Causes, Preventive Measures - Man - made Disasters | 12th Geography : Chapter 8 : Man Made Disasters Public Awareness For Disaster Risk Reduction
Chapter: 12th Geography : Chapter 8 : Man Made Disasters Public Awareness For Disaster Risk Reduction
Man - made Disasters
Man - made Disasters
Disaters induced by human beings are
man-made disasters. It includes fire accident, transport accident, structure failure,
minining accidents, explosions, stampede etc. In this lesson, we study about some
of the man-made disasters.
1. Stampede 2. Drowning 3. Fire Accident 4. Industrial Disasters, 5. Road accident
1. Stampede
The term stampede is a sudden rush of
a crowd of people, usually resulting in injuries and death from suffocation and
trampling. In stampede, the term mob or crowd is used to refer to a congregated,
active, polarized aggregate of people, which is basically heterogeneous and complex.
Its most salient features include homogeneity of thought and action among its participants
and their impulsive and irrational actions.
Causes
of stampede
Incidents of stampedes can occur in numerous
socio-cultural situations. These stampede incidents can be categorized into the
following types: Entertainment events, escalator and moving walkways, food distribution,
processions, natural disasters, power failure, religious events, fire incidents
during religious/ other events, riots, sports events and weather related events.

Large religious gatherings are the major
stampede events in developing countries like India. As stated in a newspaper in
2013, 79 percent of stampedes in India have taken place at religious events.
Stampede Management
Crowd management is defined as the systematic
planning and supervision of the orderly movement and assembly of people. Crowd control
is the restriction or limitation of group behavior.
The rules of action for stampede
1.
Notice Alternate Exit: First
thing to know in such situations is the
route out. If you are attending an event, one of the things you can do in preparation
is to try and know the topography of the place. This will help you find the exits.
So, when struck in a stampede, try to identify these exits.

2. Keep Your Hands by Your Chest: Your hands must be up by your chest like they would be in a boxing position. This makes it easy to move. It also stops your ribs from getting crushed by the crowd on both sides. When the crowd pushes you from front and back, your lungs will be affected. You will suffer of suffocation.

3.
How to move when on your feet: In the middle of a moving crowd, do not resist
the flow by standing still or sitting down. The force is too much to fight. Like
in a wave, there is force and in crowd situation. Keep moving diagonally between
the pockets of people whenever there is a lull. Try to move towards the exits but
not towards walls or fences where you might be cornered. Keep moving with the crowd
to avoid falling.

4.
How to move if you fall: If you
fall and get back on your feet, cover
your head with your hands and hurl up in a fetal position. Basically, avoid exposing
your lungs to the crowd. Keep trying to find an opportunity to get up.

5. Communicate smartly: When trapped in the crowd, use sign language such as waving your hands up one side
after another so that you will not get exhausted.
6. Conserve energy: Keep calm and do not try to scream. That only increases panic.
7.
Set a meeting place: Arrange a
meeting place, in case you get separated,
one inside and another one outside. If someone extends his/her hand for help, grab
hold to keep them up.
Child safety Tips: Take a second, take a photo. Before taking children out to any event,
pull out your phone and take a photo of each child individually a selfie. That way
you have a picture of how they looked that day. The photo can be sent to police
to aid in locating the child in case the child is lost in a crowd.
2. Drowning
Drowning is the 3rd leading cause of
unintentional injury death worldwide, accounting for 7% of all injury-related deaths.
There are an estimated 3,72,000 annual drowning deaths worldwide. Children, males
and individuals with increased access to water are most at risk of drowning. Drowning
is the process of experiencing respiratory impairment from submersion/immersion
in liquid; outcomes are classified as death, morbidity and no morbidity.
Fact File
It is one of our most visceral
fears; thrashing in the deep, far below the water’s surface, lungs burning for oxygen.
Drowning claims hundreds of thousands of lives every year, a great many of whom
are young children. Of course, exposure to water is a key factor in drowning, but
there is a strong economic correlation as well. Those in poorer countries are far
more likely to be drowning. In Bangladesh, 17,000 children drown annually that’s
46 a day.
Fresh Water and Salt Water Drown You Differently.
Fact File continue

