Chapter: Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing : Psychosocial Theories and Therapy
Interpersonal Theories
Interpersonal Theories
Harry Stack Sullivan: Interpersonal Relationships and Milieu Therapy
Harry Stack Sullivan (1892–1949) was an American psy-chiatrist who
extended the theory of personalitydevelopment to include the significance of
interpersonal relationships. Sullivan believed that one’s personality involves
more than individual characteristics, particularly how one interacts with
others. He thought that inadequate or nonsatisfying relationships produce
anxiety, which he saw as the basis for all emotional problems (Sullivan, 1953).
The importance and significance of interpersonal relationships in one’s life is
probably Sullivan’s greatest contribution to the field of mental health.
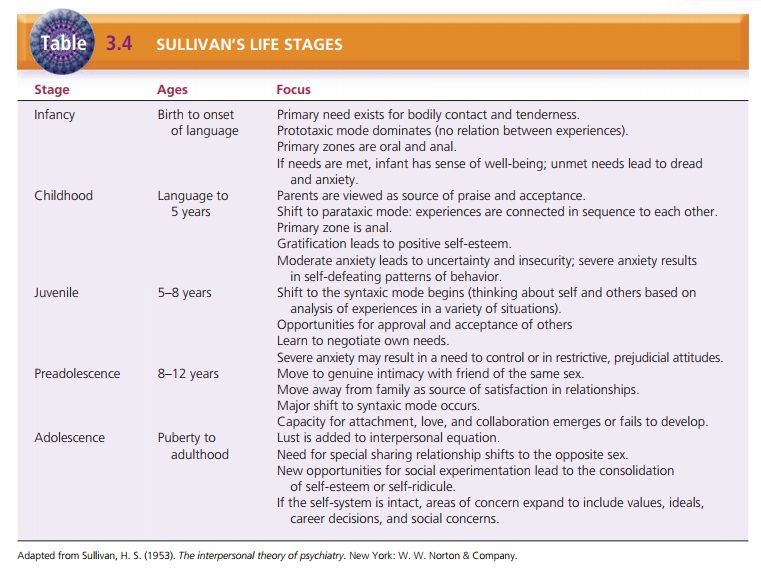
Five Life Stages. Sullivan established five
life stages of development—infancy, childhood, juvenile,
preadoles-cence, and adolescence, each focusing on various interper-sonal
relationships (Table 3.4). He also described three developmental cognitive
modes of experience and believed that mental disorders are related to the
persistence of one of the early modes. The prototaxic
mode, characteristic of infancy and childhood, involves brief, unconnected
experi-ences that have no relationship to one another. Adults with
schizophrenia exhibit persistent prototaxic experiences. The parataxic mode begins in early
childhood as the child begins to connect experiences in sequence. The child
maynot make logical sense of the experiences and may see them as coincidence or
chance events. The child seeks to relieve anxiety by repeating familiar
experiences, although he or she may not understand what he or she is doing.
Sullivan explained paranoid ideas and slips of the tongue as a per-son
operating in the parataxic mode. In the syntaxic
mode, which begins to appear in school-aged children and be-comes more
predominant in preadolescence, the person begins to perceive himself or herself
and the world within the context of the environment and can analyze
experi-ences in a variety of settings. Maturity may be defined as predominance
of the syntaxic mode (Sullivan, 1953).
Therapeutic Community or Milieu. Sullivan envisioned the goal of treatment as the establishment of satisfying inter-personal relationships. The therapist provides a corrective interpersonal relationship for the client. Sullivan coined the term participant observer for the therapist’s role, meaning that the therapist both participates in and ob-serves the progress of the relationship.
Sullivan is also credited with developing the first therapeutic community or milieu with
young men withschizophrenia in 1929 (although the term therapeutic com-munity was not used extensively until Maxwell Jones
pub-lished The Therapeutic Community
in 1953). In the concept of therapeutic community or milieu, the interaction
among clients is seen as beneficial, and treatment emphasizes the role of this
client-to-client interaction. Until this time, it was believed that the
interaction between the client and the psychiatrist was the one essential
component to the client’s treatment. Sullivan and later Jones observed that
interactions among clients in a safe, therapeutic setting provided great
benefits to clients. The concept of milieu
therapy, originally developed by
Sullivan, involved clients’ interactions
with one another, including practicing inter-personal relationship skills,
giving one another feedback about behavior, and working cooperatively as a
group to solve day-to-day problems.
Milieu therapy was one of the primary modes of treat-ment in the
acute hospital setting. In today’s health-care environment, however, inpatient
hospital stays are often too short for clients to develop meaningful
relationships with one another. Therefore, the concept of milieu therapy
receives little attention. Management of the milieu, or environment, is still a
primary role for the nurse in terms of providing safety and protection for all
clients and pro-moting social interaction.
