Chapter: Graphics and Multimedia : Multimedia Systems Design
Evolving Technologies for Multimedia Systems
EVOLVING TECHNOLOGIES FOR MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS
Multimedia applications use a
number of technologies generated for both commercial business application as
well as the video game industry.
Let us review some of these
technologies in this section.
Hypermedia documents
Hypermedia documents are
documents which have text, embedded or linked multimedia objects such as image,
audio, hologram, or full-motion video.
Hypertext
Hypertext systems allow
authors to link information together, create information paths through a large
volume of related text in documents.
It also allows to annotate
existing text, and append notes.
It allows fast and easy
searching and reading of selected excerpts.
HYPERMEDIA
It is an extension of
hypertext.
In that, we can include
texts, any kind of information that can be stored in electronic storage, such
as audio, animated video, graphics or full-motion video.
Hypermedia documents used for
electronic mail and work flow applications provide a rich functionality for
exchanging a variety of information types. The hypermedia document is a
definition of a document and a set of pointers to help locate the various
elements of the document on the network.
HYPER SPEECH
Multimedia stimulated the
development of general-purpose speech interfaces. Speech synthesis and speech
recognition are fundamental requirement for hyperspeech systems. Speech
recognition is nothing but converting the analog speech into a computer action
and into ASCII text. Speech-recognition systems cannot segment a stream of
sounds without breaks into meaningful units. The user must speak in a stilted
fashion. He should make sure to interpose silence between each word.
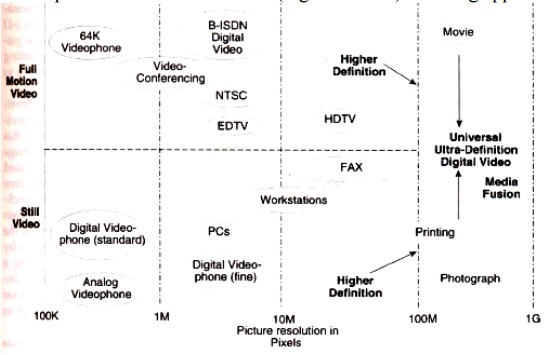
HDTV AND UDTV
HDTV is an acronym of
High-Definition Television.
The broadcasting standards
such as NTSC, PAL, SECAM, NHK have an idea of bringing the world together on a
single high-definition Television broadcasting standard.
The japanese broadcasting
services developed a 1125-line, along MUSE system. A competing standard in the
U.S. changed direction from analog to digital technology:A 1125-line digital
HDTV has been developed and is being commercialized. NHK of Japan is trying to
leapfrog the digital technology to develop ultra definition television (digital
UDTV) featuring approximately 3000 lines
3D TECHNOLOGIES AND
HOLOGRAPHY
Three-dimensional
technologies are concerned with two areas: pointing devices and displays. 3-D
pointing devices are essential to manipulate object in a 3-D display system.
3-D displays are achieved using holography techniques.
The techniques developed for
holography have been adapted for direct computer use.
Fuzzy Logic
Fuzzy logic is logic which is
used for low-level process controllers.
Use of fuzzy logic in
multimedia chips is the key to the emerging graphical interfaces of the future.
It is expected to become an integral part of multimedia hardware. Fuzzy logic
has mathematical principles. Hence, the application of multimedia can benefit
those principles.
Digital Signal Processing
Digital Signal Processing are
used in applications such as digital servos in hard disk drives, and
fax/modems. DSP technology is used in Digital wireless communications, such as
personal communication networks (pens), wireless local area networks and
digital cordless phones.
DSP Architectures and
Applications
A typical DSP operating
system architecture would contain the following subsystems:
Memory Management: DSP architectures provide dynamic allocation of
arrays from multiple segments,
including RAM, SRAM and DRAM.
Hardware-Interrupt handling: A DSP operating system must be designed to
minimize hardware-interrupt latency to ensure fast response to real time events
for applications, such as servo systems. Multitasking:
DSPs need real-time kernels that provide pre-emptive multitasking and
user-defined and dynamic task
prioritization
INTERTASK SYNCHRONIZATION AND
COMMUNICATION
Mechanisms for intertask
communication include message queues, semaphores, shared memory, and quick
response event flags. Multiple timer services: The ability for the developer to
set system clock interrupt managed timers to control and synchronize tasks is
needed for most real-time applications.
Device-Independent I/O: DSP
operating system should supports
(i) Asynchronous data stream
(ii) Synchronous message passing.
Use of DSP' s has evolved
from traditional general purpose digital signal processors to
application-specific and customizable DSPs. DSPs were conceived as math engines
with a system architecture that was like that of a mini-computer with an array
processor.
Related Topics