Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) - Introduction to EDI | 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 18 : Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
Chapter: 12th Computer Applications : Chapter 18 : Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
Introduction to EDI
Electronic Data
Interchange - EDI
Introduction
to EDI
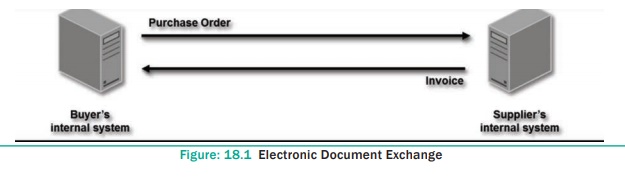
The Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the
exchange of business documents between one trade partner and another
electronically. It is transferred through a dedicated channel or through the
Internet in a predefined format without much human intervention.
It is used to transfer documents such as delivery
notes, invoices, purchase orders, advance ship notice, functional
acknowledgements etc. These documents are transferred directly from the
computer of the issuing company to that of the receiving company, with great
time saving and avoiding many errors of traditional “on paper” communications.
Before the popularization of Internet-based
E-Commerce, it was a major E-Commerce model. EDI includes data exchange between
buyers and sellers, trade partners, and also internal data exchange within
departments of a company. There are many internationally accepted EDI standard
e.g. EDIFACT, XML, ANSI ASC X12, etc. See Figure 18.1
EDI is “Paperless Trade” and EFT
(Electronic Transfer) is “Paperless Payment”
History of EDI
With the popularity of computers, many companies
and organizations use computers to store and process data. However, different
organizations use different application systems, and the format of the data
generated is not the same. When organizations need to communicate for their business
needs they have to rekey. This was time consuming and a major obstacle in the
business operations. In order to solve this problem, some enterprises have
agreed a specific standard format, which can be regarded as the origin of the
EDI application concept.
Like many other early information technologies,
EDI was also inspired by developments in Defense Research Organization. Ed Guilbert, is called as the father of
EDI. He manifested shipping standardized format (much like the 856, or ASN)
during the 1948 Berlin airlift. Guilbert with his team developed the first
standardized system for business documents, that later influenced how documents
would be passed from computer to computer. This standard helped to track “what was
contained in the shipment”, “who was delivering the cargo”, while not allowing
language barriers or confusing formats to delay the shipment.

Soon, businesses began to realize that using EDI
will smoothen the business transactions and increase the profit. These
standardizations made ordering and shipping faster, more organized, and less
expensive. Earlier, EDI documents were transmitted electronically by the use of
Radio teletype, telex messages, or telephone.
In late 1960s, shipping line, railroads, airlines,
and truck companies of USA were exchanging electronic messages for their
businesses. These messages were in different formats, and it resulted in
problems in transfer of goods. In 1968, these companies grouped together among
themselves and formed the Transportation Data Coordinating Committee (TDCC) to
develop EDI standard formats.
In 1975, first EDI standards were released by TDCC,
of which Ed Guilbert was a major contributor. In 1977, a group of supermarket
companies and their business partners begin drafting and using an EDI project.
The TDCC is renamed as Electronic Data Interchange Association (EDIA) in 1978.
Later in that year, the EDIA was undertaken by the American National Standards
Institute and becomes the ANSIX12 committee. Since then this committee is
responsible for the publication of EDI standards.
Later in 1985, UN created the EDIFACT to assist
with the global reach of technology in E -Commerce. EDIFACT is the most widely
used EDI.
The first EDI messages was sent in 1965
from the Holland-American steamship
line to Trans-Atlantic shipping company using telex messages. The computer had sent
a full page of information in roughly 2 minutes. These messages were then
written on the magnetic tapes that could be loaded onto another computer.
Related Topics