Chapter: 9th Science : Atomic Structure
Discovery of Neutrons
Discovery of Neutrons
In 1932 James Chadwick observed when Beryllium was
exposed to alpha particles, particles with about the same mass as protons were
emitted.

These emitted particles carried no electrical
charges. They were called as neutrons. Neutrons present in the nuclei of all
the atoms except of hydrogen. The mass of a neutron is almost equal to the mass
of proton. Neutron is represented by n.
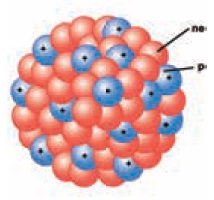
1. Composition of nucleus
Electrons have a negligible mass; hence the mass of
the atom mainly depends on the mass of the nucleus. Nucleus of an atom consists
of two components, they are protons and neutrons.
Protons are positively charged. Protons repel each
other because of their like charges. Hence more than one proton cannot be
packed in a small volume to form a stable nucleus, unless neutrons are present.
Neutrons reduce the repulsive force between the
positively charged protons
2. Nucleons
The elementary particles such as protons and
neutrons are collectively called as Nucleons. Why are atoms neutral? Because an
atom contains the same number of protons and electrons and hence it’s neutral.
Characteristics of fundamental particles
The physical and chemical properties of elements
and their compounds can be
Terminology
Atomic Number (Z)
The figure
shown here represents an atom.
Using the colour code given below
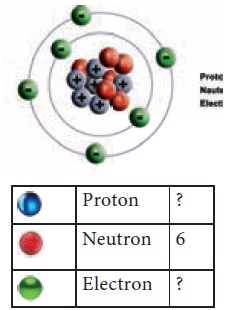
Count the number of protons, electrons and complete
the table. Are the number of protons and electrons the same?
An atom of an element has its own characteristic
number of protons in its nucleus, which distinguishes it from the atoms of
other elements. Hence proton is considered to be the nger print of an atom.
This characteristic number (Number of protons) is
called the atomic number of the element. Atomic number is denoted by Z.
What is the Atomic number of the above element?
Since there are 6 protons, the atomic number = 6.
The number of electrons = 6, which is the same as
the atomic number.
Atomic number of an atom is therefore equal to the
number of protons and it is also equal to the number of electrons present.

Illustration:
An atom has 11 protons, 11 electrons and 12
neutrons. What is the atomic number and the name of the element?
Atomic number = Number of protons = Number of
electrons
Number of protons = Number of electrons = 11
Atomic number = 11
Name of the element is Sodium.

Mass Number:(A)
From Rutherford’s experiment it was clear that the
mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus. is means that mass of an atom
is practically due to protons and neutrons which are present in the nucleus.
Protons and neutrons together are also called nucleons.
Mass
number of the element is the total number of protons and neutrons present in
the nucleus.
Mass number is denoted by A
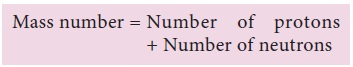
For example if an atom has 3 protons, 3 electrons
and 4 neutrons, then its mass number will be equal to 7 (3 protons+ 4 neutrons)

Symbolic
representation of an atom using Atomic Number and Mass Number
An atom can be represented by its symbol with atomic
number as subscript and mass number as superscript.

For
example, nitrogen is written as ![]()
Here 7 is its atomic number and 14 is its mass number.
Relationship between Mass Number and Atomic Number:
Mass Number (A) = Atomic Number (z) + Number of
Neutrons(n)
Atomic Number (Z) = Number of Protons or Number of
Electrons
A = Z + n
Sample Problem (solved) :
Calculate
the atomic number of an element whose mass number is 39 and number of neutrons
is 20. Also find the name of the element.
Solution:
Mass Number = Atomic Number + Number of neutrons
Atomic Number = Mass Number – Number of neutrons
= 39 – 20
Atomic Number = 19
Element having Atomic Number 19 is Potassium (K)
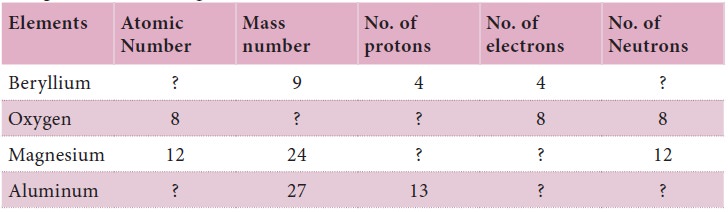
Complete
the following table: Pair work

Related Topics