Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Clinical Use of Antimicrobial Agents
Management of Antimicrobial Drug Toxicity
MANAGEMENT OF ANTIMICROBIAL DRUG TOXICITY
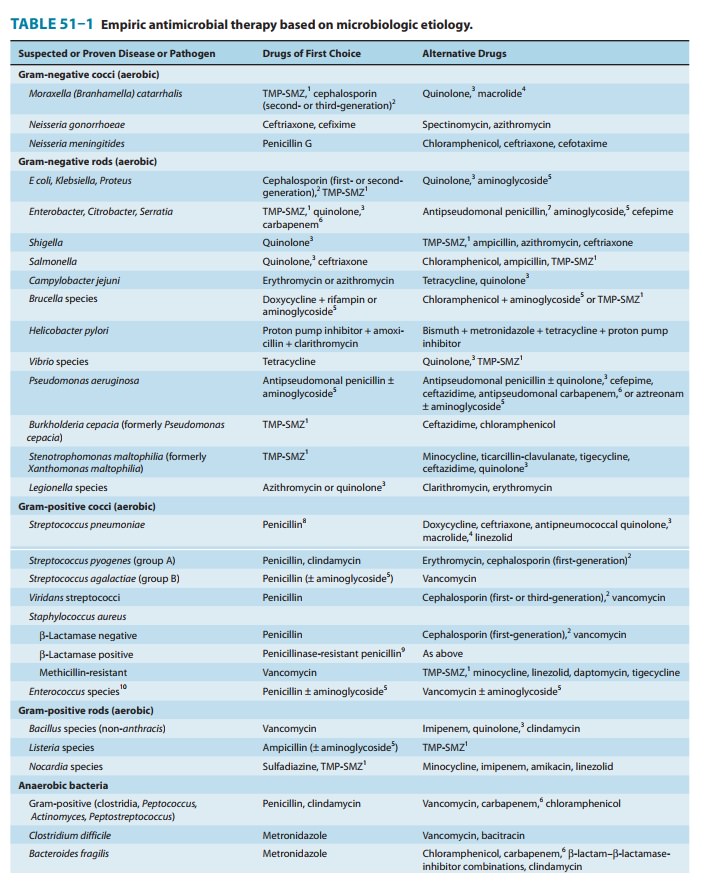
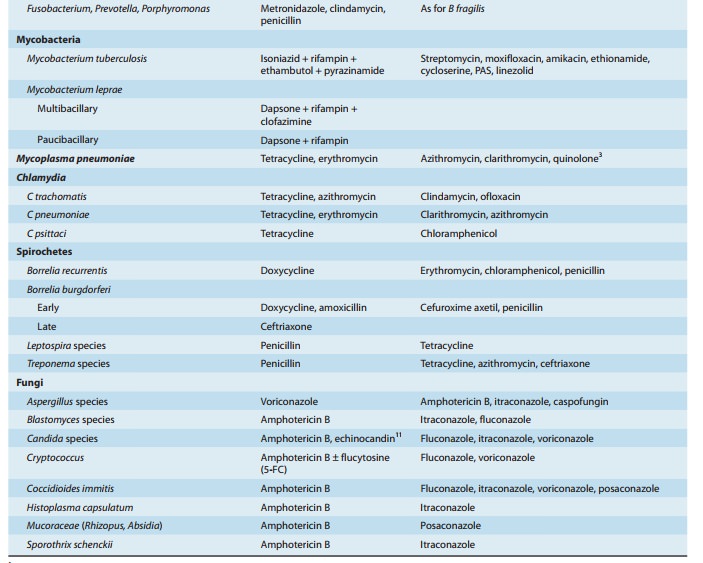
Owing to the large number of antimicrobials available, it is usually possible to select an effective alternative in patients who develop serious drug toxicity (Table 51–1). However, for some infections there are no effective alternatives to the drug of choice. For example, in patients with neurosyphilis who have a history of It is important to obtain a clear history of drug allergy and other adverse drug reactions.
A patient with a documented antimicrobial allergy
should carry a card with the name of the drug and a description of the reaction.
Cross-reactivity between penicillins and cephalosporins is less than 10%.
Cephalosporins may be administered to patients with penicillin-induced
maculopapular rashes but should be avoided in patients with a history of
penicillin-induced immediate hypersensitivity reactions. On the other hand,
aztreonam does not cross-react with penicillins and can be safely administered
to patients with a history of penicillin-induced anaphylaxis. For mild
reactions, it may be possible to continue therapy with use of adjunctive agents
or dosage reduction.
Adverse reactions to
antimicrobials occur with increased frequency in several groups, including
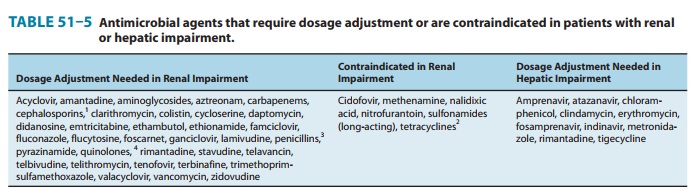
neonates, geriatric patients, renal failure patients, and AIDS patients. Dosage
adjustment of the drugs listed in Table 51–5 is essential for the prevention of
adverse effects in patients with renal failure. In addition, several agents are
contraindicated in patients with renal impairment because of increased rates of
serious toxicity (Table 51–5).
Polypharmacy also predisposes to drug interactions. Although the mechanism is not known, AIDS patients have an unusually high incidence of toxicity to a number of drugs, including clin-damycin, aminopenicillins, and sulfonamides. Many of these reac-tions, including rash and fever, may respond to dosage reduction ortreatment with corticosteroids and antihistamines.
Related Topics