Chapter: 11th Computer Science : Chapter 3 : Computer Organization
Characteristics of Microprocessors
Characteristics of Microprocessors
A Microprocessor’s
performance depends on the following characteristics:
· Clock speed
· Instruction set
· Word size
a) Clock Speed
Every microprocessor has an internal clock that regulates the speed
at which it executes instructions.
The speed at which the microprocessor executes instructions is called the clock speed. Clock speed is measured in
MHz (Mega Hertz) or in GHz (Giga Hertz).
b) Instruction Set
A command which is given to a
computer to perform an operation on data
is called an instruction. Basic set
of machine level instructions that a microprocessor is designed to execute is
called as an instruction set. This
instruction set carries out the following types of operations:
•
Data transfer
•
Arithmetic operations
•
Logical operations
•
Control flow
•
Input/output
c) Word Size
The number of bits that can be
processed by a processor in a single instruction is called its word size. Word size determines the amount of RAM
that can be accessed by a microprocessor at one time and the total number of
pins on the microprocessor. Total number of input and output pins in turn
determines the architecture of the microprocessor.
Speed Measurement
Hertz – abbreviated as Hz is the standard unit of measurement used for measuring frequency.
Since frequency is measured in cycles per second, one hertz equals one cycle per second.
Hertz is commonly used to measure wave frequencies, such as sound waves, light waves, and radio waves. For example, the average human ear can detect sound waves between 20 and 20,000 Hz. Sound waves close to 20 Hz have a low pitch and are called "bass" frequencies. Sound waves above 5,000 Hz have a high pitch and are called "treble" frequencies.
While hertz can be used to measure wave frequencies, it is also used to measure the speed of computer processors. For example, each CPU is rated at a specific clock speed. This number indicates how many instruction cycles the processor can perform in every second. Since modern processors can perform millions or even billions of instructions per second, clock speeds are typically measured in megahertz or gigahertz.
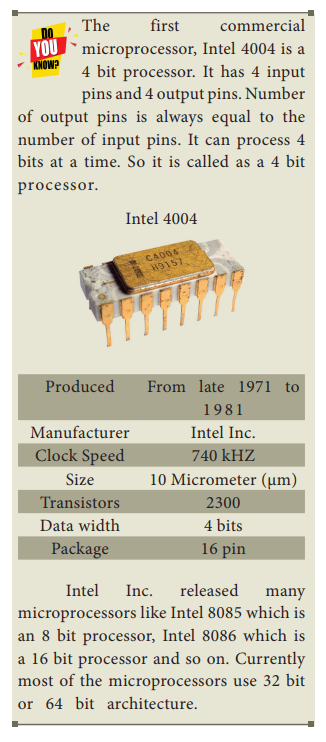
Related Topics