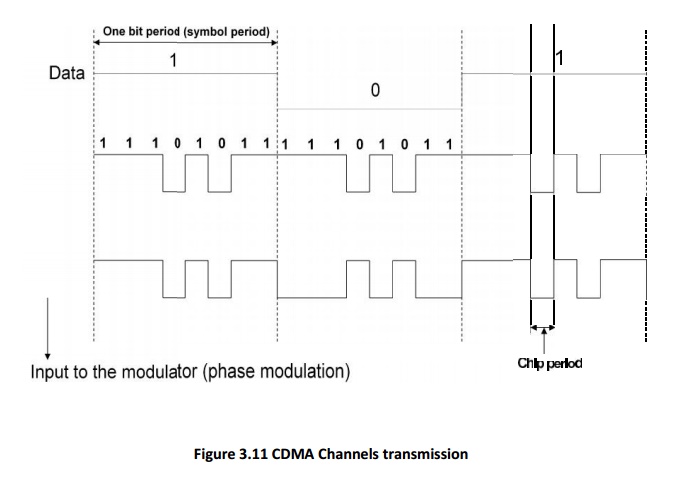
Spreading signal (code) consists of chips
Has
Chip period and and hence, chip rate
Spreading
signal use a pseudo-noise (PN) sequence (a pseudo-random sequence)
PN
sequence is called a codeword
Each
user has its own cordword
Codewords
are orthogonal. (low autocorrelation)
Chip
rate is oder of magnitude larger than the symbol rate.
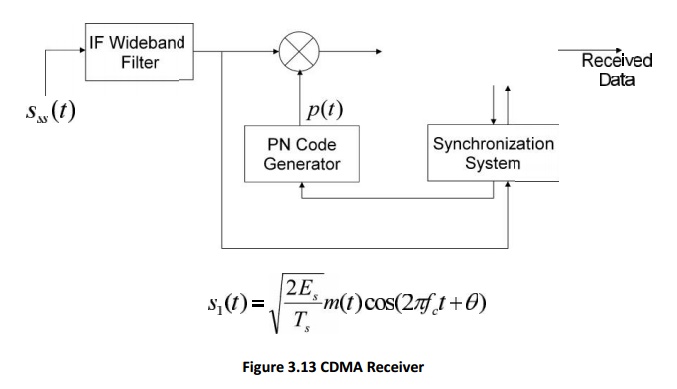
The receiver correlator distinguishes the senders signal by examining the
wideband signal with the same time-synchronized spreading code
The sent signal is recovered by despreading process at the receiver.
CDMA Advantages:
Low power spectral density.
Signal
is spread over a larger frequency band
Other
systems suffer less from the transmitter
Interference limited operation
All
frequency spectrum is used
Privacy
The
codeword is known only between the sender and receiver. Hence other users can
not decode the messages that are in transit
Reduction of multipath affects by using a larger spectrum
CDMA data:
DSSS Transmitter:
DSSS Receiver
FDMA/CDMA
Available wideband spectrum is frequency
divided into number narrowband radio channels. CDMA is employed inside each
channel.
DS/FHMA
The
signals are spread using spreading codes (direct sequence signals are
obtained), but these signal are not transmitted over a constant carrier
frequency; they are transmitted over a frequency hopping carrier frequency.
Time Division CDMA (TCDMA)
Each
cell is using a different spreading code (CDMA employed between cells) that is
conveyed to the mobiles in its range.
Inside
each cell (inside a CDMA channel), TDMA is employed to multiplex multiple
users.
Time Division Frequency Hopping
At
each time slot, the user is hopped to a new frequency according to a
pseudo-random hopping sequence.
Employed
in severe co-interference and multi-path environments.
Beams can be assigned to individual users, thereby assuring that all links
operate with maximum gain.
Adaptive beam forming can be easily implemented to improve the system capacity
by suppressing co channel interference.
Advantage of CDMA
It is recognized that CDMA’s capacity gains over TDMA
FDMA are entirely due to Its tighter, dynamic control over the use of the power
domain.
Choosing a new non-orthogonal PN sequence a CDMA system does not encounter the
difficulties of choosing a spare carrier frequency or time slot to carry a
Traffic Channel
Ensure that interference will not be too great if it begins to transmit -that
there is still enough space left in the power domain.
Disadvantages of CDMA:
Satellite transponders are channelized too narrowly for roadband CDMA, which is
the most attractive form of CDMA.
Power control cannot be as tight as it is in a terrestrial system because of
long round-trip delay.
Related Topics