Chapter: Biology: Organism and Environment
Major Eco systems
Major Eco-systems
According to the environment the ecosystem is divided into two parts,
one Terrestrial Eco-system and the
other one is Aquatic Eco-systems.
The Environment of a place depends on the topography, weather and
climate of that place. The animals or plants of a particular region are
dependant on some natural characteristics such as nature of soil, rivers,
deserts, hills, mountains, climate etc.
1. Terrestrial Ecosystem: There are different types of terrestrial eco-system in different parts of the earth surface due to difference of rainfall, temperature, wind flow etc. There are many differences in ecology of agricultural land,grassland, desert and forest. Instead there are differences in ecology of mountain, hill, plain land, cold area, temperate area and tropical area. It is not possible to describe all types of eco-system in this chapter, so two of our known eco-systems are described here briefly.
A. Eco-system of paddy field: Due to cultivation, manure and irrigation thefertility of the land is
increased. Paddy is the main plant of paddy field. Besides this there grow
grass and many other weeds. They are the producers of the eco-system. Different
types of insects infect the paddy. They are the primary consumers. Toad and different
birds lives on the insect, snake lives on toad, the predator birds lives on
small birds. When they die the saprophytic insect (ant, larvae of flies) and
bird (crow, vulture) eat them. Besides these different types of bacteria and
virus decomposes the dead bodies of plants and animals into organic compounds.
In this way the eco-system of paddy field is formed.
Their analysis is found in the following list.
Producer: Paddy, grass and weeds.
Primary consumer: Insect and worm, cow, goat.
Secondary consumer : Toad, Insect eating birds, Man (man eats cow and goat).
Tertiary consumer : Snake, predatory birds.
Decomposer: Bacteria, fungi, saprophytic animals (crow, vulture, jackle).
B. Ecosystem of forest: The forest eco-system of Bangladesh is more or lesssame in nature. But
the organisms of different food chains are different in different places.
Producer : Trees of forest, herbs shrubs.
Primary consumer: Insects and worm, deer, monkey (omnivorous),Hystrixelephant, bats.
Secondary consumer: Toad, calotis, hoppers, bats, different types of birds, tiger.
(ii) Tertiary consumer: Snake, mongoose, kite.
Decomposer: Fungus, bacteria, saprophytic insects and worm, birds and wild beast.
(2) Aquatic Ecosystem: Aquatic eco-system is divided into three categories.
(1) Pond ecosystem (2) River ecosystem and (3) Marine ecosystem.
A. Pond ecosystem: The mutual relation between the living organisms andnon- living things
of a particular area is known as ecosystem. In every ecosystem, every organism
has a definite habitat and a definite life pattern. It is the main
characteristics of an ecosystem.
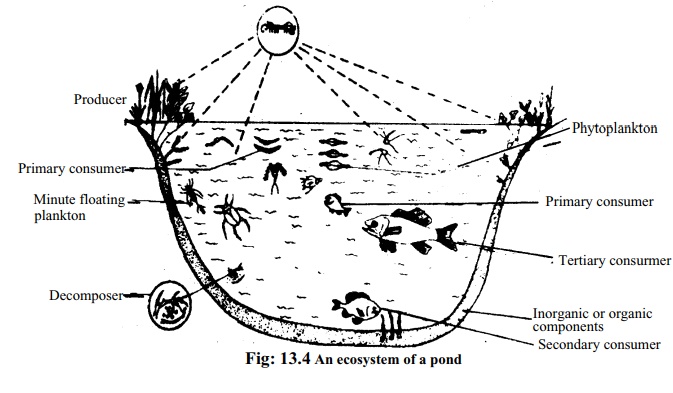
A pond is a self-sufficient and an ideal example of ecosystem. In a
pond, the intimate relation between the inhabiting living and non-living
components is well understood. The non-living objects are various types of
organic and inorganic substances such as water, sun rays, CO2, oxygen, calcium, phosphorus,
humic acid etc. The living components are producers, primary consumers,
secondary consumers, tertiary consumers and various types of decomposers.
Producers: Various types of photosynthetic algae and shallow water plantsliving in
the pond are the producers. The floating organisms are called plankton. The
minute plants of plankton type are known as phytoplankton. Green aquatic algae and other aquatic plants can
live by producing food by the process of the photosynthesis, so they are called
producers.
