Chapter: Business Science : Rural Marketing : An Overview of Rural Marketing
Mechanisms of Rural Marketing
Mechanisms of Rural Marketing
Development
programs
Green
Revolution in the Agricultural Sector
Period from 1967 to 1978 heralded a technological
thrust into rural areas aimed at improving food grain production in the country
and hence achieving food self-sufficiency.
Green
Revolution generated some notable economic results:
1. Crop
areas under high-yield varieties required fertilizers, pesticides, fungicides
and other inputs. Farm equipments like tractors with farm implements, diesel
pump sets etc. introduced mechanization into the farm sector for the first
time.
2. The
increase in farm production also introduced mechanized processing, spurring
growth of the local manufacturing sector.
The modernization and mechanization of the farm
sector boosted farm productivity, triggered industrial growth, created jobs and
initiated a change in the quality of life in villages.
White
Revolution
Ø Initiated
by the government with the aim of achieving self-sufficiency in the area of
milk production.
Ø Cornerstone
of the government dairy development policy was producing milk in rural areas
through producer cooperatives and moving processed milk to urban-demand
centres.
Ø Gave
a boost to dairy development and initiated the process of establishing the much-needed
linkages between rural producers and urban consumers.
Ø Formation
of producer‘s cooperatives ha institutionalizing milk production and
processing.
Ø Socio-economic
and demographic factors such as urbanization and changing food habits and
lifestyles have also reinforced the growth in demand for dairy products (ice
creams, chocolate, yoghurt, butter, flavoured milk etc.).
Ø Milk
production has increased from 17 million tonnes in 1950-51 to 84.6 million
tonnes in 2001-02.
Ø Most
successful story in dairy development has been in Gujarat, Punjab, Haryana,
Uttar Pradesh and Andhra pradesh.
The
NGO Movement
Ø Important
in providing assistance at the grassroots level assimilation of technological
extensions in rural areas.
Ø Stepped
in to create awareness, build skills, introduce technology and develop capacities
for maintenance and sustainability.
Ø Government
programmes implemented through NABARD, CAPART, KVIC and others are given shape
by these organizations.
Ø Introduction
of low-cost spindles, weaving machinery, technology for leather processing,
food processing, natural resources management etc have been some contributions
in bringing about change at the grassroots.
Ø NGO‘shave
been also active in providing basic health and child care services, running
homes
for destitute and the distressed and providing education and training
opportunities.
Infrastructure facilities
Road Connectivity
Good road connectivity, particularly in rural areas,
between sub-divisional towns and district headquarters is often the primary
means of supplementing public efforts directed at providing basic health and
educational services, as well as infrastructural support for production and
trade and commerce at the local village level.
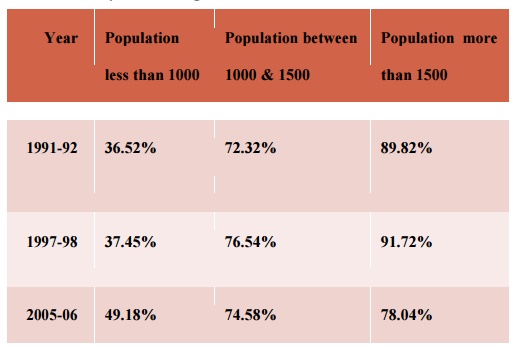
It is particularly relevant in the Indian context
where over 70% of the population continues to live in rural areas and where
over 50% of villages with population of less than 1000 have yet to be connected
by roads.
Among the major states, Kerala has the highest road
length per hundred square kilometres (375 km in 1997).
Road connectivity at the village level
Post Offices
India with its 1,55,279 post offices as on 31 March
2002 (138756 post offices are in rural areas) has a postal network that is the
largest in the world. On an average, a post office serves an area of 21.17 km
and a population of 6614 persons.
For providing postal services, the whole country has
been divided into 22 postal circles. Each circle is further divided into
regions. A postmaster general who is the postal manager of the area heads each
region.
Post offices in the country are categorized as head,
sub and branch post offices.
Rural
Health Services
Sub-centers: The health Sub-Centre is the contact
point between the primary health care system and the community. The Staff at
health Sub-Centres are assigned tasks related to
Ø Interpersonal
communication in order to bring about behavioral change in relation to maternal
and child health, family welfare, nutrition, immunization, control of diarrhoea
and control of communicable diseases.