Hildegard Peplau: Therapeutic Nurse–Patient Relationship
Hildegard Peplau (1909–1999; Figure 3.2) was a nursing the-orist
and clinician who built on Sullivan’s interpersonal theories and also saw the
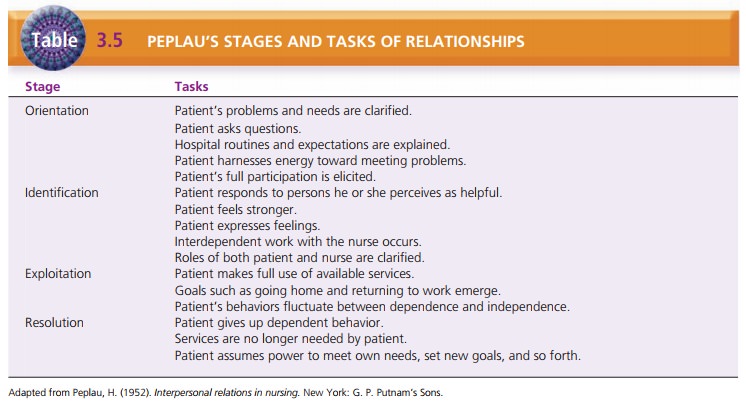
role of the nurse as a participant observer. Peplau developed the concept of
the therapeutic nurse–patient relationship, which includes four phases: orientation, identification,
exploitation, and resolution (Table 3.5).

During these phases, the client accomplishes certain tasks and
makes relationship changes that help the healing process (Peplau, 1952).
·
The orientation phase is
directed by the nurse and in-volves engaging the client in treatment, providing
ex-planations and information, and answering questions.
·
The identification phase
begins when the client works interdependently with the nurse, expresses
feelings, and begins to feel stronger.
·
In the exploitation phase,
the client makes full use of the services offered.
In the resolution phase,
the client no longer needs pro-fessional services and gives up dependent
behavior. The relationship ends.
Peplau’s concept of the nurse–client relationship, with tasks and
behaviors characteristic of each stage, has been modified but remains in use
today .
Roles of the Nurse in the Therapeutic
Relationship. Peplau also wrote about the roles of the nurse in the
therapeutic relationship and how these roles help meet the client’s needs. The
primary roles she identified are as follows:
·
Stranger––offering the client the same
acceptance and courtesy that the
nurse would to any stranger;
·
Resource person––providing specific answers to
ques-tions within a larger context;
·
Teacher––helping the client to learn
formally or informally;
·
Leader––offering direction to the
client or group;
·
Surrogate––serving as a substitute for
another such as a parent or sibling;
·
Counselor––promoting experiences leading
to health for the client such as
expression of feelings.
Peplau also believed that the nurse could take on many other roles,
including consultant, tutor, safety agent, medi-ator, administrator, observer,
and researcher. These were not defined in detail but were “left to the
intelligence and imagination of the readers” (Peplau, 1952, p. 70).
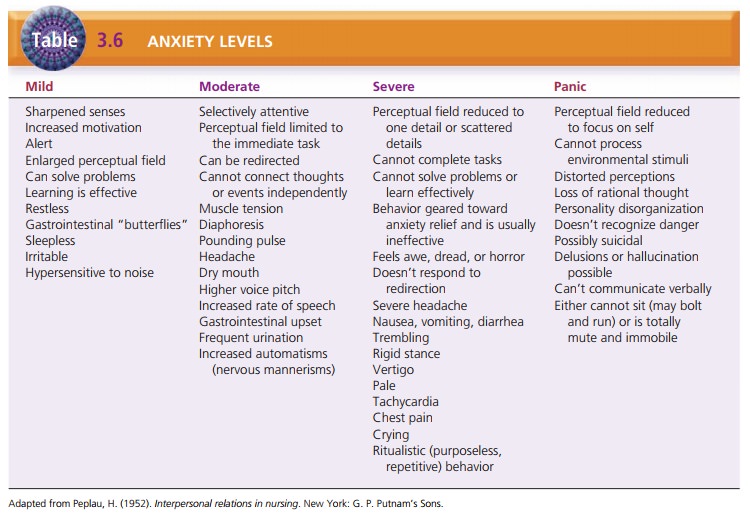
Four Levels of Anxiety. Peplau defined anxiety as the
ini-tial response to a psychic threat. She described four levels of anxiety:
mild, moderate, severe, and panic (Table 3.6). These serve as the foundation
for working with clients with anxiety in a variety of contexts .
1.
Mild anxiety is a positive state of
heightened awareness and sharpened
senses, allowing the person to learn new behaviors and solve problems. The
person can take in all available stimuli (perceptual field).
2.
Moderate anxiety involves a decreased
perceptual field (focus on immediate
task only); the person can learn new behavior or solve problems only with
assistance. Another person can redirect the person to the task.
3. Severe anxiety involves feelings of dread or terror. The person cannot be redirected to a task; he or she focuses only on scattered details and has physiological symptoms of tachycardia, diaphoresis, and chest pain. A person with severe anxiety may go to an emergency department, believing he or she is having a heart attack.
4. Panic anxiety can involve loss of rational thought, delu-sions, hallucinations,
and complete physical immobil-ity and muteness. The person may bolt and run
aimlessly, often exposing himself or herself to injury.
Related Topics