Primary consumers: These are various types of floating minute insects, larvaeof mosquito
and other microscopic animals like zooplankton etc. Floating minute animals are
called zooplankton. These consumers cannot manufacture their own food and they
live on by eating the producers directly.
Secondary consumers: Small fishes, some aquatic insects, prawns, frog etc.are secondary
consumers. They can neither manufacture their own food nor accept the producers
as food. They live on by eating the primary consumers:
Tertiary consumers: Small fishes, prawn and all other animal that feeds, uponthe secondary
consumers are known as tertiary consumers. Large fishes like shoal, boal,
vetki, stork and heron are the tertiary or highest consumers.
Decomposer: In pond water, various types of fungi and bacteria live as,saprophytes
which are- known as decomposer. These decomposers can live by floating on water
or live at the bottom clay. They attack living or dead consumers and help to
rot. As a result, organic and inorganic chemical substances usable by the
producers are fornmed again. The producer community of the pond use these
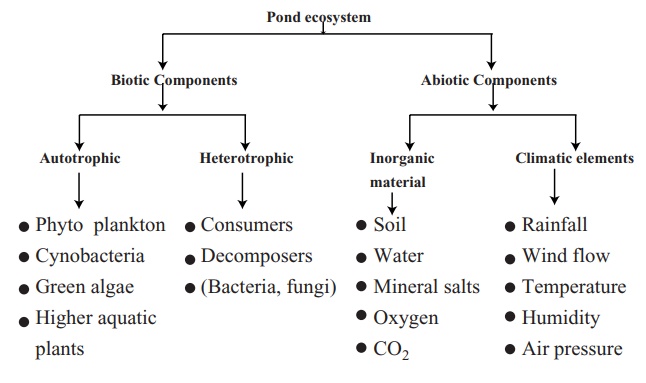
decomposed elements. The flow chart gives an idea about the components of pond
ecosystem.
B. River Ecosystem: water body often the rivers may have strong currents. Forthis reason,
there is a noticeable difference between the environment and the living communities
of rivers with those of the ponds. In river there are different types of algae
fishes like Hilsha, Pungas, Chital, Boal etc. live in the rivers. The bodies
of. these fishes are laterally compressed. For this feature of their body shape
they are capable of moving easily in strong current. Near the bank of the river
where the current is less, living communities like those of the ponds grow
there. In the ecosystem of rivers the food chain is short e.g. Algae, Hilsa,
Boal.
(iii) Marine Ecosystem: The water of the sea is saline. In the saline water thesea there lives
numerous phytoplanktons and zooplanktons. Coral, Prawn Starfish, Snail, various
types of small and large fishes, tortoise, dolphin, shark. whale etc. live in
the sea. Phytoplankton and sea algae are the only producer in marine
environment. Prawn, bivalve, zooplankton, minute pelagic animals and small
fishes are the primary consumers. Large fishes, tortoises, whales etc. are the
secondary ones. The sharks and various predatory fishes the tertiary ones.
Generally the small fishes are herbivorous. The starfish, prawns, snails are
detritus eating animals. The food chain of whale is also short like that of
hilsa such as plankton, whale, plankton, small bivalve's and whale.
Ecosystem is a self-sufficient
unit: Every ecosystem is more or less a
self-controlled unit. In nature the number of a particular living being cannot
increase too much. All organisms are interrelated with each other in the form
of food and consumers chain. Any one of these systems cannot be completely
eliminated easily. The proportionate number of different level of biotic
communities always remains more or less unchanged.
In spite of various changes in the environments, the natural balance is
maintained for a long time. By some reason, if the number of a particular
animal of a place increases, the number of other living beings of that
ecosystem will change in such a manner that the balance of the number of other
living beings is maintained. If it is discussed with example, it will be easy
to understand. Suppose in a forest, tiger, deer, cows, pigs etc. live. Deer and
pig are the foods of tigers. If the number of deer and pigs increase, the tiger
will have enormous quantity of food and consequently the tiger Production will
increase and if the number of tiger's increases, large number of deer and pigs
will be killed, as a result, the number of deer and pigs will be decreased.
This will cause a dirth of food for tigers and the number of tigers will be
decreased. On the other hand, if the number of tiger decreases the number of
deer and pigs will increase. In this way, through decrease and increase of
different animal population of the ecosystem of an area is automatically
controlled.
Related Topics