Chapter: Object Oriented Programming(OOP) : Overview of Java
Java - Operators
OPERATORS
•
The Assignment Operator and Expressions
•
Arithmetic Operators
•
Operator Precedence
•
Integer Division and Modulus
•
Division by Zero
•
Mixed-Type Arithmetic and Type Casting
•
Shortcut Operators
Assignment Operator
Syntax:
target =
expression;
expression: operators and operands that evaluate to
a single value --value is then assigned to target
--target must be a variable (or constant) --value
must be compatible with target's data type
Examples:
int
numPlayers = 10; // numPlayers holds 10 numPlayers = 8; // numPlayers now holds
8 int legalAge = 18;
int
voterAge = legalAge; The next statement is illegal
int
height = weight * 2; // weight is not defined int weight = 20;
and generates the following compiler error: illegal
forward reference
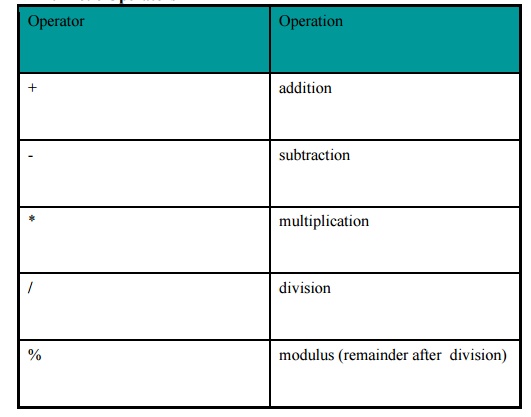
Arithmetic Operators
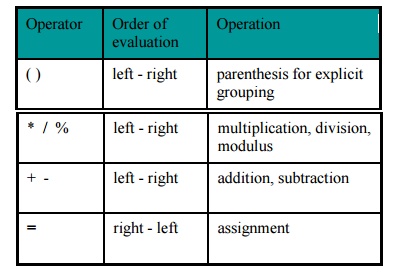
Operator Precedence
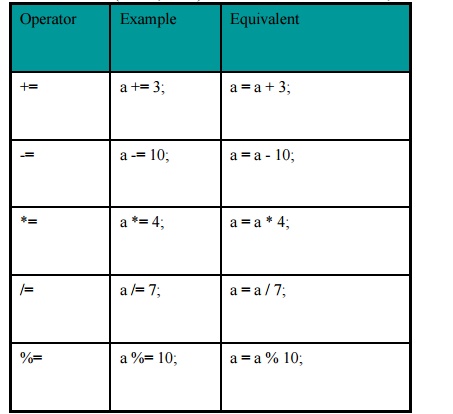
Shortcut Operators
++ increment
by 1-- decrement by 1
Example:
count++; //
count = count + 1;
count--; // count = count - 1;
Postfix
version (var++, var--): use value of var in expression, then increment or
decrement. Prefix version (++var, --var): increment or decrement var, then use
value in expression
Related Topics