Ø Primary
health Centres : First contact point between the village community and a
medical officer. These are established and maintained by the State Government
under
the Minimum Needs / Basic Minimum Services
Programme.
Ø Manned
by a medical officer and is supported by 14 paramedical and other staff.
Ø Activities
include curative, preventive and promotive health care as well as family
welfare services.
Ø Community
Health Centres : Established and maintained by the State Governments under the
MNP/BMS programme. Four medical specialists, i.e. surgeon, physician,
gynaecologist and paediatrician supported by 21 paramediacal and other staff.
30
indoorbeds, with X-ray, labour room, operation
theatre and laboratory facilities.
Radio
From six radio stations at the time of Independence,
All India Radio today has 208 radio stations. All Stations of All India Radio
broadcast farm programmes and home programmes directed at rural audience. The
thrust of the broadcast is on increasing production of agri-products and
various programmes adopted by the Government of India.
Television
DD-1 operates through a network of 1042 terrestrial
transmitters of varying powers reaching over 87% of the population. Over the
years, the viewership of Doordarshan as increased enormously, reaching 7.5
crore homes. Community television sets have been introduced under various
schemes operated by Central and State Government.
Telecom
Services
By 2004, over 80% of all villages had been connected
through 5.4 lakh Village Public Telephones. Similarly, 1.42 crore telephone
connections had been given in rural areas.
People who are unable to afford a telephone facility
of their own can now have access to VPTs in rural areas in addition to Public
Call Offices.
Rural credit institution
§ Asmitha
–Provides rural poor women access to financial resources in the form of
collateral free small loans for income generation and livelihood promotion. This
enables them to set-off small start up business, which soon translates into
adequate nutrition, medical aid and education. With increased businesses, these
low-income women become economic agents intrinsic to development rather than
simply homemakers
§ Bandhan
MF- Bandhan was set up to address the dual objective of poverty alleviation and
women empowerment. The microfinance activities are carried on by Bandhan
Financial Services Pvt. Ltd. (BFSPL), incorporated under the Companies Act,
1956 and also registered as a Non Banking Financial Company (NBFC) with the
Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
§ That
apart, Bandhan is also engaged in de entity.
§ Cashpor
India –Our mission is to identify and motivate poor women in the rural areas
and to deliver financial services to them in an honest, timely and efficient
manner so that our Vision is realized and CASHPOR itself becomes a financially
sustainable micro finance institution for the poor.
§ Grameen
Foundation –Works in 6 key areas : Connecting microfinance institutions with
capital markets, Strengthening organizations by building people practices,
Harnessing the power of technology, Helping track peopl knowledge widely for
broader impact and Social Business
§ Grameen
Koota –Grameen Koota recognises the future competition and challenge of
retaining exclusivity of clients. Instead of targeting a high market share in
high competition areas we will focus on incre becoming a preferred microfinance
provider. We will leverage our existing goodwill with the community and have a
strong focus on orienting our field staff towards this objective.
§ Hand
in Hand –is a development organisation whose objective is to eliminate poverty
by creating enterprises and jobs?
§ Focusing
on help to self-help, we take a holistic approach that combines microfinance
and support for women to start enterprises with work in four other areas that
matter most
too poor communities: education and child labour
elimination, health and sanitation, a sustainable local environment and
information technology access. With currently more than 450,000 members in
Tamil Nadu, Karnataka and Madhya Pradesh, who have collectively started more
than 250,000 micro-enterprises, our goal is to create 1.3 million jobs by 2013.
Supported by international offices in the UK and Sweden, we are now taking our
model to South Africa, Afghanistan and Latin America.
Micro Credit India –Microcredit Foundation of India
(MFI) is a not-for-profit Section 25 Company in Tamil Nadu dedicated to
promoting entrepreneurship and community level
action in rural areas as a means to sustainable
economic prosperity. Today MFI works primarily with women. Through its field
staff, MFI helps them form Self Help Groups (SHGs), trains them in good
financial practice, facilitates access to microcredit loans, equips them with
business skills and facilitates access to new markets for their products.