At first glance, it would
appear that swimming in the ocean is far more dangerous than swimming in a lake.
Crashing waves and riptides can easily sweep beachgoers to their doom. But shockingly
enough, about 90 percent of drowning cases occur in freshwater. The reason involves
a bit of chemistry. Fresh water is more similar in composition to our own blood
than salt water. When it is inhaled into the lungs, it passes into the bloodstream
through osmosis. When the blood is so radically diluted, cells burst, leading to
organ failure. The entire process takes two to three minutes.
Ocean water contains far
more salt than human blood. When it is aspirated, the body attempts to regulate
itself by transferring water into the lungs, thickening the blood. It takes considerably
longer to kill a person, between 8 to 10 minutes, allowing a much greater chance
of rescue.
Males are especially at risk of drowning, with twice the overall mortality rate of females. Studies suggest that the higher drowning rates among males are due to increased exposure to water and riskier behavior such as swimming alone, drinking alcohol before swimming alone and boating. Drowning accounts for 75% of deaths in flood disasters.
Prevention
There are many actions to prevent drowning.
Installing barriers (e.g. covering wells, using doorway barriers and playpens, fencing
swimming pools etc.) to control access to water hazards.
Community-based, supervised child care
for pre-school children can reduce drowning risk. Teaching school -age children
basic swimming, water safety and safe rescue skills is another approach.
Setting and enforcing safe boating, shipping
and ferry regulations is an important part of improving safety on the water and
preventing drowning. Building resilience to flooding and managing flood risks through
better disaster preparedness planning, land use planning, and early warning systems
can prevent drowning during flood disasters.
3. Fire Accident
Massive forest fires may start in hot
and droughty weather as a result of lightning, and human carelessness or from other
causal factors. Fires can lead to the destruction of buildings, wooden bridges and
poles, power, transmission and telecommunication lines, warehouses of containing
oil products and other fuel. It causes injury to people and animals
Students’ activity
Mock Drill: To escape a fire, stop, drop,
and roll. In case your clothes burn, stop running, drop on the floor and roll to stop fire spreading.
During droughts or windy weather, fire
may destroy low vegetation and trees. The spreading speed of low fire is 1-3 m/sec
and high fire may reach up to 100m/sec.
Think why?
Smoke kills more than fire.
Rule of actions for Fire Accident-Do’s
1. When Fire
accident occurs, warning should be given by shouting or ringing bell.
2. Extinguish
the fire using sand and other fire extinguishers.
3. Main switch
should be switched off immediately.
4. If clothes
started burning, the victim should roll on the ground to extinguish the fire.
5. The combustible
materials found near the fire accident place, have to be discarded so that the fire
does not spread to them.
6. If fire
breaks out with smoke spreading, cover the nose, crawl and move out.
7. Think
that life is more valuable than belongings.
8. Move from the fire accident place
to a safe place.

