Chapter: Mobile Communication
Mobile Communication Systems
Mobile Communication Systems
Contents:
1.
GSM Architecture-Location tracking and call
setup
2.
Mobility management
3.
Handover-Security-GSM
4.
SMS
International roaming for GSM
5.
Call recording functions-subscriber and service
data mgt
6.
Mobile Number portability
7.
VoIP service for Mobile Networks
8.
GPRS
Architecture-GPRS procedures
9.
Billing
Pre requisite Discussion :
In this unit we discuss Digital
cellular networks are the segment of the market for mobile(GSM) and wireless
devices which are growing most rapidly. They are the wireless extensions of
traditional PSTN or ISDN networks and allow for seamless roaming with the same
mobile phone nation or even worldwide. Today, these systems are mainly used for
voice traffic. However, data traffic is continuously growing and, therefore,
this chapter presents
1. GSM: Architecture
Concept:
Global system for mobile
communication founded in 1982. Most successful Digital Mobile Telecommunication
System. Used by over 800 million people in more than 190 countries. System
Architecture
Radio subsystem
Network and switching subsystem
Operation Subsystem
SMS Concept:
A useful service for very simple
message transfer is the short message service (SMS) which offers transmission of
messages of up to 160 characters.
SMS messages do not use the standard
data channels of GSM but exploit unused capacity in the signalling channels.
Sending and receiving of SMS is
possible during data or voice transmission. SMS was in the GSM standard from
the beginning
The successor of SMS, the enhanced
message service (EMS),
offers a larger message size (e.g., 760 characters, concatenating several SMs),
formatted text, and the transmission of animated pictures, small images and
ring tones in a standardized way EMS never really took off as the multimedia
message service (MMS)
was available.
MMS offers the transmission of
larger pictures (GIF, JPG, WBMP), short video clips etc. and comes with mobile
phones that integrate small cameras.
Another non-voice tele service is group 3 fax, which is available
worldwide.
In this service, fax data is
transmitted as digital data over the analog telephone network according to the
ITU-T standards T.4 and T.30 using modems.
Typically, a transparent fax service
is used, i.e., fax data and fax signaling is transmitted using a transparent
bearer service.
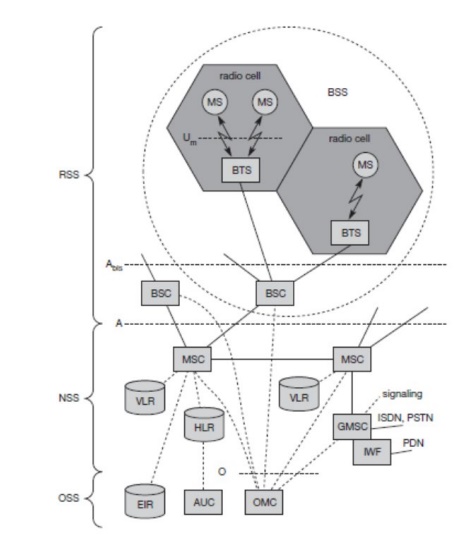
Mobile
station (MS):
The MS comprises all user equipment
and software needed for communication with a GSM network.
Significance:
Provides an interrupted connection
between two or several users
2. Mobility Management:
Concept:
An MS consists of user independent
hard- and software and of the subscriber
identity module (SIM), which
stores all user-specific data that is relevant to GSM.3 While an MS can be identified via the international mobile equipment identity (IMEI), a user can
personalize any MS using his or her SIM,
i.e., user-specific mechanisms like charging
and authentication are based on the SIM, not on the device itself. Device-specific
mechanisms, e.g., theft protection, use the device specific IMEI.
Without the SIM, only emergency calls are
possible.
The SIM card contains many identifiers and
tables, such as card-type, serial number, a list of subscribed services, a personal identity number (PIN), a PIN unblocking key (PUK), an authentication key Ki, and the international mobile subscriber identity
(IMSI)
Significance:
The most advantageous thing is that while
moving between one base station to other base station it provides an
uninterrupted connection
3. GSM HANDOVER
Concept:
Cellular systems require handover procedures,
as single cells do not cover the whole service area. The smaller the cell size
and the faster the movement of a mobile station through the cells The more
handovers of ongoing calls are required. A handover should not cause a cut-off,
also called call drop. GSM aims at maximum handover duration of 60ms. 2 Basic
Reasons for a Handover
The mobile station moves out of the range of a
BTS of a certain antenna of a BTS respectively.
The received signal level decreases continuously
until it alls below the minimal requirements or communication.
The error rate maygrow due to intererance, the
distance to the BTS may be too high.
All these effects may diminish the quality of the radio link and make radio
transmission impossible in the near future.
