Chemistry - Laws of Chemical combination | 9th Science : Atomic Structure
Chapter: 9th Science : Atomic Structure
Laws of Chemical combination
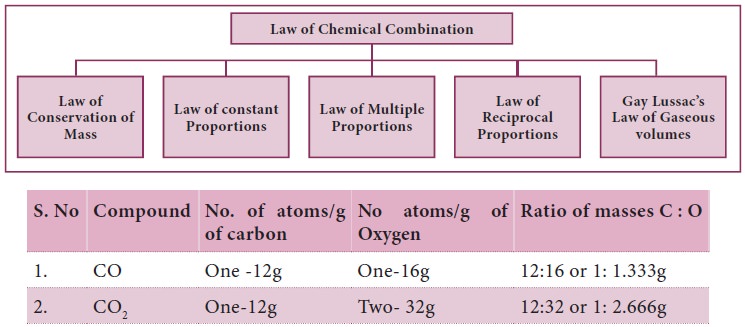
Laws of Chemical combination
Out of these five laws you already know the first
two laws. Let us see the next three laws in detail in this chapter.
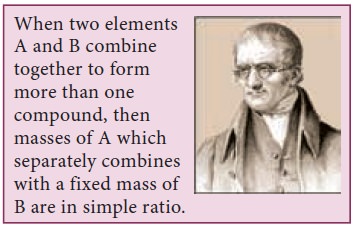
1. Law of multiple proportions
This law was proposed by John Dalton in 1804.
To illustrate the law let us consider the following
example.
Carbon combines with oxygen to form two different
oxides, carbon monoxide(CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
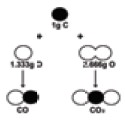
The ratio of masses of oxygen in CO and CO2
for xed mass of carbon is 1: 2. Isn’t this a simple ratio? Let us take one more
example. Sulphur combines with oxygen to form sulphur dioxide and sulphur
trioxide. The ratio of masses of oxygen in SO2 and SO3
for xed mass of Sulphur is 2:3.
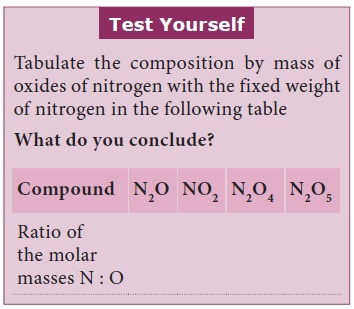

Sample Problem (Solved)
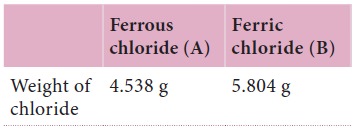
Iron forms two different chlorides, namely ferrous
and ferric chlorides. Each of these chlorides was prepared from 2 gram of iron.
It was found that 4.538 gram ferrous chloride and 5.804 gram ferric chloride
were produced. Show that these observations are according to the law of multiple
proportions.
Solution:
Here iron is forms different chlorides. The weight
of iron taken in both cases is the same. i.e. 2.0 g. Therefore, we have
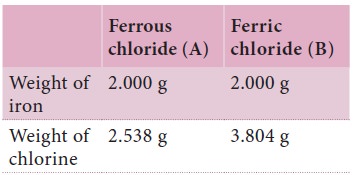
The proportion of chlorine in this compound is
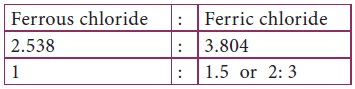
The proportion by weight of chlorine is indicated
by a simple ratio. Thus Law of multiple proportions is verified

Related Topics