Preventive Measures
1. Create
a safe zone between the house and flammable plants.
2. Cut off
all the branches of trees with below three meter height standing near your house.
3. Remove
moss and dry branches from plants standing near the house.
4. Clean
ditches and pits from dry branches and leaves.
5. Keep flammable
materials in the checked safe containers.
6. Ask your
relative or friend living in a different location to be your contact person.
7. Have a fire extinguisher and know
how to use it.
A natural gas vent in Iraq
known as The Eternal Fire of Baba Gurgur, meaning 'Father of Fire' has been burning
continuously for over 4,000 years, and it has been mentioned by Herodotus, and Plutarch.
During fire accident
1. When water
cannot be used (because the equipment is plugged-in) or there is no water and the
fire is not strong, you can use cooking soda or calcite soda, washing powder, sand,
soil.
2. Keep your
head no higher than 30 cm above the floor; above this height accumulation of heavy
harmful gases may exists.
3. If there
is no opportunity to leave the room, move towards a window, and try to get the attention
of people by giving signals.
4. If your
clothing has caught fire do not run because this will intensify burning. Take the
clothes off, throw them in a safe place and put out the fire.
5. If you are near a fire in a forest
and cannot extinguish the fire by yourself, immediately inform people who are nearby
about the necessity to leave the hazard zone.
Tips to use fire extinguisher:
Put out small fire with
fire extinguisher or cover the source of fuel with blanket. For fire extinguisher
remember to use pull safety pin from handle. Aim at the base of the flame. Squeeze
the trigger handle. And sweep from side to side at the base of the flame.
Things that must never be done during a fire
1. Never
pour water on burning electrical equipment if it is switched on. If a TV set, a
refrigerator is burning, turn off the electricity from the main switch.
2. Do not
jump from windows of upper floors.
3. Do not
panic.
4. Do not try to extinguish the fire
by yourself.
4. Industrial Disasters
Industrial hazards consist of four principle
hazards. The hazards encountered are fire, explosion, toxic release and environmental
damage. This is because industries engage in different processes involving a wide
range of different raw materials, waste products and final products. Danger originates
from technological or industrial accidents, dangerous procedures, infrastructure
failures or certain human activities. It may cause the loss of life or injury, property
damage, social and economic disruption or environmental degradation.
Fire:
This is the most frequent hazard. Fire can also produce toxic fumes like Acrolein,
Carbon monoxide and Cyanides. Physical structures can be damaged either by the intensity
of the heat or combustion. It may also have an effect on essential services like
power and instrumentation.
Explosion:
Explosions is the result of a shock wave. This overpressure can kill
people but usually the indirect effects of collapsing buildings, breaking of glasses
and falling of debris causes far more loss of life and severe injuries. There are
different types of explosions which include gas explosions and dust explosions.
Gas explosions occur when a flammable gas mixes with air. Dust explosions occur
when flammable solids, especially metals, in the form of fine powders are intensively
mixed with air and ignited.
Chemical
release: Sudden release of toxic vapours has the potential to cause
death and severe injuries several kilometres from the release point. They are carried
by water and air. Their release into public sewage systems, rivers, canals and other
water courses, either directly or through contaminated water used in fire fighting
can result in serious threat to public. The number of casualties depends on the
weather conditions, population density in the path of the cloud and the effectiveness
of the emergency arrangements.
Environmental Damage: Release of other substances, not directly toxic to humans can cause major pollution problems. It is becoming increasingly recognized that damage to natural resources such as plant and animal life can have serious long term consequences. E.g. destruction of trees is increasing the effect of global warming and extinction of animals are severely disrupting food webs and causing an increase in pests.
Means
of reducing the industrial hazards
Process
of Safety Management: Reliability assessment of process equipment, incorporating
safety tips, scrubbing system, etc, should be done before effecting major process
changes.
Safety
Audits: Periodical assessment of safety procedures, performance of safety
systems and gadgets along with follow up measures should be carried out.
Emergency
Planning: A comprehensive risk
analysis indicating the impact of consequences and practiced emergency procedures should be done. This can be done
by communities as well as national or regional corporation authorities.
Training:
Proper training of employees and protective
services should be done.
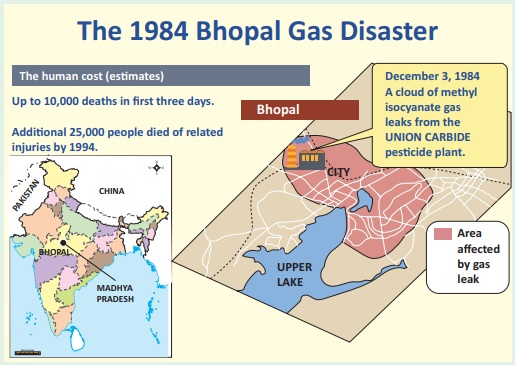
5. Road accident
It is estimated that 1.34 million people
are killed in the road accidents every year. Road accident is the 8th leading cause
of death globally. Every year, up to 50 million people suffer serious, life-altering
injuries which, in many low- and middle-income countries.
Primary road safety risk factors in low
and middle-income countries include:
1. Speeding
2. Drink-driving