The wired infrastructure (MSC, BSC) may decide
that the traffic in one cell is too high and shift some MS to another cells
with a lower load. Handover may be due to load balancing.
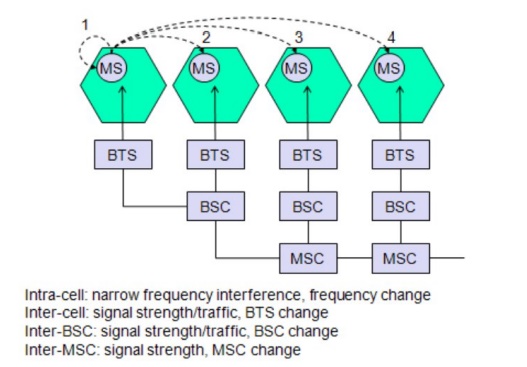
Types
of Handover in GSM 4
Possible Handover Scenarios in GSM
1. Intra-Cell Handover
2. Inter-Cell,Intra BSC Handover
3. Inter BSC,Intra-MSC Handover
4. Inter MSC Handover
1. Intra-cell
handover: o Within a cell
o Narrow band interference could make transmission
at a certain frequency impossible. o The BSC could then decide to change the
carrier frequency.
2. Inter-cell,
intra BSC handover:
o The mobile station moves from one cell to
another, but stays within the control of the same BSC.
o The BSC then performs a handover, assigns a
new radio channel in the new cell and releases the old one .
3.
Inter BSC, intra MSC handover: o BSC controls a limited number of cells;
o GSM also has to perform handovers between
cells controlled by different BSCs. o This handover then has to be controlled
by the MSC.
4.
Inter MSC handover:
o A handover could be required between two
cells belonging to different MSCs. o Now both MSCs perform the handover
together.
Necessary
Information for a Handover
To provide all the necessary information for a
handover due to a weak link
MS and BTS both perform periodic measurements
of the downlink and uplink quality respectively. (Link quality comprises signal
level and bit error rate.)
Measurement reports are sent by the MS about every
half second and contain the quality of the current link used for transmission
as well as the quality of certain channels in neighboring cells ( the BCCHs).
Significance:
The most advantageous thing is that while
moving between one base station to other base station it provides an
uninterrupted connection
4. SMS International
roaming for GSM Concept:
GSM offers several security services
using confidential information stored in the AUC and in the individual SIM.
The SIM stores personal, secret data
and is protected with a PIN against unauthorized use.
The security services offered by GSM
are
Access
control and authentication:
The authentication of a valid user
for the SIM. The user needs a secret PIN to access the SIM.
The next step is the subscriber
authentication. This step is based on a challenge-response scheme.
Confidentiality:
All user-related data is encrypted.
After authentication BTS and MS
apply encryption to
Voice
Data and
Signaling
This confidentiality exists only
between MS and BTS.
Significance:
All data is encrypted before
transmission, and user identifiers.
GSM transmits a temporary identifier
(TMSI), which is newly assigned by the VLR after each location update.
5. Call recording functions-subscriber and service data mgt Concept:
Call recording is becoming
increasingly important, with technology changing and working habits becoming
more mobile. Addressing mobile recording is now the subject of many financial
regulators' recommendations. It is also increasingly important to business
continuity planning, especially for pandemic planning.
The actual recording takes place on
a recording system with software for the management of calls and security of
recordings. Most call recording software applications rely on an analogue
signal via either a call recording adapter or a telephony board.
Digital lines cannot be recorded
unless the call recording system can capture and decode the proprietary digital
signaling, which some modern systems can. Sometimes a method is supplied with a
digital PBX that can process the proprietary signal (usually a conversion box)
before being channeled to a computer for recording. Alternatively a hardware
adapter can be used on a telephone handset as the digital signal is converted at
that point to analogue.
VoIP Recording is usually restricted
to streaming media recorders or software developed by the soft phone or IP PBX
creator. There are also solutions which use packet capture technology to
passively record VoIP phone calls on the LAN.
Hardware is required to make the
voice signal available to the computer equipment. Some of today's call
recording software is sold as a turn-key solution with hardware.
Direct recording of mobile phone
calls requires a hardware adapter connected to the handset. There are many
other ways to record mobile phone calls. One approach is to route calls via a
new PBX system linked to the recorder. However, such systems are typically
expensive to purchase and change the way that calls are made, incurring running
costs. Another approach links directly into existing recording systems from a
PDA phone. Both of these approaches allow recordings to be time stamped, often
required for legal reasons. Recording directly onto mobile devices does provide
a legally valid recording in many countries.
Significance:
∑ Records the call for future
use(References)
∑ Manages the Call whenever the user
seems busy
∑ Service provided(data) can be
monitored in a fair manner
6. Mobile Number Portability:
Concept:
MNP is a boon to the customer as he
is allowed to keep the same mobile number even he switches over to other
operator.
