Computer Organization | Computer Science - Answer the following questions | 11th Computer Science : Chapter 3 : Computer Organization
Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 3 : Computer Organization
Answer the following questions
Fundamentals of Computers
Computer Organization
Evaluation
Answer the following questions
Part – II
1. What are the parameters which influence the characteristics of a microprocessor?
Answer:
A Microprocessor’s performance depends on the following
characteristics:
(i) Clock speed
(ii) Instruction set
(iii) Word size
2. What is an instruction?
Answer: A command which is given to a computer to perform an operation
on data is called an instruction.
3. What is a program counter?
Answer: The Program Counter (PC) is a special register in the CPU which
always keeps the address of the next instruction to be executed.
4. What is HDMI?
Answer: High-Definition Multimedia Interface is an audio/video
interface which transfers the uncompressed video and audio data from a video
controller, to a compatible computer monitor, LCD projector, digital television
etc.
5. Which source is used to erase the content of a EPROM?
Answer: Ultra-violet-rays
is used to erase the content of a EPROM.
Part – III
1. Differentiate Computer Organization from Computer Architecture.
Answer:
(i) Computer Organization deals with the hardware components
that are transparent to the programmer.
(ii) Computer architecture deals with the engineering considerations
involved in designing a computer.
2. Classify the microprocessor based on the size of the data.
Answer: Microprocessors can process instructions. The microprocessors
can be classified as follows based on the size of the data.
(i) 8-bit microprocessor
(ii) 16-bit microprocessor
(iii) 32-bit microprocessor
(iv) 64-bit microprocessor
3. Write down the classifications of microprocessors based on the instruction set.
Answer: The two types of microprocessors wich are based on their
instruction sets.
(i) Reduced Instruction Set Computers (RISC)
(ii) Complex Instruction Set Computers (CISC)
4. Differentiate PROM and EPROM.
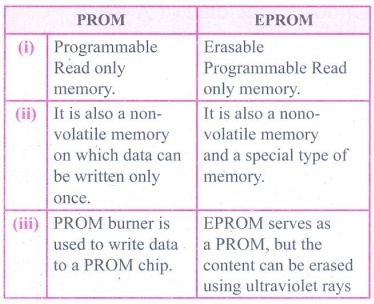
PROM
(i) Programmable Read only memory.
(ii) It is also a non-volatile memory on which data can be
written only once.
(iii) PROM burner is used to write data to a PROM chip.
EPROM
(i) Erasable Programmable Read only memory.
(ii) It is also a nono-volatile memory and a special type of
memory.
(iii) EPROM serves as a PROM, but the content can be erased
using ultraviolet rays
5. Write down the interfaces and ports available in a computer.
Answer:
(i) Serial Port
(ii) Parallen Port
(iii) USB 3.0
(iv) VGA Connector
(v) Audio Plugs
(vi) PS/2 Port
(vii) SCSI Port
(viii) High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI).
6. Differentiate CD and DVD
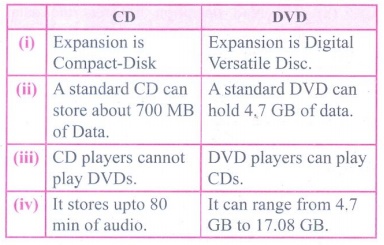
CD
(i) Expansion is Compact-Disk
(ii) A standard CD can store about 700 MB of Data.
(iii) CD players cannot play DVDs.
(iv) It stores upto 80 min of audio.
DVD
(i) Expansion is Digital Versatile Disc.
(ii) A standard DVD can hold 4,7 GB of data.
(iii) DVD players can play CDs.
(iv) It can range from 4.7 GB to 17.08 GB.
7. How will you differentiate a flash memory and an EEPROM?
Answer: Flash memory devices:
(i) Flash memory is an electronic (solid-state) non-volatile
computer storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed.
(ii) Flash memories can be used in personal computers, Personal
Digital Assistants (PDA), digital audio players, digital cameras and mobile
phones.
(iii) Flash memory offers fast access times. The time taken to
read or write a character in memory is called access time.
(iv) Examples for Flash memories are pen drives, memory cards
etc.
EEPROM:
(ii) Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory can be
erased by exposing it to an electrical charge.
(ii) EEPROM is non-volatile.
(iii) EEPROM is slower in performance.
Part – IV
1. Explain the characteristics of a microprocessor.
Answer: A Microprocessor’s performance depends on the following
characteristics:
(i) Clock speed
(ii) Instruction set
(iii) Word size
(i) Clock Speed
Every microprocessor has an internal clock that regulates the
speed at which it executes instructions. The speed at which the microprocessor
executes instructions is called clock speed. Clock speed is measured in MHz
(Mega Hertz) or in GHz (Giga Hertz).
(ii) Instruction
set: A command which is given to a computer to perform an operation
on data is called an instruction. Basic set of machine level instructions that
a microprocessor is designed to execute is called as an instruction set. This
instruction set carries out the following types of operations:
1. Data transfer
2. Arithmetic operations
3. Logical operations
4. Control flow
5. Input/output.
(iii) Word Size :
The number of bits that can be processed by a processor in a
single instruction is called its word size. Word size determines the amount of
RAM that can be accessed by a microprocessor at one time and the total number
of pins on the microprocessor. Total number of input and output pins in turn
determines the architecture of the microprocessor.
