Chapter: Object Oriented Programming(OOP) : Overview of Java
Java - Classes and Objects,Methods
CLASSES AND OBJECTS,METHODS
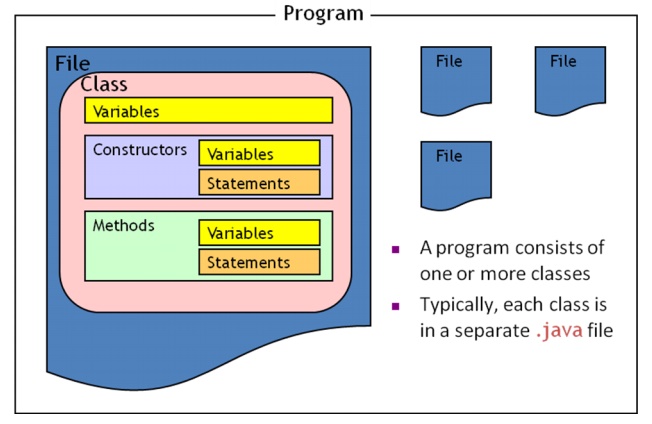
n A Java program consists of one
or more classes
n A class is an abstract
description of objects
n Here is an example class:
class Dog { ...description of a dog goes
here... }
Here are
some objects of that class:

Here
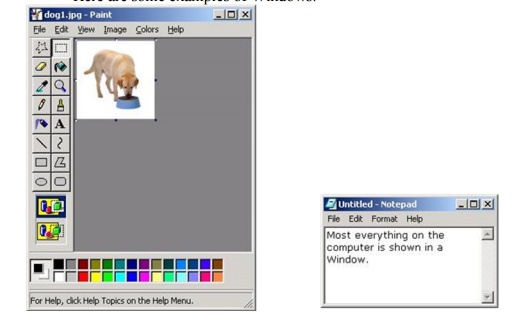
is another example of a class:
class
Window { ... }
Here
are some
examples of Windows:
1. Classes contain data
definitions
n Classes
describe the data held by each of its objects
n Example:
n class
Dog { String name; int age;
...rest
of the class...
}
n A class
may describe any number of objects
n Examples:
"Fido", 3; "Rover",
5; "Spot", 3;
n A class
may describe a single object, or even no objects at all
2. Classes contain methods
n A class
may contain methods that describe the behavior of objects
n Example:
n class Dog
{
...
void bark() {
System.out.println("Woof!");
}
}
n When we
ask a particular Dog to bark, it says “Woof!”
n Only Dog
objects can bark; the class Dog cannot bark
3. Methods contain statements
n A
statement causes the object to do something
n (A better
word would be “command”—but it isn’t)
n Example:
n System.out.println("Woof!");
n This
causes the particular Dog to “print” (actually, display on the screen) the
characters Woof!
Methods
may contain temporary data
n Data
described in a class exists in all objects of that class
n Example:
Every Dog has its own name and age
n A method
may contain local temporary data that exists only until the method finishes
n Example:
n void
wakeTheNeighbors( ) {
int i =
50; // i is a temporary variable while (i > 0) {
bark( );
i = i – 1;
}
}
Classes always contain constructors
n A
constructor is a piece of code that “constructs,” or creates, a new object of
that class
n If you
don’t write a constructor, Java defines one for you (behind the scenes)
n You can
write your own constructors
n Example:
n class Dog
{
String
name; int age;
Dog(String n, int age) { name = n;
this.age
= age;
}
}
Diagram
of program structure
class Dog { String name; int age;
Dog(String n, int age) { name = n;
this.age
= age;
}
void bark() {
System.out.println("Woof!");
}
void wakeTheNeighbors( ) { int i = 50;
while (i > 0) { bark( );
i = i –
1;
}
}
public static void main(String[ ] args) { Dog fido
= new Dog("Fido", 5);
fido.wakeTheNeighbors();
}
} // ends the class
Method Definitions
• Method
definition format
return-value-type
method-name( parameter-list )
{
declarations
and statements
}
– Method-name: any valid identifier
– Return-value-type: data type of the result
•
void - method returns nothing
•
Can return at most one value
– Parameter-list: comma separated list,
declares parameters
•
Method call must have proper number and type of
parameters
– Declarations and statements: method body
(block)
•
Variables can be declared inside blocks (can be nested)
•
Method cannot be defined inside another function
– Program control
– When method call encountered
•
Control transferred from point of invocation to
method
– Returning control
•
If nothing returned: return;
– Or until reaches right brace
•
If value returned:
return expression;
– Returns the value of expression
– Example user-defined method:
Public int square( int y )
{
return y
* y
}
•
Calling methods
– Three ways
•
Method name and arguments
– Can be used by methods of same class
– square( 2 );
•
Dot operator - used with objects
– g.drawLine( x1, y1, x2, y2 );
•
Dot operator - used with static methods of classes
– Integer.parseInt( myString );
– More Chapter 26
•
More GUI components
– Content Pane - on-screen display area
•
Attach GUI components to it to be displayed
•
Object of class Container (java.awt)
– getContentPane
•
Method inherited from JApplet
•
Returns reference to Content Pane
Container
c = getContentPane();
– Container method add
•
Attaches GUI components to content pane, so they can
be displayed
•
For now, only attach one component (occupies entire
area)
•
Later, learn how to add and layout multiple
components
c.add(
myTextArea );
Related Topics