3 options : Service portability
Location Portability Number portability
MNP Priniciple in INDIA:
Applicable only for mobile Numbers
Applicable only in intra licensed
area
Applicable irrespective of
Technology
LRN based routing DoT
Significance:
All mobile users can use MNP to get
best tariff and network coverage without changing the number.
7. VOIP Service for mobile networks
Concept:
Voice over Internet protocol is
simply the transmission of voice traffic over ip ased networks. Mobile VOIP is
delivered by a third party service provider a WIFI or 3G network cellular
network that a mobile device is connected to.
Mobile VOIP service providers
typically require a user to download software onto their mobile device in order
to gain access to their service.
Voip sends your calls across the
internet
Phone calls are sent through VOIP
phone adaptor to regular or cordless telephone.
Significance:
Used by all network service
providers for help purposes ncluding toll free numbers.
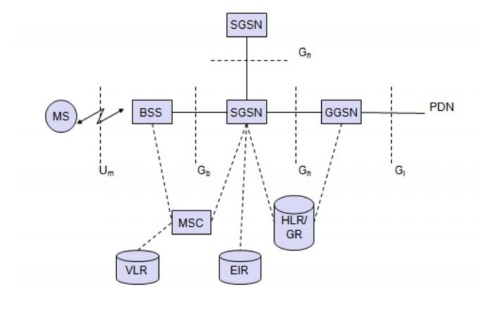
8. GPRS SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
Concept:
The GPRS architecture introduces two new
network elements, which are called
GPRS support nodes (GSN) and are in fact
routers.
All GSNs are integrated into the standard GSM
architecture, and may new interfaces have been defined .
GGSN
- Gateway GPRS Support Node :-
The gateway GPRS support node (GGSN) is the
inter working unit between the GPRS network and external packet data networks
(PDN).
This node contains routing information for GPRS
users, performs address conversion, and tunnels data to a user via
encapsulation.
The GGSN is connected to external networks
(e.g., IP or X.25) via the Gi interface and transfers packets to the SGSN via
and IP-based backbone network (Gn interface).
Other New Element SGSN Serving GPRS Support Node :-
The other new element is the serving GPRS
support node (SGSN) which supports the MS via the Gb interface.
The SGSN, for example, requests user address
form the GPRS register (GR), keeps track of the individual Mss location, is responsible for collecting
billing information (e.g., counting bytes), and performs several security
functions such as access control.
The SGSN is connected to a BSC via frame relay
and is basically on the same hierarchy level as an MSC.
GPRS
Register (GR)
The GR, which is typically a part of the HLR,
stores all GPRS relevant data. GGSNs can be compared with home and foreign
agents, respectively, in a mobile IP network.
As shown in figure below, packet data is
transmitted form a PDN, via the GGSN and SGSN directly to the BSS and finally
to the MS.
The MSC, which is responsible for data
transport in the traditional circuit switched GSM, is only used for signaling
in the GPRS scenario.
Before sending any data over the GPRS network,
an MS must attach to it, following the procedures of the mobility management.
CKSN Cipher
key sequence number (CSKN)
The attachment procedure includes assigning a
temporal identifier, called a temporary logical link identity (TLLI), and a
ciphering key sequence number (CKSN) for data encryption.
For each MS, a GPRS context is set up and
stored in the MS and in the corresponding SGSN. This context comprises the
status of the MS (which can be ready, idle, or standby), the CKSN, a flag
indicating if compression is used, and routing data (TLLI, the routing area RA,
a cell identifier and a packet data channel, PDCH, identifier).
Besides attaching and detaching mobility
management also comprises functions for authentication, location management,
and ciphering (here, the scope of ciphering lies between MS and SGSN, which is
more than in standard GSM).
In idle mode an MS is not reachable
and all contexts is deleted.
In the standby state only movement
across routing areas is updated to the SGSN but not changes of the cell.
Permanent paging.
The update procedure in standby mode
is a compromise. Only in the ready state every movement of the MS is indicated
to the SGSN.
Significance:
Provides Data connection for several
Mobile Stations from the Base Stations.
9. Billing:
Concept:
As you travel, each network you
access data or phone calls through sends a bill to your carrier back home. One
your bills start coming in, your carrier mails it to you. Sometimes it can take
several months to reconcile all the charges you've racked up while traveling.
I've completely switched my travel calls to You Roam since I travel a lot. It lets you make and receive calls on
your own number over Wi-Fi, 3G or a local sim anywhere in the world for free or
really cheap.
Significance:
Allows the network provider
companies, to process their billing procedures with their code of conduct.
Application:
∑ Provides the GSM architecture for
nowadays Mobile usage.
∑ This is mainly used in the Voice IP
call features