2. How the read and write operations are performed by a processor? Explain.
Answer: (i) The Central Processing Unit(CPU) has a Memory Data Register
(MDR) and a Memory Address Register (MAR).
(ii) The Memory Data Register (MDR) keeps the data which is
transferred between the Memory and the CPU. The Program Counter (PC) is a
special register in the CPU which always keeps the address of the next
instruction to be executed.
(iii) A bus is a collection of wires used for communication
between the internal components of a computer.
(iv) The address bus is used to point a memory location. A
decoder, a digital circuit is used to point to the specific memory location
where the word can be located.
(v) The read operation fetches data from memory and transfers to
MDR. A single control line performs two operations like read write using 1 or O.
(vi) Also, the write operation transfers data from the MDR to
memory.
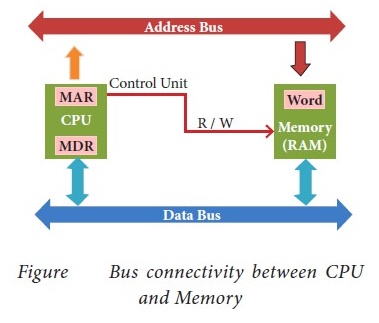
(vii) The word in the RAM has the same size (no. of bits) as the
Memory Data Register (MDR).
(viii)The data bus has eight parallel wires to transfer data either from MDR to word or word to MDR based on the control (Read or write).
(ix) This control line is labeled as R/W, which becomes 1 means
READ operation and 0 means WRITE operation. The content of MDR and the Word
before the READ operation. Also figure shows the content of MDR and the Word
after the READ operation.
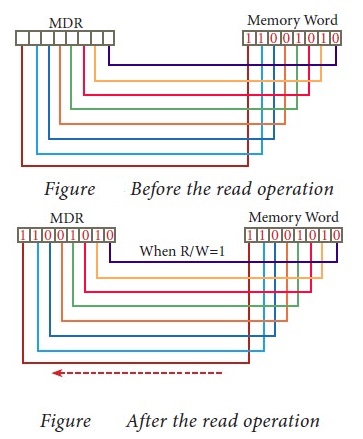
(x) The read operation transfers the data (bits) from memory
word to data register. The write operation transfers the data (bits) from
memory data register to word.
3. Arrange the memory devices in ascending order based on the access time.
Answer: A memory is just like a human brain. It is used to store data
and instructions. Computer memory is the storage space in the computer, where
data and instructions are stored. There are two types of accessing methods to
access (read or write) the memory.
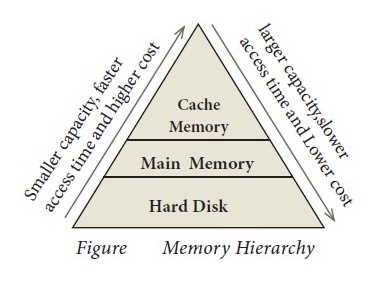
They are sequential access and random access. In sequential
access, the memory is accessed in an orderly manner from starting to end. But,
in random access, any byte of memory can be accessed directly without
navigating through previous bytes. Different memory devices are arranged
according to the capacity, speed and cost as shown in Figure.
4. Explain the types of ROM.
Answer: Read-only
memory (ROM) :
(i) Read only memory refers to special memory in a computer with
pre-recorded data at manufacturing time which cannot be modified.
The stored programs that start the computer and perform
diagnostics are available in ROMs.
(ii) ROM stores critical programs such as the program that boots
the computer. Once the data has been written onto a ROM chip, it cannot be
modified or removed and can only be read.
(iii) ROM retains its contents even when the computer is turned
off. So, ROM is called as a non-volatile memory.
Programmable
Read-Only Memory (PROM) :
(i) Programmable read-only memory is also a non-volatile memory
on which data can be written only once. Once a program has been written onto a
PROM, it remains there forever.
(ii) Unlike the main memory, PROMs retain their contents even
when the computer is turned off.
(iii) PROM is manufactured as a blank memory, whereas a ROM is
programmed during the manufacturing process itself. PROM programmer or a PROM
burner is used to write data to a PROM chip. The process of programming a PROM
is called burning the PROM.
Erasable
Programmable Read-Only Memory (EPROM)
(i) Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory is a special type of
memory which serves as a PROM. The content can be erased using ultraviolet
rays.
(ii) An EPROM differs from a PROM. PROM can be written only once
and cannot be erased.
(iii) EPROMs are used widely in personal computers because they
enable the manufacturer to change the contents of the PROM to replace with
updated versions or erase the contents before the computer is delivered.
Electrically
Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EEPROM)
(i) Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory can be
erased by exposing it to an electrical charge.
(ii) Like other types of PROM, EEPROM retains its contents even
when the power is turned off. Comparing with all other types of ROM, EEPROM is
slower in performance.
Related Topics