MYRADA – MYRADA is a Non Governmental Organisation
managing rural development programmes in 3 States of South India and providing
on-going support including deputations
of staff to programmes in 6 other States. It also promotes the Self Help
Affinity strategy in Cambodia, Myanmar and Bangladesh New Life –New Life
designs projects based on survey of the socio,economic problems of the project
area and support the poor, abused and abandoned children and women by executing
the projects with a defined goals/objectives. The current projects of New Life
includes orphanages for children of incarcerated parents,Save children from
Child Labour,Ensuring primary education for the rural children in India,Early
learning centres for children of vulnerable community groups,Read to Lead
Project, Taking care of the medical needs of Physically handicapped and
Mentally retarded children.
RangDe –Rang De‘s mission is to make microcr
household by lowering loan interest rates through innovative means. Rang De is committed to
enabling individuals to
become social investors
through a transparent platform. While strive to improve Rangde.org
as an interface, we work extensively with our field partners to ensure that we
do not compromise on our vision –making credit available at affordable rates.
Role of cooperative institution
Cooperative society is
an organization of group of people with collective responsibilities and
thoughts for the development of needy, especially under privileged.
Cooperatives helped in the development of agriculture, banking, credit,
agro-processing, storage, marketing, dairy, fishing and housing and its network
covers 85 per cent of rural households. It occupies a key position in
agricultural development with support in resource and input use, harvesting of
water resources, marketing channels, storage facilities, distribution channels,
value addition, market information and a regular monitoring network system.
Cooperatives are also engaged in economic activities like disbursement of
credit, distribution of agricultural inputs (seeds, fertilizers, and
agrochemicals), etc.
Financial service
Input supply services Marketing services Consumer
services Welfare Services
Extension services Training centre Scholarships
Regulated market
A regulated market
or controlled market, is a market where the government controls the
forces of supply and demand, such as who is allowed to enter the market or what
prices may be charged.[1] It is common for some markets to be
regulated under the claim that they are natural monopolies. For example,
telecommunications, water, gas or electricity supplies. Often, regulated
markets are established during the partial privatization of government
controlled utility assets.
A variety of forms of regulations exist in a
regulated market. These include controls, oversights, anti-discrimination,
environmental protection, taxation and labor laws. In a regulated market, the
government regulatory agency may legislate regulations that privilege special
interests, known as regulatory capture.
Agriculture Export Zone
An Agri Export Zone or
AEZ is a specific geographic region in a country demarcated for setting up
agriculture based processing industries, mainly for export. The term is widely
used mainly inIndia.
AEZ are to be
identified by the State Government, who would evolve a comprehensive package of
services provided by all State Government agencies, State agriculture
universities and all institutions and agencies of the Union Government for
intensive delivery in these zones. Corporate sector with proven credentials
would be encouraged to sponsor new agri export zone or take over already
notified agri export zone or part of such zones for boosting agri exports from
the zones.
Establishments of
marketing departments for various agricultural & non-agricultural produce
KAPPAC
COIR BOARD
Main motive of this
board is to purchase the coconut and prepare the coconut fibre. Scheme
Rejuvenation, modernization, & technology up
gradation of coir industry Scheme of fund for regeneration of traditional
industries
Skill upgradation & quality improvement scheme
Science & technology scheme
Export market promotion scheme Domestic market
promotion scheme
Trade & Industry related functional support
service scheme Welfare measures.
COFFEE BOARD
Employee Welfare Scheme
Allocation
of fund for each region
I.
Educational stipends
II.
Incentive award
III.
Financial assistance.
NHB (NATIONAL HOUSING BANK)
The Sub-Group on
Housing Finance for the Seventh Five Year Plan (1985-90) identified the
non-availability of long-term finance to individual households on any
significant scale as a major lacuna impeding progress of the housing sector and
recommended the setting up of a national level institution.
NHB has been established to achieve, inter alia, the
following objectives –
a. To
promote a sound, healthy, viable and cost effective housing finance system to
cater to all segments of the population and to integrate the housing finance
system with the overall financial system.
b. To
promote a network of dedicated housing finance institutions to adequately serve
various regions and different income groups.
c.
To augment resources for the sector and
channelise them for housing.
d.
To make housing credit more affordable.
e. To
regulate the activities of housing finance companies based on regulatory and
supervisory authority derived under the Act.
f. To
encourage augmentation of supply of buildable land and also building materials
for housing and to upgrade the housing stock in the country.
g.
To encourage public agencies to emerge
as facilitators and suppliers of serviced land, for
housing.
INITIATIVES
Residential mortgage backed securitization process
of national housing bank Reserve mortgage loan
Reverse mortgage loan enabled annuity Housing
finance
Retail deposits
Related Topics