Chapter: Professional Ethics in Engineering : Engineering Ethics
Kohlberg and Gilligan Views
KOHLBERG AND GILLIGAN VIEWS:
Kohlberg
Theory
These theories are based on the sorts of
reasoning and motivation adopted by individuals with regard to moral questions.
Lawrence
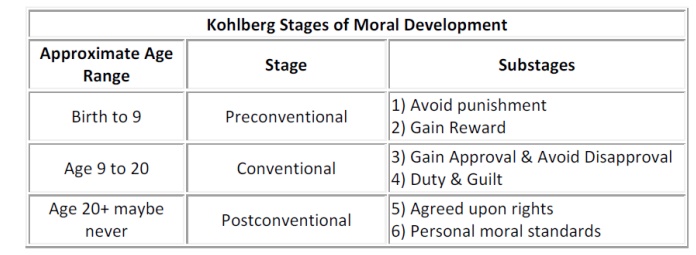
Kohlberg‟s Theory
ü According to Kohlberg, the people progressed in
their moral reasoning through a series of stages. His theory is based on the
foundation that morality is a form of reasoning that develops I structural
stages.
ü The three levels of moral development, suggested
by Kohlberg, are:
1. Pre-conventional level;
2. Conventional level; and
3. Post –conventional level.
1.
Pre- conventional level
ü The pre-conventional level of moral development
is based to derive benefits for oneself.
ü In the first level, individual behave according
to socially acceptable norms, which are taught mainly by parents and teachers.
ü At this level, individuals are motivated mainly
by their interest to avoid punishment, or by their desire to satisfy their own
needs, or by the external power exerted on them.
ü This is the level of development of all young
children and some adults, who are unable to reach beyond a certain limit.
2.
Conventional level
ü In the second level, the moral thinking and
behavior of the individual are determined by the standards of their family,
community, and society. That is, the norms or customs of one‘s
family/community/society are accepted and adopted as the ultimate standard of
morality.
ü At this level, individuals are motivated by the
desire to please others and to meet the social units‘ expectations, without
bothering much about their self-interest.
ü Thus as per the second level, individuals give
more importance to loyalty and close identification with others, than their own
self-interest.
ü Many studies of Kohlberg reveal that most
adults are living at this level only.
ü The second level of moral thinking is found in
society generally. That‘s why it is named as ‗conventional‘ level of moral
development
3.
Post –Conventional level
ü In the post-conventional level, the individuals
are guided by strong principles and convictions, not by selfish needs or
pressures from society.
ü According to Kohlberg, these individuals are
called as 'autonomous‘, because they think for/by themselves and also they do
not believe that customs are always right.
ü The people at this level want to live by
general principles that are universally applied to all people. They always
desire to maintain their moral integrity, self Kohlberg felt that the majority
of adults do not reach the post-conventional level.
Gilligan Theory
ü Carol
Gilligan, a former
student and colleague
of Kohlberg, has
criticized
Kohlberg‘s theory as male blased.
ü She also charged Kohlberg that Kohlberg‘s
studies were concluded with male samples only and also his approach is
dominated by a typical preoccupation with general rules and rights.
ü According to Gilligan, males have tendency to
over-ride the importance of moral rules and convictions while resolving moral
dilemmas; whereas females have tendency to try hard to preserve personal
relationships with all people invlolved in a situation.
ü Also Gilligan felt that men mostly focus their
attention on content of the problem, whereas women focus their attention on the
context i.e., situation of the problem.
ü Gilligan refers her context-oriented emphasis
on maintaining personal relationships as the ethics of care, and contrasts it
with Kohlberg‘s ethics of rules and rights.
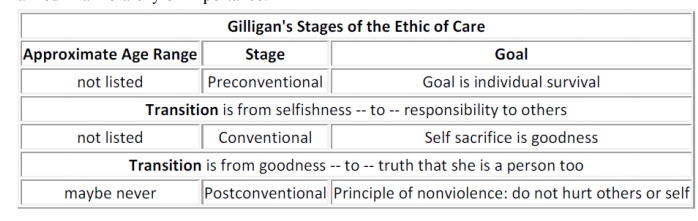
Gilligan‟s Levels Of Moral Development
1.
Pre-conventional level
ü This is almost the same as Kohlberg‘s first
level.
ü That is, in this level an individual is
concerned with self-centered reasoning.
2.
Conventional level
ü This level differs from Kohlberg‘s second level.
ü According to Gilligan, women will not hurt
others and have a willingness to sacrifice their own interests in order to help
others.
3.
Post-conventional level
ü This level also differs from Kohlberg‘s third
level.
ü In this level, the individual is able to
maintain balance between his own needs with the needs of others.
ü The balancing can be achieved through
context-oriented reasoning i.e., examining all facts, people and circumstances
involved, rather than by applying abstract rules ranked in a hierarchy of
importance.
Related Topics