Atomic Structure | Chemistry - Law of Reciprocal Proportions | 9th Science : Atomic Structure
Chapter: 9th Science : Atomic Structure
Law of Reciprocal Proportions
Law of Reciprocal Proportions
The law of
reciprocal proportions was proposed by Jeremias Ritcher in 1792.

It states that, “If two different elements combine
separately with the same weight of a third element, the ratios of the masses in
which they do so are either the same or a simple multiple of the mass ratio in
which they combine.”
Let us study the following example Here carbon
combines with hydrogen and oxygen to form Methane (CH4) and CO2
(carbon dioxide) respectively. Hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water.
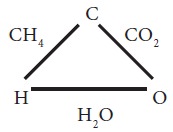
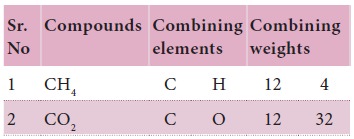
It is seen that in CH4 the ratio of
masses C : H = 3:1
In CO2 the ratio of masses of C : O =
3:8
Here hydrogen and oxygen combine with the same mass
of carbon. They also combine with each other to form water (H2O)
What is the ratio of masses of H and O in H2O?
It is 2: 16 or 1:8 which is same as 4:32, which is
the ratio of the different masses of hydrogen and oxygen combining with the
same mass of carbon.
This illustrates the law of reciprocal proportions.
Let us consider one more example.
Sulphur combines with oxygen to form sulphur
dioxide, carbon combines with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and carbon combines
with sulphur to form carbon disulphide
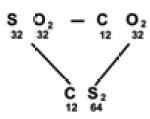
The ratio of masses of carbon and sulphur which
combine with fixed mass (32 parts) of oxygen is
12:32 or 3:8
…………..(1)
In CS2 ratio of masses of carbon and
sulphur is in the ratio
12:64 or 3:16 …………………(2)
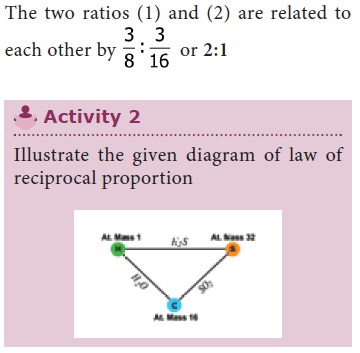
Solved problem
Hydrogen sulphide (H2 S) contains 94.11%
sulphur, water (H2O) contains 11.11% hydrogen and sulphur dioxide
(SO2) contains 50% of oxygen. Show that the results are in agreement
with the law of reciprocal proportions.
Solution
In 100g of water, the weight of hydrogen = 11.11 g
The weight of oxygen = 100 – 11.11 = 88.89 g
In 100g of sulphur dioxide, the weight of sulphur =
50 g
Weight of oxygen = 100 – 50 = 50 g
The ratio between the weight of oxygen and Hydrogen
is 88.89:11.11 i.e. 8:1 (1)
In hydrogen sulphide, the weight of sulphur = 94.11
g
The weight of hydrogen = 100 – 94.11 = 5.89 g
The ratio between the weight of sulphur and
hydrogen is 94.11: 5.89 ie. 16: 1 … (2)
The two ratios 1 and 2 are related as 8/1: 16/1
(or) 1 : 2
These are simple multiples of each other. The ratio
between the weight of sulphur (32) and oxygen (16) which combine separately
with the weight of Hydrogen (2) supports the
law of reciprocal proportions.
1. Gay Lussac’s law of Combining Volumes

Step 1: Hydrogen combines with oxygen to form water
(word equation)
Step2: H2 + ½ O2→ H2O
(skeletal equation)
Step3: 2H2(g)+ O2(g)→ 2H20
(g) (balanced equation)
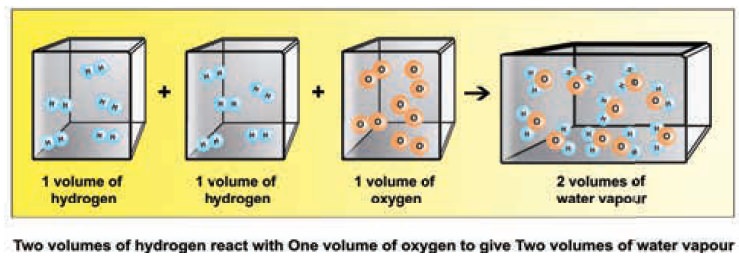
(2 Volumes) + (1 Volume)→(2 Volumes) (2:1:2)
i.e. two volumes of hydrogen react with 1 volume of
oxygen to form two volumes of water vapour. i.e. the ratio by volume which
gases bears is 2:1:2 which is a
simple whole number ratio.
It follows that at a given temperature and pressure
the volumes of all gaseous reactants and products bear a simple whole number
ratio to each other.
Let us consider one more example:
Step 1: Hydrogen combines with chlorine to form
hydrogen chloride
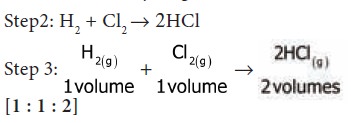
i.e. one volume of hydrogen reacts with one volume
of chlorine to form two volumes of HCl gas. i.e. the ratio by volume which
gases bears is 1:1:2 which is a
simple whole number ratio.

Solved Problem
Methane burns in oxygen to form carbon dioxide and
water vapour as given by the equation
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g)
+ 2H2O(g)
Calculate: (i) the
volume of oxygen needed to burn
completely 50 cm3 of methane and the volume of carbon dioxide formed in this
case.
Solution:

Related Topics