Control of Microorganisms by Chemical Methods | Microbiology - Disinfectants, Antiseptics and Antibiotics | 12th Microbiology : Chapter 3 : Control of Microorganisms by Chemical Methods
Chapter: 12th Microbiology : Chapter 3 : Control of Microorganisms by Chemical Methods
Disinfectants, Antiseptics and Antibiotics
Disinfectants, Antiseptics and Antibiotics
Disinfection
is the elimination of microorganisms from inanimate objects or surfaces. The
term disinfectant is used for an agent used to disinfect inanimate objects or
surfaces but is generally toxic to use on human tissues. Antiseptic refers to
an agent that kills or inhibits growth of microorganisms but is safe to use on
human tissues.
Antibiotics
produced by microorganisms which kill or inhibit the growth of other microbes.
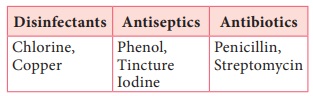
Following
Table gives few examples of antimicrobial chemical agents that destroy unwanted
microorganisms.
Basic
terms used in chemical control of microorganism are mentioned in Table 3.1 and
Table 3.2 Describes the difference between Bactericidal and Bacteriostatic agents.

Basic terms used in Chemical sterilization
Disinfection: The selective elimination of certain undesirable
microorganisms to prevent their transmission directed against their metabolism
or structure; applies to the use directly on inanimate objects.
Antisepsis: Prevention of the growth or activity of
microorganisms by inhibition or killing; applies to the use of chemicals on
living tissue
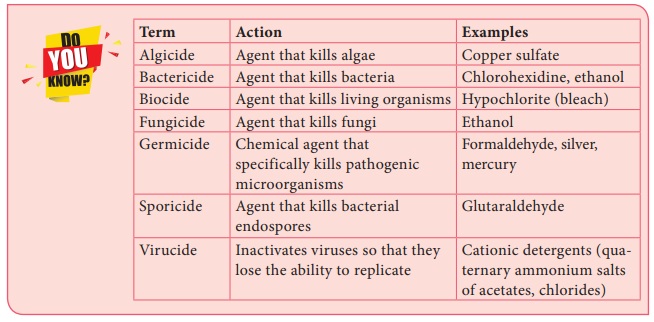
-cide: Suffix used to denote agents, usually chemical,
that kill. Commonly used terms are bactericide, fungicide, virucide, and
algicide. The term germicide is used if the agents kill pathogens but not
necessarily spores. An agent that kills bacterial spores is a sporicide.
-static: Suffix used to denote agents, usually chemical, that prevents growth but do not necessarily kill the organism or bacterial spores. Commonly used terms include bacteriostatic and fungistatic.
Table 3.2: Difference between Bactericidal and Bacteriostatic
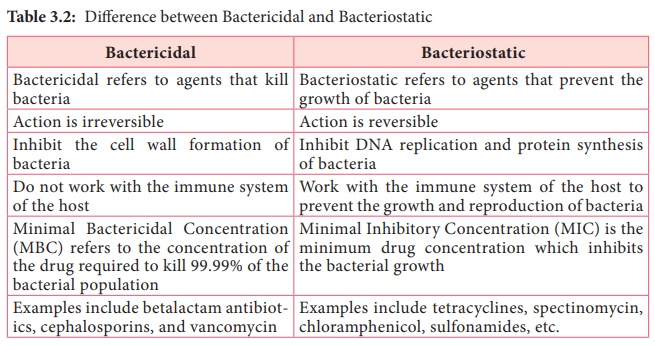
Bactericidal
•
Bactericidal refers to agents that kill bacteria
• Action
is irreversible
• Inhibit
the cell wall formation of bacteria
• Do not
work with the immune system of the host
• Minimal
Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) refers to the concentration of the drug
required to kill 99.99% of the bacterial population
•
Examples include betalactam antibiot- ics, cephalosporins, and vancomycin
Bacteriostatic
•
Bacteriostatic refers to agents that prevent the growth of bacteria
• Action
is reversible
• Inhibit
DNA replication and protein synthesis of bacteria
• Work
with the immune system of the host to prevent the growth and reproduction of
bacteria
• Minimal
Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) is the minimum drug concentration which
inhibits the bacterial growth
•
Examples include tetracyclines, spectinomycin, chloramphenicol, sulfonamides, etc.
Related Topics