Chapter: Graphics and Multimedia : Multimedia Systems Design
Multimedia Systems Architecture
Multimedia Systems Architecture
Multimedia encompasses a
large variety of technologies and integration of multiple architectures
interacting in real time. All of these multimedia capabilities must integrate
with the standard user interfaces such as Microsoft Windows.
The following figure describes the architecture of a multimedia
workstation environment. In this
diagram.
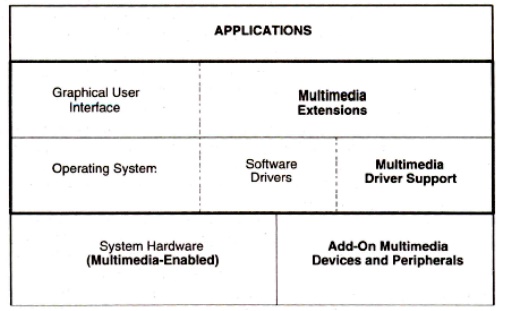
The right side shows the new
architectural entities required for supporting multimedia applications.
For each special devices such
as scanners, video cameras, VCRs and sound equipment-, a software device driver
is need to provide the interface from an application to the device. The GUI
require control extensions to support applications such as full motion video
High Resolution Graphics
Display
The various graphics
standards such as MCA, GGA and XGA have demonstrated the increasing demands for
higher resolutions for GUls.
Combined graphics and imaging
applications require functionality at three levels. They are provided by three
classes of single-monitor architecture.
(i)
VGA mixing: In VGA mixing, the image
acquisition memory serves as the display source memory, thereby fixing its position and size on screen:
(ii)
VGA mixing with scaling: Use of scalar ICs allows
sizing and positioning of images in pre-defined windows.
Resizing the window causes
the things to be retrieved again.
(iii)
Dual-buffered
VGA/Mixing/Scaling: Double buffer schemes maintain the original images in a decompression buffer and the resized
image in a display buffer.
The IMA Architectural
Framework
The Interactive Multimedia
Association has a task group to define the architectural framework for
multimedia to provide interoperability. The task group has C0ncentrated on the
desktops and the servers. Desktop focus is to define the interchange formats.
This format allows multimedia objects to be displayed on any work station.
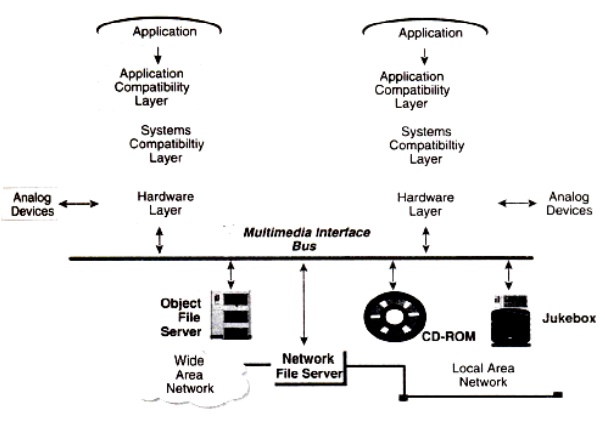
The architectural approach
taken by IMA is based on defining interfaces to a multimedia interface bus.
This bus would be the interface between systems and multimedia sources. It
provides streaming I/O service"s, including filters and translators Figure 3.4 describes the generalized
architectural approach
Network Architecture for
Multimedia Systems:
Multimedia systems need
special networks. Because large volumes of images and video messages are being
transmitted.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
technology (A TM) simplifies transfers across LANs and W ANs.
Task based Multi level
networking
Higher classes of service
require more expensive components in the' workstations as well as in the
servers supporting the workstation applications.
Rather than impose this cost
on all work stations, an alternate approach is to adjust the class of service
to the specific requirement for the user. This approach is to adjust the class
of services according to the type of data being handled at a time also.
We call this approach
task-based multilevel networking.
High speed server to server
Links
Duplication: It is the process of duplicating an object that the user can
manipulate. There is no requirement for
the duplicated object to remain synchronized with the source (or master)
object. Replication: Replication is
defined as the process of maintaining two or more copies of the same object in a network that periodically
re-synchronize to provide the user faster and more reliable access to the data
Replication is a complex process.
Networking Standards: The two well-known networking standards are Ethernet and token
ring. ATM and FDDI are the two
technologies which we are going to discuss in detail.
ATM: ATM is a acronym for Asynchronous Transfer Mode. It's topology was
originally designed for broadband
applications in public networks.
ATM is a method of
multiplexing and relaying (cell-switching) 53 byte cells. (48 bytes of user
information and 5 bits of header information).
Cell Switching: It is a form of fast packet switching based on
the use of cells. Cells: Short,
fixed length packets are called cells.
ATM provides high capacity,
low-latency switching fabric for data. It is independent of protocol and distances.
ATM effectively manage a mix of data types, including text data, voice, images
and full motion video. ATM was proposed as a means of transmitting multimedia
applications over asynchronous networks.
FDDI: FDDI is an acronym of Fiber Distributed Data Interface. This FDDI
network is an excellent candidate to
act as the hub in a network configuration, or as a backbone that interconnects
different types of LANs.
FDDI presents a potential for
standardization for high speed networks.
The ANSI standard for FDDI
allows large-distance networking. It can be used as high-performance backbone
networks to complement and extend current LANs.
Related Topics