Chapter: Microprocessor and Microcontroller : Interfacing Microcontroller
Interfacing a Microprocessor to Keyboard
Interfacing a Microprocessor to
Keyboard
When you press a key on your computer, you are
activating a switch. There are many different ways of making these switches. An
overview of the construction and operation of some of the most common types.
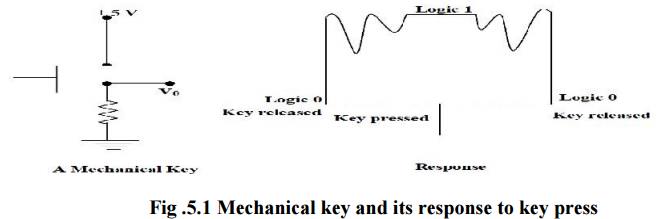
ü Mechanical
key switches: In mechanical-switch keys, two pieces of metal are pushed
together when you press the key. The actual switch elements are often made of a
phosphor-bronze alloy with gold platting on the contact areas. The key switch
usually contains a spring to return the key to the nonpressed position and
perhaps a small piece of foam to help damp out bouncing.
Some mechanical key switches now consist of a
molded silicon dome with a small piece of conductive rubber foam short two
trace on the printed-circuit board to produce the key pressed signal.
Mechanical switches are relatively inexpensive but
they have several disadvantages. First, they suffer from contact bounce. A
pressed key may make and break contact several times before it makes solid
contact.
Second, the contacts may become oxidized or dirty
with age so they no longer make a dependable connection.
Higher- quality mechanical switches typically have
a rated life time of about 1 million keystrokes. The silicone dome type
typically last 25 million keystrokes.
ü Membrane
key switches: These switches are really a special type of
mechanical switches. They consist of a three-layer plastic or rubber
sandwich.
The top
layer has a conductive line of silver ink running under each key position. The
bottom layer has a conductive line of silver ink running under each column of
keys.
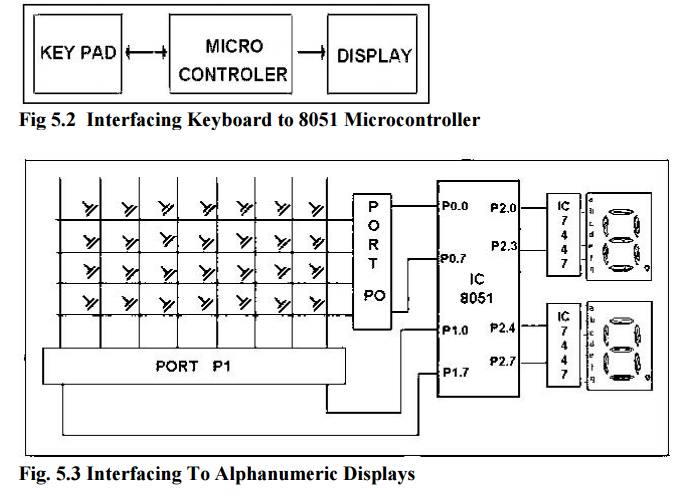
The key board interfaced is a matrix keyboard. This
key board is designed with a particular rows and columns. These rows and
columns are connected to the microcontroller through its ports of the micro
controller 8051. We normally use 8*8 matrix key board. So only two ports of
8051 can be easily connected to the rows and columns of the key board.
Whenever a key is pressed, a row and a column gets
shorted through that pressed key and all the other keys are left open. When a
key is pressed only a bit in the port goes high which indicates microcontroller
that the key is pressed. By this high on the bit key in the corresponding
column is identified.
Once we
are sure that one of key in the key board is pressed next our aim is to identify
that key. To do this we firstly check for particular row and then we check the
corresponding column the key board.
To check
the row of the pressed key in the keyboard, one of the row is made high by
making one of bit in the output port of 8051 high . This is done until the row
is found out.
Once we get the row next out job is to find out the
column of the pressed key. The column is detected by contents in the input
ports with the help of a counter. The content of the input port is rotated with
carry until the carry bit is set.
The
contents of the counter is then compared and displayed in the display. This
display is designed using a seven segment display and a BCD to seven segment
decoder IC 7447. The BCD equivalent number of counter is sent through output
part of 8051 displays the number of pressed key.
• To give
directions or data values to users, many microprocessor-controlled instruments
and machines need to display letters of the alphabet and numbers. In systems
where a large amount of data needs to be displayed a CRT is used to display the
data. In system where only a small amount of data needs to be displayed, simple
digit-type displays are often used.
• There are
several technologies used to make these digit-oriented displays but we are
discussing only the two major types.
• These are
light emitting diodes (LED) and liquid-crystal displays (LCD).
• LCD
displays use very low power, so they are often used in portable,
battery-powered
instruments.
They do not emit their own light, they simply change the reflection of
available light. Therefore, for an instrument that is to be used in low-light
conditions, you have to include a light source for LCDs or use LEDs which emit
their own light.
Related Topics