Computer Organization - Memory Devices | 11th Computer Science : Chapter 3 : Computer Organization
Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 3 : Computer Organization
Memory Devices
Memory Devices
A memory is just like
a human brain. It is used to store data and instructions. Computer memory is
the storage space in the computer, where data and instructions are stored.
There are two types of accessing methods to access (read or write) the memory.
They are sequential access and random access. In sequential access, the memory
is accessed in an orderly manner from starting to end. But, in random access,
any byte of memory can be accessed directly without navigating through previous
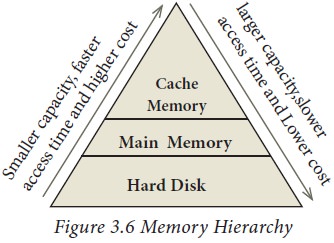
bytes. Different memory devices are arranged according to the capacity, speed
and cost as shown in Figure 3.6.
The main memory is
otherwise called as Random Access Memory. This is available in
computers in the form of Integrated Circuits (ICs). It is the place in a
computer where the Operating System, Application Programs and the data in current
use are kept temporarily so that they can be accessed by the computer’s
processor. The smallest unit of information that can be stored in the memory is
called as a bit. The memory can be accessed by a collection of 8 bits which is
called as a byte. The bytes are referred by ‘B’. If a computer has 1 megabyte
of memory, then it can store 10,48,576 bytes (or characters) of information.
[Hence 1MB is 1024KB and 1 KB is 1024 Bytes, So 1024X1024 =10,48,576 Bytes]
RAM is a volatile memory, which means that the information stored in it is not permanent. As soon as the power is turned off, whatever data that resides in RAM is lost. It allows both read and write operations.
2. Types of RAM
There are two basic
types of RAM
· Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
·
Static RAM (SRAM)
These two types differ
in the technology they use to hold data. Dynamic RAM being a common type needs
to be refreshed frequently. Static RAM needs to be refreshed less often, which
makes it faster. Hence, Static RAM is more expensive than Dynamic RAM.
3. Read Only Memory (ROM)
Read Only Memory
refers to special memory in a computer with pre-recorded data at manufacturing
time which cannot be modified. The stored programs that start the computer and
perform diagnostics are available in ROMs. ROM stores critical programs such as
the program that boots the computer. Once the data has been written onto a ROM
chip, it cannot be modified or removed and can only be read. ROM retains its
contents even when the computer is turned off. So, ROM is called as a non-volatile
memory.
3.1 Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM)
Programmable read only
memory is also a non-volatile memory on which data can be written only once.
Once a program has been written onto a PROM, it remains there forever. Unlike
the main memory, PROMs retain their contents even when the computer is turned
off.
The PROM differs from
ROM. PROM is manufactured as a blank memory, whereas a ROM is programmed during
the manufacturing process itself. PROM programmer or a PROM burner is used to
write data to a PROM chip. The process of programming a PROM is called burning
the PROM.
3.2 Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM)
Erasable Programmable
Read Only Memory is a special type of memory which serves as a PROM, but the
content can be erased using ultraviolet rays. EPROM retains its contents until
it is exposed to ultraviolet light. The ultraviolet light clears its contents,
making it possible to reprogram the memory.
An EPROM differs from
a PROM, PROM can be written only once and cannot be erased. EPROMs are used
widely in personal computers because they enable the manufacturer to change the
contents of the PROM to replace with updated versions or erase the contents
before the computer is delivered.

3.3 Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM)
Electrically Erasable
Programmable Read Only Memory is a special type of PROM that can be erased by
exposing it to an electrical charge. Like other types of PROM, EEPROM retains
its contents even when the power is turned off. Comparing with all other types
of ROM, EEPROM is slower in performance.
4. Cache Memory
The cache memory is a
very high speed and expensive memory, which is used to speed up the memory
retrieval process. Due to its higher cost, the CPU comes with a smaller size of
cache memory compared with the size of the main memory. Without cache memory,
every time the CPU requests the data, it has to be fetched from the main memory
which will consume more time. The idea of introducing a cache is that, this
extremely fast memory would store data that is frequently accessed and if
possible, the data that is closer to it. This helps to achieve the fast
response time, Where response Time, (Access Time) refers to how quickly the
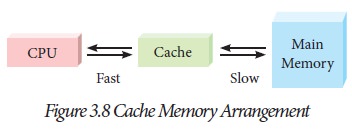
memory can respond to a read / write request. Figure 3.8 shows the arrangement
of cache memory between the CPU and the main memory.
Related Topics