Chapter: Graphics and Multimedia : Multimedia Systems Design
Defining Objects for Multimedia Systems
DEFINING OBJECTS FOR MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS
The basic data types of
object using in multimedia include text, image, audio, holograms and
full-motion video.
TEXT
It is the simplest of data
types and requires the least amount of storage. Text is the base element of a
relational database.
It is also the basic building
of a document.
The major attributes of text
include paragraph styling, character styling, font families and sizes, and
relative location in a document
HYPERTEXT
It is an application of
indexing text to provide a rapid search of specific text strings in one or more
documents. It is an integral component of hypermedia documents. A hypermedia
document is the basic complex object of which text is a sub object.
Sub-objects include images,
sound and full motion video.
A hypermedia document always
has text and has one or more other types of sub-objects
IMAGES
Image object is an object
that is represented in graphics or encoded form. Image object is a subobject of
the hypermedia document object. In this object, there is no direct relationship
between successive representations in time.
The image object includes all
data types that are not coded text. It do not have a temporal property
associated with them.
Thc data types such as
document images, facsimile systems, fractals, bitmaps, meta files, and still
pictures or still video frames are grouped together.
Figure 3.6 describes a
hierarchy of the object classes
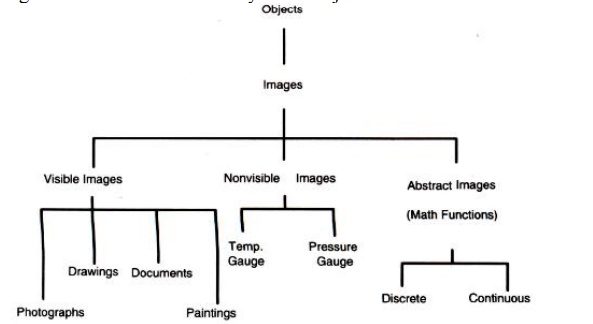
Non-Visible: This type of images are not stored as images. But they are
displayed as images. Example: Pressure
gauges, and temperature gauges.
Abstract: Abstract images are computer-generated images based on some
arithmetic calculations. They are
really not images that ever existed as real-world objects. Example of these
images is fractals.
AUDIO AND VOICE
Stored-Audio and Video
objects contain compressed audio information. This can consist of music,
speech, telephone conversation and voice commands. An Audio object needs to
store information about thc sound clip.
Information here means length
of the sound clip, its compression algorithm, playback characteristics, and any
annotations associated with the original clip.
FULL MOTION AND LIVE VIDEO
Full motion video refers to
pre-stored video clips. Live video refers to live and it must be processed
while it is being captured by the camera. . From a storage perspective, we should
have the information about the coding algorithm used for compression. It need
decoding also.
From a processing
perspective, video should be presented to user with smooth and there should not
be any unexpected breaks.
Hence, video object and its
associated audio object must be transferred over the network to the
decompression unit. It should be then played at the fixed rate specified for
it.
For successful playback of
compressed video, there are number of technologies. They are database storage,
network media and protocols, decompression engines and display engines.
Related Topics