Chapter: Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing : Psychosocial Theories and Therapy
Existential Theories
Existential Theories
Existential theorists believe that behavioral deviations result
when a person is out of touch with himself or her-self or the environment. The
person who is self-alienated is lonely and sad and feels helpless. Lack of
self-awareness, coupled with harsh self-criticism, prevents the person from
participating in satisfying relationships. The person is not free to choose
from all possible alternatives because of self-imposed restrictions.
Existential theorists believe that the person is avoiding personal
responsibility and giv-ing in to the wishes or demands of others.
All existential therapies have the goal of helping the person
discover an authentic sense of self. They emphasize personal responsibility for
one’s self, feelings, behaviors, and choices. These therapies encourage the
person to live fully in the present and to look forward to the future. Carl
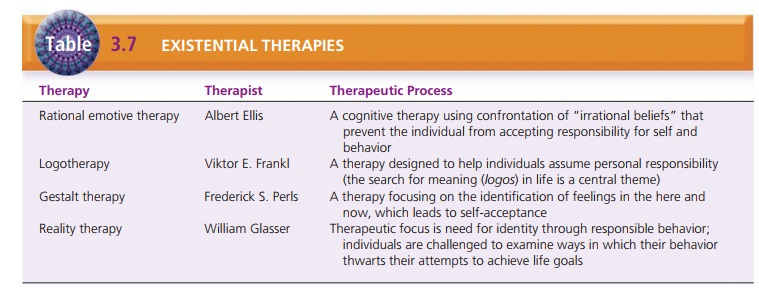
Rogers is sometimes grouped with existential therapists. Table 3.7 summarizes
existential therapies.
Cognitive Therapy
Many existential therapists use cognitive therapy, which focuses on immediate thought
processing—how a person perceives or interprets his or her experience and
determines how he or she feels and behaves. For example, if a person interprets
a situation as dangerous, he or she experiences anxiety and tries to escape.
Basic emotions of sadness, ela-tion, anxiety, and anger are reactions to
perceptions of loss, gain, danger, and wrongdoing by others (Beck & Newman,
2005). Aaron Beck is credited with pioneering cognitive therapy in persons with
depression.
Rational Emotive Therapy
Albert Ellis, founder of rational emotive therapy, identified 11
“irrational beliefs” that people use to make themselves unhappy. An example of
an irrational belief is “If I love someone, he or she must love me back just as
much.” Ellis claimed that continuing to believe this patently untrue statement
will make the person utterly unhappy, but he or she will blame it on the person
who does not return his or her love. Ellis also believes that people have
“automatic thoughts” that cause them unhappiness in certain situa-tions. He
used the ABC technique to help people identify these automatic thoughts: A is
the activating stimulus or event, C is the excessive inappropriate response,
and B is the blank in the person’s mind that he or she must fill in by
identifying the automatic thought.
Viktor Frankl and Logotherapy
Viktor Frankl based his beliefs in his observations of peo-ple in
Nazi concentration camps during World War II. His curiosity about why some
survived and others did not led him to conclude that survivors were able to
find meaning in their lives even under miserable conditions. Hence, the search
for meaning (logos) is the central
theme in logo-therapy. Counselors and therapists who work with clients in
spirituality and grief counseling often use the concepts that Frankl developed.
Gestalt Therapy
Gestalt therapy, founded by Frederick “Fritz” Perls, emphasizes
identifying the person’s feelings and thoughts in the here and now. Perls
believed that self-awareness leads to self-acceptance and responsibility for
one’s own thoughts and feelings. Therapists often use gestalt therapy to
increase clients’ self-awareness by having them write and read letters, keep
journals, and perform other activi-ties designed to put the past to rest and
focus on the present.
Reality Therapy
William Glasser devised an approach called reality therapy that
focuses on the person’s behavior and how that behav-ior keeps him or her from
achieving life goals. He devel-oped this approach while working with persons
with delinquent behavior, unsuccessful school performance, and emotional
problems. He believed that persons who were unsuccessful often blamed their
problems on other people, the system, or the society. He believed they needed
to find their own identities through responsible behavior. Reality therapy
challenges clients to examine the ways in which their own behavior thwarts
their attempts to achieve life goals.
Related Topics