3. Non-use, or improper use of helmets,
and
4. Non-use, or improper use of seatbelts
Strengthening the capability of the road
traffic police to enforce traffic laws is fundamental to deterring road users from
violating the laws, to reduce harm and to reduce inappropriate and unsafe behaviors
on the roads.
Basic road safety rules for students:
1.
Aware of the road signals
Assist students to learn the traffic
lights and signs. Check out the relevance of each color:
* Green light
is an indication for “go”- Whenever the signal turns green, the vehicle can move
ahead.
* Red light
is an indication “to stop”- All the vehicles have to stop, when the red light is
on.
* Yellow
light is an indication “to slow down”- When the yellow light turns on, you should
slow down your vehicle and prepare to stop.
* “Walking
man” signal at intersections are constructed for the pedestrians. Recall the fact
that you will be authorized to cross the road only when the signal turns green.
Ensure that there are no vehicles, both on the left and right side of the road.
* Never attempt to cross the road, if the signboard signifies “Don’t walk” message or the walking symbol turns red.
2. Stop, look, and cross
In fact, students will either walk to
school or to the bus stop for waiting their respective school bus. The only task
of students is to cross the road prudently, right after the school bus drops them
off. Hence, we should undertake the responsibility to provide adequate guidance
for crossing the road cautiously.
We teach them to be aware of various
road signs and recommend them to utilize the zebra crossing while crossing the road.
If there are no markings or signs, the following procedures can be worthwhile:
* Check the
right side, after that to the left side of the road for the incoming vehicles.
* If you
notice a vehicle is approaching, wait for the vehicle to pass and then safely cross
the road.
* Do not
cross the road at the turns, it is unsafe.
* Never cross the road between the stopped
vehicles.
However, accompaniment is required for
the children aged below 6 years and you should compulsorily hold their hands while
crossing the road.
3.
Listen
Educate the child to be extra vigilant
while they cross the road at the turns. As a consequence, listening can only aid
them. For this reason, instruct your child to listen and ensure whether a vehicle
is approaching or not. Ordinarily, vehicles apply horns at turns and at unmanned
intersections to provide a warning to other road users. Meanwhile, you can interpret
the following instances to students:
* If a horn
is heard, stop and cross only after ensuring that no vehicle approaches you from
left or right side of the road.
4. Don’t
rush on roads
Students will not be tolerant and have
a tendency to dash across the road to reach the other side. In addition, they become
absent-minded when they are having fun and henceforth bound across or along the
road. Therefore, teach them to remain placid while they are near the road.
5.
Relevance of Sidewalks
Persuade students to avail the service
of sidewalks whenever they walk on the road. Demonstrate them how to cross the road
safely. Motivate them to avail the sidewalks even though it is not a busy street.
6.
Crossroads and pedestrian crossings
Students will have a tendency to scoot
across the street. This will become particularly perilous since vehicles will never
slow down unless there is a cross road or relevant signal. Notify your students
to cross only at intersections and avail the pedestrian crossings. If there is no
crossroad or pedestrian crossing, you can admonish students to comply the rules
mentioned above.
7.
Place the hands inside the vehicle
A multitude of students have the habit
of placing their hands outside the vehicle while it is moving. They will lay their
head out and wave with exhilaration. This is a familiar sight among the school bus
students. Nevertheless, these behaviors can have significant consequences. Due to
carelessness, they will be injured by vehicles, which advance from the opposite
direction.

8.
Never cross road at bends
Bends are evidently the blind spot for motorists. When you attempt to cross at bends, the driver will be unable to recognize you and stop the car at the right time. As a result, students will be hurt while crossing at bends
9.
Remain safe on a bicycle
If students ride bicycle to reach the
school, ensure that they adhere to the following cycling rules:
* Utilize
the bicycle lane. If such a lane does not exist, ride the bike either on the extreme
left or right side of the road and glide along with the traffic.
* Never permit
your students to ride on congested streets without your supervision.
10. Staying
safe in a moving vehicle
In a moving vehicle, you can ensure the
student’s safety with the assistance of a seat belt. Let them practice the following
safety rules in your absence:
* Never stand,
stroll or sprint inside a moving vehicle.
* Remain
seated and hold the rails on the seats until the school bus halts.
* Do
not put your hands outside the moving vehicle.
11.
Get off the vehicle at the curb side
Ask your students to memorize the following
safety tips and conform to the rules while they get down from the school bus:
* Ensure
that you reach the bus stop prior to the scheduled bus timing in order to avert
the circumstance of running behind the school bus.
* Form a queue to board or descend the
school bus.
* Disembark
the school bus at the curbside in order to evade unnecessary endangerment and hindrance
to other vehicles.

Related Topics