Microbiology - Mode of Action of Antibiotics | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 3 : Control of Microorganisms by Chemical Methods
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 3 : Control of Microorganisms by Chemical Methods
Mode of Action of Antibiotics
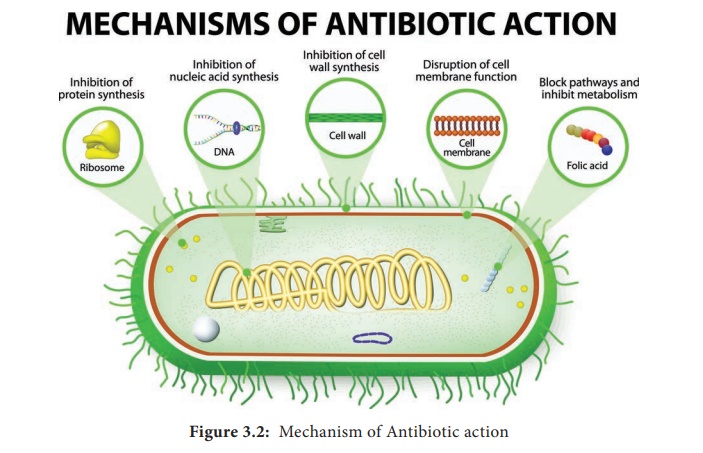
Mode of Action of Antibiotics
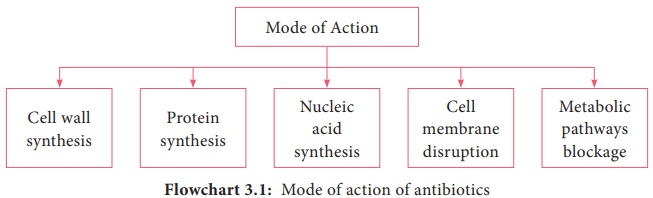
The mode
of action of antibiotics varies as they damage pathogens in several ways
(Flowchart 3.1). Some of the important actions of therapeutic drugs in
microbial pathogens are as follows.
Cell wall
synthesis, Protein synthesis, Nucleic acid synthesis, Cell membrane disruption
and Metabolic pathways blockage.The mode of action of antibiotics varies as they
damage pathogens in several ways (Flowchart 3.1). Some of the important
1. Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis
The most
selective therapeutic antibiotics are those that interfere with the synthesis
of bacterial cell walls. These drugs posses a high therapeutic index because
bacterial cell walls have a unique structure which is not found in eukaryotic
cells. The important cell wall attacking drugs are Penicillin, Cephalosporin,
Ampicillin, Methicillin and Vancomycin.
2. Inhibition of Protein Synthesis
Many
therapeutic antibiotics discriminate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic
ribosomes and inhibit protein synthesis. The therapeutic index of these drugs
is fairly high, but not as favourable as that of cell wall synthesis
inhibitors. Several of these drugs are medically useful and effective research
tools because they block individual steps in protein synthesis. Some
therapeutic drugs bind to 30S while others attach to 50S ribosomal subunits.
Example Streptomycin, Chloramphenicol, Tetracyclin and Erythromycin
A chemotherapeutic agent destroys or inhibit the intracellular parasite by penetrating the cells and tissues of the host in effective concentrations
3. Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis
Some
antimicrobial drugs or antibiotics inhibit nucleic acid synthesis. These are
not selectively toxic as other drugs. This is due to the fact that prokaryotic
and eukaryotic nucleic acid synthesis mechanisms do not vary greatly. Example
Quinolones, Novobiocin, Actinomycin and Rifampin
4. Disruption of Cell Membrane
There are
some antimicrobial drugs or antibiotics that act as cell membrane disorganizing
agents. Polymyxins are such drugs of clinical importance.
E.g.
Polymyxin B and Polymyxin E (colistin)
5. Blocking Metabolic Pathways
Some
therapeutic drugs act as antimetabolites and block the functioning of metabolic
pathways. They competitively inhibit the key enzymes in the metabolic pathway. Example
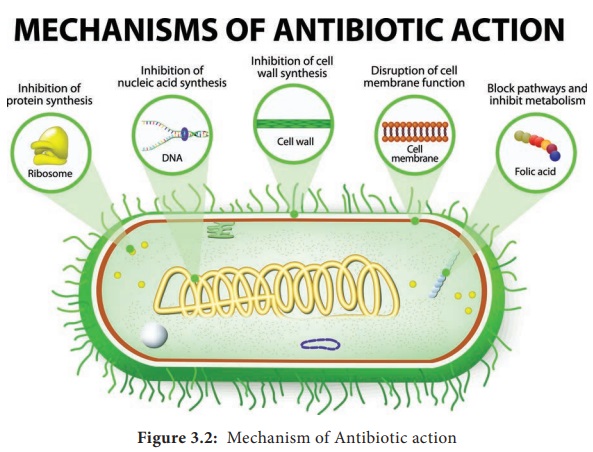
Sulfonamides, Trimethoprim, Dapsone and Isoniazid (Figure 3.2).
Related Topics