Economics - Methods of Measuring National Income | 12th Economics : Chapter 2 : National Income
Chapter: 12th Economics : Chapter 2 : National Income
Methods of Measuring National Income
Methods of Measuring National Income
All goods and services produced in the country must be counted and
converted against money value during a year. Thus, whatever is produced is
either used for consumption or for saving. Thus, national output can be
computed at any of three levels, viz., production, income and expenditure.
Accordingly, there are three methods that are used to measure national income.
1. Production or value added method
2. Income method or factor earning method
3. Expenditure method
And if these methods are done correctly, the following equation
must hold
Output = Income = Expenditure

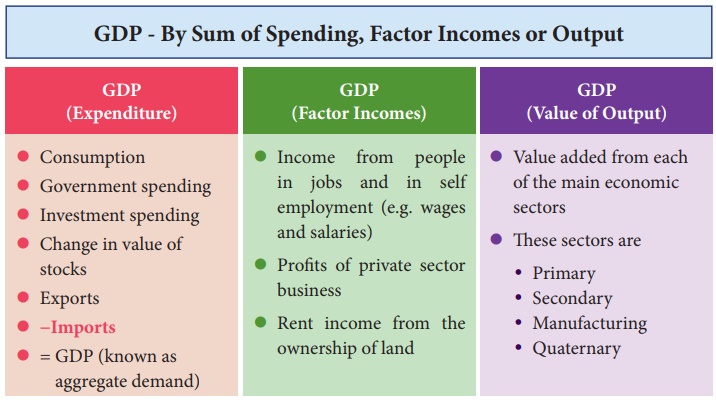
This is because the three methods are circular in nature. It
begins as production, through recruitments of factors of production, generating
income and going as incomes to factors of production.
1. Product Method
Product method measures the output of the country. It is also
called inventory method. Under this method, the gross value of output from
different sectors like agriculture, industry, trade and commerce, etc., is
obtained for the entire economy during a year. The value obtained is actually
the GNP at market prices. Care must be taken to avoid double counting.
The value of the final product is derived by the summation of all
the values added in the productive process. To avoid double counting, either
the value of the final output should be taken into the estimate of GNP or the
sum of values added should be taken.
In India, the gross value of the farm output is obtained as
follows :
(i) Total production of 64 agriculture commodities is estimated.
The output of each crop is measured by multiplying the area sown by the average
yield per hectare.
(ii) The total output of each commodity is valued at market
prices.
(iii) The aggregate value of total output of these 64 commodities
is taken to measure the gross value of agricultural output.
(iv) The net value of the agricultural output is measured by
making deductions for the cost of seed, manures and fertilisers, market
charges, repairs and depreciation from the gross value.
Similarly, the gross values of the output of animal husbandry,
forestry, fishery, mining and factory establishments are obtained by
multiplying their estimates of total production with market prices. Net value
of the output in these sectors is derived by making deductions for cost of
materials used in the process of production and depreciation allowances, etc.
from gross value of output.
Net value of each sector measured in this way indicates the net
contribution of the sector to the national income.
Precautions
The product method is followed in the underdeveloped countries, but
it is less reliable because the margin of error in this method is large. In
India, this method is applied to agriculture, mining and manufacturing,
including handicrafts.
1. Double counting is to be avoided under value added method. Any
commodity which is either raw material or intermediate good for the final
production should not be included. For example, value of cotton enters value of
yarn as cost, and value of yarn in cloth and that of cloth in garments. At
every stage value added only should be calculated.
2. The value of output used for self consumption should be counted
while measuring national income.
3. In the case of durable goods, sale and purchase of second hand
goods (for example pre owned cars) should not be included.
2. Income Method (Factor Earning Method)
This method approaches national income from the distribution side.
Under this method, national income is calculated by adding up all the incomes
generated in the course of producing national product.
Steps involved
1.
The enterprises are classified into various industrial groups.
2.
Factor incomes are grouped under labour income, capital income and
mixed income.
a.
Labour income - Wages and salaries, fringe benefits, employer’s
contribution to social security.
b.
Capital income – Profit, interest, dividend and royalty
c.
Mixed income – Farming, sole proprietorship and other professions.
3.
National income is calculated as domestic factor income plus net
factor incomes from abroad. In short,
Y = w + r + i + π + (R-P)
w = wages, r = rent, i = interest, π = profits,
R = Exports and P = Imports
This method is adopted for estimating the contributions of the
remaining sectors, viz., small enterprises, banking and insurance, commerce and
transport, professions, liberal arts and domestic service, public authorities,
house property and foreign sector transaction.
Data on income from abroad (the rest of the world sector or
foreign sector) are obtained from the account of the balance of payments of the
country.
Precautions
While estimating national income through income method, the
following precautions should be taken.
Items not to be included
1. Transfer payments are not to be included in estimation of
national income as these payments are not received for any services provided in
the current year such as pension, social insurance etc.
2. The receipts from the sale of second hand goods should not be
treated as part of national income as they do not create new flow of goods or
services in the current year.
3. Windfall gains such as lotteries are also not to be included as
they do not represent receipts from any current productive activity.
4. Corporate profit tax should not be separately included as it
has been already included as a part of company profit.
Items to be included
1. Imputed value of rent for self occupied houses or offices is to
be included.
2. Imputed value of services provided by owners of production
units (family labour) is to be included.
3. The Expenditure Method (Outlay method)
Under this method, the total expenditure incurred by the society
in a particular year is added together. To calculate the expenditure of a
society, it includes personal consumption expenditure, net domestic investment,
government expenditure on consumption as well as capital goods and net exports.
Symbolically,
GNP = C + I + G + (X-M)
C - Private consumption expenditure
I - Private Investment Expenditure
G - Government expenditure
X-M = Net exports
Precautions
1. Second hand goods: The expenditure made on second hand goods
should not be included.
2. Purchase of shares and bonds : Expenditures on purchase
of old shares and bonds in the secondary market should not be included.
3. Transfer payments : Expenditures towards payment incurred by
the government like old age pension should not be included.
4. Expenditure on intermediate goods : Expenditure on seeds and
fertilizers by farmers, cotton and yarn by textile industries are not to
be included to avoid double counting. That is only expenditure on final
products are to be included.
National Income (NNPFC) = Gross Value Added by all the production
Enterprises within the Domestic Territory of the Country – Depreciation – Net
Indirect Taxes + Net Factor Income from Abroad
[Where, Net Indirect Taxes = Indirect tax – Subsidies]
[Gross Value Added = Value of Output – Intermediate Consumption]
Value of Output = Sales + Change in Stock
Where, Change in Stock = Closing Stock – Opening Stock
Note: If entire out put is sold within the year, then value of output
will be equal to sales itself.
or
Value of Output = Price x Quantity Sold
GDPMP = Private Final Consumption + Government Final Consumption
Expenditure + Gross Domestic Capital Formation + Net Exports (Exports –
Imports)
Related Topics